Lentils Nutrition Values Facts And Its Health Properties
About Lentils
Scientifically known as Lens culinaris; It belongs to the lens genus and the family of fabaceae. The word lentil is derived from Latin word lens and coincidentally the shape of these beans look like that of convex shaped lens. This is also mentioned in the bible where Esau gave up his birth right for a bowl of lentils and a loaf of bread. It has been a part of human diet even before the advent of Neolithic age and lots of lives depended on lentils for their survival. One of the oldest crops cultivated; these crops age to 13,000 years back. It was also called a poor a man’s food or peasants food as it was readily available and inexpensive crop. Poor catholic of the olden days who could not afford fish substituted it with lentils. There are 3 varieties of lentil the French lentil, the Indian lentil and the Egyptian lentil. The French lentil has a grey exterior and yellow interior, the Indian lentil has are yellow lentils with no coat, the red Egyptian lentils have no seed coat and is red in colour. Lentils are available throughout the year and are dried as soon as they are grown and sold as pulses. Lentil are popularly known as Dal in India; cooked majorly in every household.
Nutrition Facts
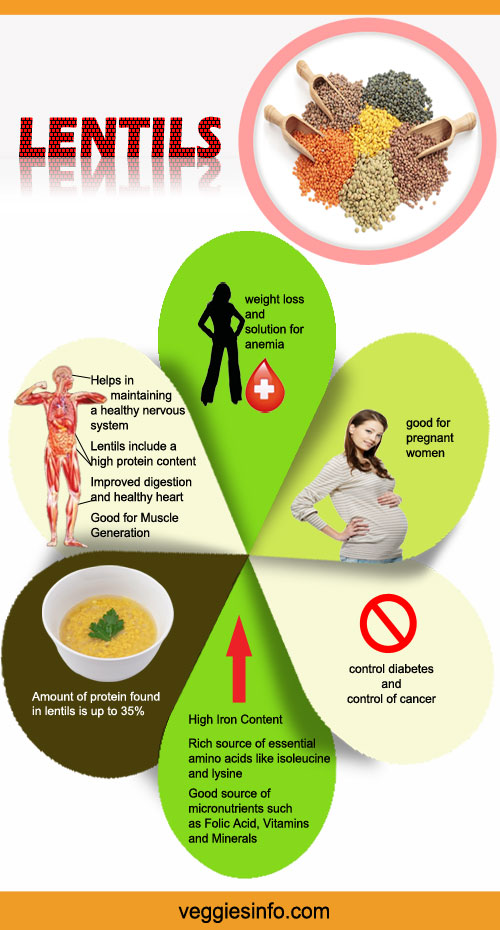
- Rich source of essential amino acids like isoleucine and lysine.
- Good source of micronutrients such as vitamins and minerals.
- Amount of protein found in lentils is up to 35%.
- Good for Muscle Generation.
- Good Source of Folic Acid.
- High Iron Content.
Health Benefits
- It includes a High Protein Content.
- Improved digestion and healthy heart.
- Control diabetes and control of cancer.
- Weight loss and solution for anemia.
- Good for pregnant women.
- Helps in maintaining a healthy nervous system.
Even though lentils is considered to be a less important food as it is cheaply priced and easily available it is very nutritious and health benefiting. A cup of lentils of 190g consist of 230 calories which is moderately low. It consist of cholesterol lowering compounds that help in keeping the cholesterol levels under check. If you love your heart and want to know what to do in order to take care of it? Switch over to lentils and see the difference. This is not because of the fibre content available in lentils but also the magnesium and folate content that is found abundance in lentils. Folate helps in reducing a compound called homocysteine that is responsible to in damaging arteries and thus keeping it under control will lead to a good heart health and a healthy future. Magnesium content in lentil helps in easy flow of blood and oxygen through the veins without clogging the arteries.
It has both soluble and insoluble fibre, soluble fibre helps in controlling and stabilizing blood sugar levels in the body; also regulates the excretion of insulin by the pancreas. Iron rich foods are a must for growing children and aging adults as it is a good for generating haemoglobin that helps transporting oxygen from the lungs to various other parts of the body such as brain, heart and lungs.
