Radish | Health Information and Nutritional Benefits
About Radish
Scientifically known as Raphanus sativus; radish belongs to the Raphanus genus and the family of brassicaceae. These tap root vegetable is consumed everywhere in the world as a crunchy vegetable of the salad bowl. This is a little different from other vegetables owing to its sharp and spicy taste. The taste of this vegetable is highly influenced by glucosinolate, myrosinase, and isothiocyannate ; compounds found in radish. According to historical evidence and archaeological findings radish is a vegetable that was first found in South East Asia; its wild roots were found in parts of India, China and Central Asia where it was supposedly found. This vegetable was the first to be introduced to the Americans by the Europeans. This tap root grows really fast in moist soil and germinates within a span of 3 – 4 days of its plantation. It also is an acting companion to other plants as its strong odour that keeps insect and pest away from attacking the plant.
Radish Nutrition Value
- Provides just 16 Calories Per 100 g.
- Very good source of anti-oxidants, electrolytes, minerals, vitamins and dietary fiber.
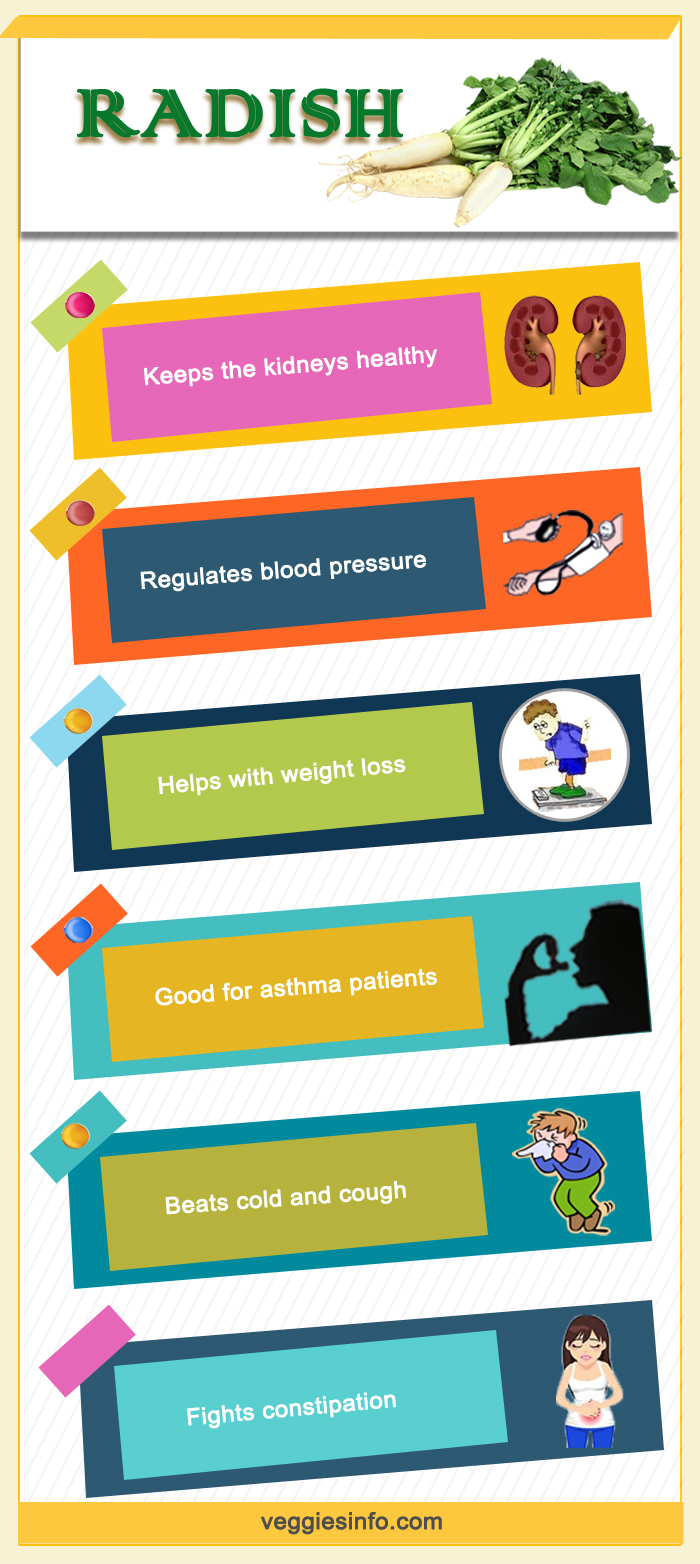
Benefits Of Radish
- Lowers cancer risk.
