Yardlong Bean Types And Uses
Yardlong Bean AKA pea bean
Plants and trees provide food, gives shelter, provides rich oxygen, inhales bad gases, improves the soil and refreshes the air through flowers. It renders maximum justice to the earth till the time it lives on this earth. Even after death, it provides wood, leaves and seeds. So the plants always make it a point to help the other species, some way or the other. This topic will deal with a plant named Yardlong Bean which comes under the kingdom Fabaceae. The botanical name of this plant is vigna unguiculata sesquipedalis. The other common names bora, bodi, long-podded cowpea, asparagus bean, pea bean, snake bean or Chinese long bean.
Properties
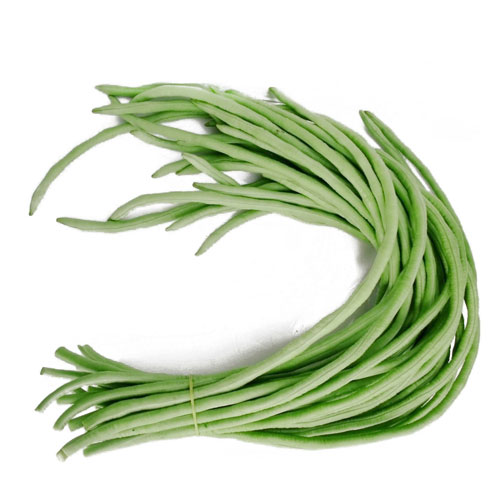
Yardlong bean is a legume which is cultivated for consuming it as a green pods. This bean is only one and a half foot long and not yard long. Yardlong bean does not come under the genus of common bean and this plant is a perennial climbing plant. These plants are generally found in subtropical, tropical and warmer parts of South Asia, Southeast Asia and southern China. This plant comes under the variety of the cowpea and the immature pod attains length of 35 to 75 cm. Yardlong is very similar to green bean. This pods forms 60 days after sowing. It hangs in groups of two or more. Yardlong attracts pollinators like yellowjackets and ants.
Types Of Yardlong bean
There are two types of beans inside the pods, they are
- Red seeds
- Black Seeds
Black seeded pods are fit for human consumption. The mature bean is often dried, stored and cooked as a pulse. The young leaves and stem tips are also fit for human consumption. Yardlong grow on twinning, delicate stems with a tenacious root system. This plant tolerates acidic soil and grows well in well-drained soil. It needs full sun to grow wonderfully. This plant needs a trellis for best production even though it can grow on its own. Yardlong tolerates hot weather and also drought. This plant will not perform well during cold temperatures since they are very sensitive to these types of climates. This plant has rich vitamins and minerals.
Various Uses Of Yardlong bean
- The vegetable will be tasty and good if they are picked before they attain fullest maturity.
- The overlooked beans are used in soups.
- Yardlong beans grow slowly compared to bush beans. But when they start producing they grow wonderfully and quickly.
- Yardlong is classified under ornamental plants category and it has wonderful violet-blue flowers.
- The beans and leaves are good for deer, small mammals and birds.
| Principle | Nutrient Value | Percentage of RDA |
|---|---|---|
| Energy | 47 Kcal | 2% |
| Carbohydrates | 8.35 g | 6% |
| Protein | 2.8 g | 5% |
| Total Fat | 0.40 g | 2% |
| Cholesterol | 0 mg | 0% |
| Vitamins | ||
| Folates | 62 µg | 15.50% |
| Niacin | 0.410 mg | 2% |
| Pantothenic acid | 0.055 mg | 1% |
| Pyridoxine | 0.024 mg | 2% |
| Riboflavin | 0.110 mg | 9% |
| Thiamin | 0.107 mg | 9% |
| Vitamin A | 865 IU | 29% |
| Vitamin C | 18.8 mg | 31% |
| Electrolytes | ||
| Sodium | 4 mg | <1% |
| Potassium | 240 mg | 5% |
| Minerals | ||
| Calcium | 50 mg | 5% |
| Copper | 0.048 µg | 5% |
| Iron | 0.47 mg | 6% |
| Magnesium | 44 mg | 11% |
| Manganese | 0.205 mg | 9% |
| Phosphorus | 59 mg | 8% |
| Selenium | 1.5 µg | 3% |
| Zinc | 0.37 mg | 3% |
Benefits Of Yardlong bean
- Increased yield of crops: Planting a yard-long bean will result in increased yields of beans compared to regular-sized beans. This can be especially beneficial for farmers who are looking to maximize their crop yields.
- Improved nutrition: Yard-long beans are packed with more nutrients than regular-sized beans, making them a great choice for people looking to add more nutrition to their diets.
- Extended growing season: Yard-long beans can be harvested in the summer and fall, providing an extended growing season for gardeners.
- Variety: Yard-long beans come in a variety of colors, shapes, and sizes, allowing gardeners to add some diversity to their gardens.
- Easy to grow: Yard-long beans are relatively easy to grow and require minimal maintenance. This makes them an ideal choice for novice gardeners.