Safflower Medicinal And Health Uses
Safflower And Its Amazing Medicinal Values
Millions of people drink a cup of tea either mixed with milk or without milk in the morning and without a cup of tea many consider the day as complete waste. After water, tea is the most consumed drink in the world.
There are different types of tea such as Black tea, Green tea, Flowering tea, Oolong tea, delicate tea and brewed tea. It is imperative to note that Assam is the world’s largest tea growing region in the world. This state alone produces 400 million of kg of tea annually.
This topic will deal with annual herbaceous plant named Safflower. The botanical name of this plant is Carthamus tinctorius.
Cultivation And Growth
This annual herbaceous plant is commercially cultivated for vegetable oil which is extracted from the seeds of the plant. The plants reach a height of 150 cm with globular flower heads having yellow, orange or red flowers.
Usually 15 to 20 seeds are seen in the one to five flower heads on the branch.
Native And Production
This plant is a native to arid environments having seasonal rain and has a taproot which enables it to thrive in such environments.
This plant is one of the oldest crops and chemical analysis of ancient Egyption textles dated to the Twlefth Dynasty identified dyes and garlands made from safflowers were found in tomb of the pharaoh Tuntakhamun.
The Greek name of safflower is kārthamos. This plant was very popular during 19th century and was called as carthamine. The annual production of this minor crop is around 600,000 tons.
This plant is commercially grown in countries such as India, USA, Mexico, Ethiopia, Kazakhstan, China, the Arab World, Argentina, Tanzania and Australia. The other common name of this plant is Sallflower, Beni, Chimichanga or Carthamus tinctorius and Kareza.
Safflower Various Uses
- The seeds are used as a coloring, flavoring, medicines and dyes.
- This plant is grown for the past fifty years mainly for the vegetable oil which is extracted from the seeds.
- Safflower oil is used as sunflower oil. It is used mainly in cosmetics, salad dressing and for the production of margarine.
- Many consume this as a nutritional supplement.
- There are two type of safflower that produces different kinds of oil.
