Yam Dioscorea AKA Sweet potato
Yam-Types and Benefits
Yam is a perennial vine plant which is generally cultivated all over the world for its rich and edible tubers. The botanical name of this plant is Dioscorea.
Properties
This plant comes under the family Dioscoreaceae and is grown in the countries like Africa, Asia, Latin, America, the Caribbean, and the Oceania. Yams are a native of Africa and Asia and they are related to lilies and grasses. The size of the potato varies from small to very large. There are more than six hundred varieties of yam and maximum varieties almost 96% are grown in the country of Africa. The maximum size of yam can be around 60 kg.
Types Of Yam
There are different types of yam which are found throughout the humid tropics. Some of the known varieties under dioscorea are rotundata, alata, polystachya, bulbifera,cayenensis, esculenta, dumetorum and trifida.
D. rotundata
D. rotundata is also called white yam. The most prevalent yam in many countries is d.rotundata and d. cayenensis. The rotundata is generally called as white yam and cayenensis is called yellow yam. Both are classified as same species and there are more than two hundreds cultivated varieties between them. White yam’s tuber is cylindrical in shape and has a brown skin and white flesh. Yellow yam has yellow flesh and color caused by the presence of carotenoids. The variety named kokoro is used for making yam chips. Yellow has a longer period of vegetation compared to white yam. The vines of these plants grow as long as 39 feet and the tubers weight about 5 kg. The tubers are generally harvested after 7 to 12 months. “Pounded yam” dish is very famous in Africa.
D. alata
The next important variety which is grown by many countries are D. alata which is also called winged yam and purple yam is cultivated lavishly in southeast Asia and has the largest distribution throughout the world. This is grown in in Asia, the Pacific islands, Africa, and the West Indies.
Different Names Of D. alata
The tubers are cylindrical and have white flesh which is extremely watery. The Philippine people call this yam as “ube” and use this yam as an ingredient in sweet desserts. Indonesians call this as ubi. Vietnamese call this as khoai mo and they use it in the soup. Indians call this yam as ratalu or violet yam. Hawaiians call this yam as uhi and Japanese call it as daijo or beniimo.
D. Polystachya
D. Polystachya is a well known variety in China and the Chinese yam is very famous in this country. This plant is small compared to African vines. These plants grow up to 3m long. The Chinese yams are frost tolerant and can be cultivated in cooler condition. This yam was introduced in Europe during 19th century and has become very famous in many countries in Europe including France. These tubers are harvested after 6 months from the date of planting.
d. bulbifera
The Chinese use these yams as ingredients in noodles and for other dishes. The next popular yam is d. bulbifera which is also called air potato is famous in Africa and Asia. The vines reach 6 m or more in length the bulbils which grow at the base are used as edible ones. The weight of the potato is around 2 kg. Some varieties can be eaten raw while some require boiling or cooking.
D. esculent
D. esculent is a will bitter yam vines which is a native of Southeast Asia and it is the third most cultivated species. It is very famous throughout the world. The vines reach a 3 m in length and the tubers are very small. The tubers are eaten raw or cooked.
D.dumetorum
D. Dumetorum is also called as bitter yam which is very popular in West Africa. This yam can be cultivated easily without any difficulty and requires very less labor.
D. trifida
The next variety is D. trifida which is also called cush-cush yam which is found in Guyana region of South America. Yams occupy 5 million hectares in about 47 countries. In West and Central Africa the plants are intercropped with cereals and vegetables. Yams are often attacked by various pests and require good maintenance. The production will be wonderful when the annual rainfall is over 1500 mm. White, yellow and water yams produce a single large tuber per year which will weighs 5 to 10 kg. The production levels of yams are very low. Labor charges for cultivation are very high.
Nutritional Value
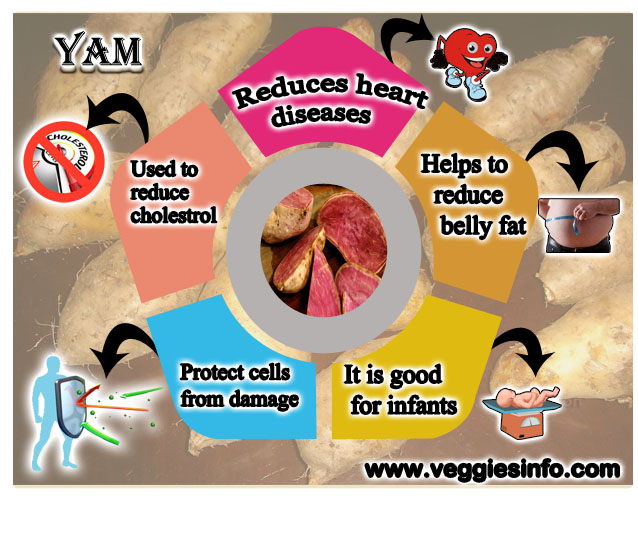
- Yam, like other root crops, is not a good source of essential amino acids.
- It is rich in phenylalanine and threonine but limiting in the sulphur amino-acids, cystine and methionine and in tryptophan.
- Yam consuming areas of Africa have a high incidence of kwashiorkor, a serious medical condition in children caused by protein deficiency.
- Experts emphasize the need to supplement a yam-driven diet with more protein-rich foods in order to support active and healthy growth in infants.
- But the tubers are rich in vitamin B6 and vitamin c.
- It has valuable nutrients and minerals which are essential to maintain good health.
| Principle | Nutrient Value | Percentage of RDA |
|---|---|---|
| Energy | 108 Kcal | 5% |
| Carbohydrates | 27.88 g | 21% |
| Protein | 1.53 g | 3% |
| Total Fat | 0.17 g | 0.50% |
| Cholesterol | 0 mg | 0% |
| Dietary Fiber | 4.1 g | 11% |
| Vitamins | ||
| Folates | 23 µg | 6% |
| Niacin | 0.552 mg | 3.50% |
| Pantothenic acid | 0.314 mg | 7% |
| Pyridoxine | 0.293 mg | 23% |
| Riboflavin | 0.032 mg | 2.50% |
| Thiamin | 0.112 mg | 9.50% |
| Vitamin C | 17.1 mg | 28.50% |
| Vitamin A | 138 IU | 5% |
| Vitamin E | 0.35 mg | 2% |
| Vitamin K | 2.3 µg | 2% |
| Electrolytes | ||
| Sodium | 9 mg | 0.50% |
| Potassium | 816 mg | 17% |
| Minerals | ||
| Calcium | 17 mg | 2% |
| Copper | 0.178 mg | 20% |
| Iron | 0.54 mg | 7% |
| Magnesium | 21 mg | 5% |
| Manganese | 0.397 mg | 17% |
| Phosphorus | 55 mg | 8% |
| Selenium | 0.7 µg | 0.50% |
| Zinc | 0.24 mg | 2% |
| Phyto-nutrients | ||
| Carotene-β | 83 µg | — |
| Crypto-xanthine | 0 µg | — |
| Lutein- zeaxanthin | 0 µg | — |