| Principle | Nutrient Value | Percentage of RDA |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamins | ||
| Choline | 96.4 mg | |
| Folate | 479.00 mcg | |
| Folic acid | 0.00 mcg | |
| Niacin | 2.605 mg | 13 % |
| Pantothenic acid | 2.140 mg | 21 % |
| Riboflavin | 0.211 mg | 12 % |
| Thiamin | 0.873 mg | 58 % |
| Vitamin A | 39.00 IU | 1 % |
| Vitamin A, RAE | 2.00 mcg | |
| Carotene, alpha | 0.00 mcg | |
| Carotene, beta | 23.00 mcg | |
| Cryptoxanthin, beta | 0.00 mcg | |
| Lutein + zeaxanthin | 0.00 mcg | |
| Lycopene | 0.00 mcg | |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.00 mcg | 0 % |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.540 mg | 27 % |
| Vitamin C | 4.5 mg | 8 % |
| Vitamin D | 0.00 IU | 0 % |
| Vitamin E | 0.49 mg | 2 % |
| Tocopherol, alpha | 0.49 mg | |
| Tocopherol, beta | 0.00 mg | |
| Tocopherol, delta | 0.00 mg | |
| Tocopherol, gamma | 4.23 mg | |
| Tocotrienol, alpha | 0.00 mg | |
| Tocotrienol, beta | 0.00 mg | |
| Tocotrienol, delta | 0.00 mg | |
| Tocotrienol, gamma | 0.00 mg | |
| Vitamin K | 5.0 mcg | 6 % |
| Minerals | ||
| Calcium, Ca | 35.00 mg | 4 % |
| Copper, Cu | 0.754 mg | 38 % |
| Iron, Fe | 6.51 mg | 36 % |
| Magnesium, Mg | 47.00 mg | 12 % |
| Manganese, Mn | 1.393 mg | 70 % |
| Phosphorus, P | 281.00 mg | 28 % |
| Potassium, K | 677.00 mg | 14 % |
| Selenium, Se | 0.1 mcg | 0 % |
| Sodium, Na | 6.00 mg | 0 % |
| Zinc, Zn | 3.27 mg | 22 % |
| Proteins and Aminoacids | ||
| Protein | 24.63 g | 49 % |
| Alanine | 1.029 g | |
| Arginine | 1.903 g | |
| Aspartic acid | 2.725 g | |
| Cystine | 0.322 g | |
| Glutamic acid | 3.819 g | |
| Glycine | 1.002 g | |
| Histidine | 0.693 g | |
| Isoleucine | 1.065 g | 76 % |
| Leucine | 1.786 g | 65 % |
| Lysine | 1.720 g | 82 % |
| Methionine | 0.210 g | 20 % |
| Phenylalanine | 1.215 g | 69 % |
| Proline | 1.029 g | |
| Serine | 1.136 g | |
| Threonine | 0.882 g | 84 % |
| Tryptophan | 0.221 g | 79 % |
| Tyrosine | 0.658 g | 38 % |
| Valine | 1.223 g | 67 % |
| Carbohydrates | ||
| Carbohydrate | 63.35 g | 21 % |
| Fiber | 10.7 g | 43 % |
| Sugars | 2.03 g | |
| Fructose | 0.27 g | |
| Galactose | 0.00 g | |
| Glucose (dextrose) | 0.00 g | |
| Lactose | 0.00 g | |
| Maltose | 0.30 g | |
| Starch | 49.90 g | |
| Sucrose | 1.47 g | |
| Fats and Fatty Acids | ||
| Fat | 1.06 g | 2 % |
| Saturated fatty acids | 0.154 g | 1 % |
| Butanoic acid | 0.000 g | |
| Decanoic acid | 0.000 g | |
| Dodecanoic acid | 0.000 g | |
| Hexadecanoic acid | 0.136 g | |
| Hexanoic acid | 0.000 g | |
| Octadecanoic acid | 0.015 g | |
| Octanoic acid | 0.000 g | |
| Tetradecanoic acid | 0.003 g | |
| Monounsaturated fatty acids | 0.193 g | |
| Docosenoic acid | 0.000 g | |
| Eicosenoic acid | 0.006 g | |
| Hexadecenoic acid | 0.003 g | |
| Octadecenoic acid | 0.184 g | |
| Polyunsaturated fatty acids | 0.526 g | |
| Docosahexaenoic n-3 acid | 0.000 g | |
| Docosapentaenoic n-3 acid | 0.000 g | |
| Eicosapentaenoic n-3 acid | 0.000 g | |
| Eicosatetraenoic acid | 0.000 g | |
| Octadecadienoic acid | 0.414 g | |
| Octadecatetraenoic acid | 0.000 g | |
| Octadecatrienoic acid | 0.112 g | |
| Fatty acids, total trans | 0.000 g | |
| Sterols | ||
| Cholesterol | 0.00 mg | 0 % |
| Others | ||
| Alcohol, ethyl | 0.0 g | |
| Ash | 2.71 g | |
| Caffeine | 0.00 mg | |
| Theobromine | 0.00 mg | |
| Water | 8.26 g |
How To Enjoy Lentils
Lentils are legumes that are not just healthy but tasty as well. Cooked lentil can be added to salads of tomatoes and chopped onions and finished it with a dash of lemon juice making it a healthy cold salad. Indians make dal chawal a dish made in every house hold; cooked lentil in turmeric and other condiments often accompaniment to steamed rice. The Moroccans enjoy the nutrition of lentils in thick lentil soups.