- Regulates blood pressure.
- Good for diabetics.
- Beats cold and cough.
- Helps you recover from jaundice.
- Fights constipation.
- Helps with weight loss.
- Good for asthma patients.
- Keeps you looking younger.
- Keeps the kidneys healthy.
| Principle | Nutrient Value | Percentage of RDA |
|---|---|---|
| Energy | 16 Kcal | 1% |
| Carbohydrates | 3.40 g | 3% |
| Protein | 0.68 g | 1% |
| Total Fat | 0.10 g | <1% |
| Cholesterol | 0 mg | 0% |
| Dietary Fiber | 1.6 g | 4% |
| Vitamins | ||
| Folates | 25 µg | 6% |
| Niacin | 0.254 mg | 1.5% |
| Pyridoxine | 0.071 mg | 5.5% |
| Riboflavin | 0.039 mg | 3% |
| Vitamin A | 7 IU | <1% |
| Vitamin C | 14.8 mg | 25% |
| Vitamin E | 0 mg | 9% |
| Vitamin K | 1.3 µg | 1% |
| Electrolytes | ||
| Sodium | 39 mg | 2.5% |
| Potassium | 233 mg | 5% |
| Minerals | ||
| Calcium | 25 mg | 2.5% |
| Copper | 0.050 mg | 5% |
| Iron | 0.34 mg | 4% |
| Magnesium | 10 mg | 2.5% |
| Manganese | 0.069 mg | 2.5% |
| Zinc | 0.28 mg | 2% |
| Phyto-nutrients | ||
| Carotene-ß | 4 µg | — |
| Carotene-a | 0 µg | — |
| Lutein- zeaxanthin | 10 µg | — |
Radish is a popular and one of the highly consummated vegetable in the world. Owing to its health benefits radish comes across as a wonder vegetable that needs to be incorporated in everyone’s diet. Consuming radish can prove to treat a person diagnosed with jaundice as it removes bilirubin. The Black radish variety is mostly used for treating jaundice. It restores the blood levels to normalcy and builds immunity to fight against the disease. The detoxifying compounds present in the food helps purifying blood and discarding waste from liver and stomach. Radish is also known for its ailing properties that help in treating piles. It facilitates water retention in the body and enhances digestive process that relieves the body from constipation. Food rich in diuretic properties such as radish helps in healing urinary disorders and fixes constipation that poses as a threat for the occurrence of piles. Radishes are rich in roughage and high in water content too; this food aids in weight loss as it keeps one full for a longer period. Colon cancer, breast cancer, prostate cancer can be avoided because of the folic acid, Vitamin C, anthocyanins present in radish helps in fighting against these life taking diseases. Radish is also known for controlling diabetes and regulates the absorption of sugar in the blood levels. Blood pressure a common sighted problem by many today can be majorly relieved on consumption of radish.
How To Enjoy Radish
The parts of radish that are edible are its roots, flowers and leaves. The leafy greens of radish can be prepared in to curry using Indian condiments and can be eaten as accompaniments with Indian breads. The root of radish is used to make pickles in many parts of India using oil and salt for preservatives. These tap root of this vegetable can be eaten raw in salads or be sautéed and added with other vegetables as a part of other dishes. Radish is added to European cuisine and also appears in potato soup with leeks. Adding then to healthy smoothies is a good addition to the diet.