- The fatty acids that are produced by this plant are monounsaturated fatty acid and polyunsaturated fatty acid.
- The former is used as edible oil and the later is used in painting factories.
- The edible oil helps regulate sugar levels and breakdown fatty-acid.
- This edible oil has the ability to reduce the weight and fat hormone.
| Principle | Nutrient Value | Percentage of RDA |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamins | ||
| Folate | 160.00 mcg | |
| Folic acid | 0.00 mcg | |
| Niacin | 2.284 mg | 11 % |
| Pantothenic acid | 4.030 mg | 40 % |
| Riboflavin | 0.415 mg | 24 % |
| Thiamin | 1.163 mg | 78 % |
| Vitamin A | 50.00 IU | 1 % |
| Vitamin A,RAE | 3.00 mcg | |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.00 mcg | 0 % |
| Vitamin B6 | 1.170 mg | 58 % |
| Vitamin C | 0.0 mg | 0 % |
| Vitamin D | 0.00 IU | 0 % |
| Minerals | ||
| Calcium, Ca | 78.00 mg | 8 % |
| Copper, Cu | 1.747 mg | 87 % |
| Iron, Fe | 4.90 mg | 27 % |
| Magnesium, Mg | 353.00 mg | 88 % |
| Manganese, Mn | 2.014 mg | 101 % |
| Phosphorus, P | 644.00 mg | 64 % |
| Potassium, K | 687.00 mg | 15 % |
| Sodium, Na | 3.00 mg | 0 % |
| Zinc, Zn | 5.05 mg | 34 % |
| Protiens and Aminoacids | ||
| Protein | 16.18 g | 32 % |
| Alanine | 0.772 g | |
| Arginine | 1.749 g | |
| Aspartic acid | 1.807 g | |
| Cystine | 0.311 g | |
| Glutamic acid | 3.699 g | |
| Glycine | 1.010 g | |
| Histidine | 0.452 g | |
| Isoleucine | 0.717 g | 51 % |
| Leucine | 1.154 g | 42 % |
| Lysine | 0.534 g | 25 % |
| Methionine | 0.284 g | 27 % |
| Phenylalanine | 0.806 g | 46 % |
| Proline | 0.726 g | |
| Serine | 0.812 g | |
| Threonine | 0.586 g | 56 % |
| Tryptophan | 0.183 g | 65 % |
| Tyrosine | 0.531 g | 30 % |
| Valine | 1.025 g | 56 % |
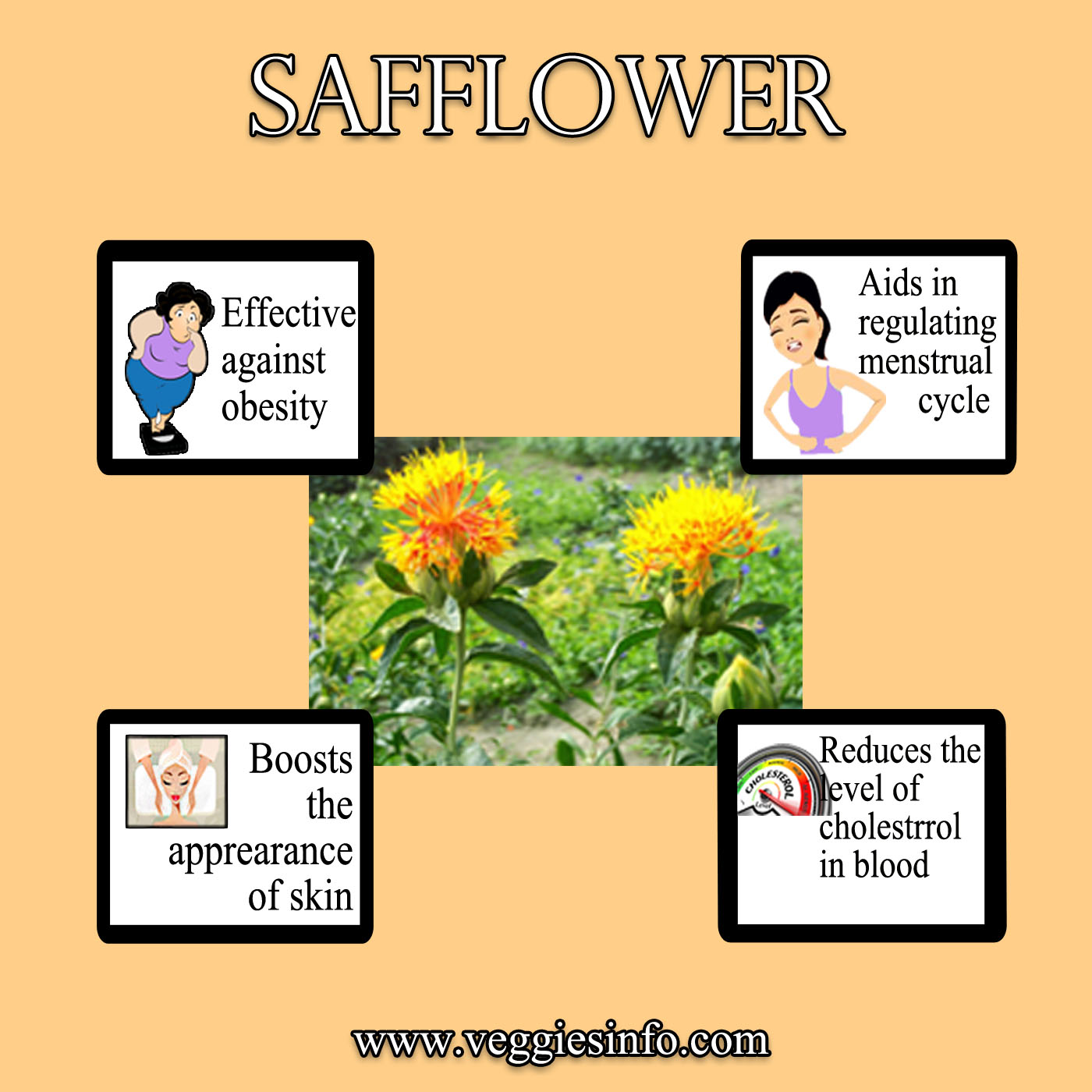
Safflower Health Benefits
Safflower Facts
It is also called “bastard saffron”. Dried flowers are used in textile dye. Cotton and wool can be dyed with this plant.
Safflower is used in a carbonated soft drink named Tizer.
The ancient Egyptians use it to garland on the mummies.
Chinese use the dried flowers in traditional medicine.
The Chinese use it to alleviate pain, increase circulation and reduce bruising.
Indians use the flowers for the treating the measles, fevers and eruptive skin problems occurring in Children.