Cabbage Uses , Nutrition Values , Benefits
About Cabbage
Cabbage also scientifically known as Bassica Oleracea; belongs to the bassicaceae and the mustard family. It is a leafy green vegetable that is highly consumed in every part of the world. The term cabbage is derived from the French word ‘’caboche’’ which means head. This is because the shape of a cabbage looks like that of a head. This can be green or red/ purple in colour. They are tap root plants and are cotyledons. The cabbage head is compact with tightly wrapped leaves forming a round shape. The history of cabbage is very extensive; they were believed to be originated in Britain and continental Europe. The ancient Romans believed that cabbage was a table luxury and also offered it to God. This vegetable is available throughout the year and follows a biennial cycle of growth. The time span taken for the growth of the cabbage depends on the variety of the vegetable. Some take 70 days while the late variety takes 120 days for them to reach maturity.
Cabbage Nutrition Facts
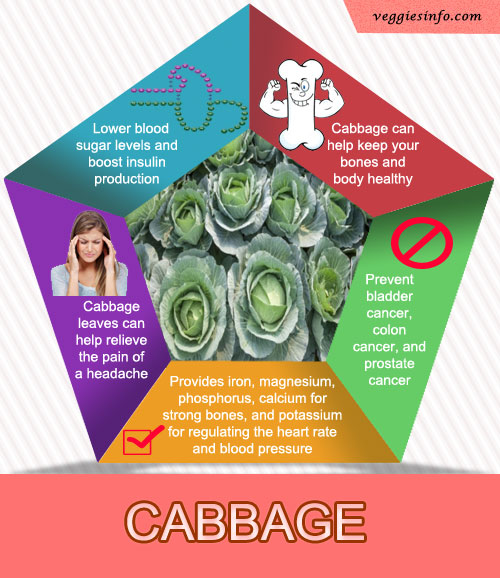
- Provides iron, magnesium, phosphorus, calcium for strong bones.
- Potassium for regulating the heart rate and blood pressure.
- Cabbage is a very good source of Vitamin K.
- Vitamin-K has the potential role in bone metabolism through promoting osteotrophic activity.
- Vitamin-K also has established role in the cure of Alzheimer’s disease.
Cabbage Benefits
- Prevent bladder cancer, colon cancer, and prostate cancer.
- This leaves can help relieve the pain of a headache.
- Lower blood sugar levels and Boost Insulin Production.
- It can help keep your bones and body healthy.
| Principle | Nutrient Value | Percentage of RDA |
|---|---|---|
| Energy | 25 kcal | 1% |
| Carbohydrates | 5.8 g | 4% |
| Protein | 1.3 g | 2% |
| Total Fat | 0.1 g | 0.5% |
| Cholesterol | 0 mg | 0% |
| Dietary Fiber | 2.50 mg | 6% |
| Vitamins | ||
| Folates | 53 µg | 13% |
| Niacin | 0.234 mg | 1.5% |
| Pantothenic acid | 0.212 mg | 4% |
| Pyridoxine | 0.124 mg | 10% |
| Riboflavin | 0.040 mg | 3% |
| Thiamin | 0.061 mg | 5% |
| Vitamin A | 98 IU | 3% |
| Vitamin C | 36.6 mg | 61% |
| Vitamin K | 76 µg | 63% |
| Electrolytes | ||
| Sodium | 18 mg | 1% |
| Potassium | 170 mg | 3.5% |
| Minerals | ||
| Calcium | 40 mg | 4% |
| Iron | 0.47 mg | 6% |
| Magnesium | 12 mg | 3% |
| Manganese | 0.160 mg | 7% |
| Phosphorus | 26 mg | 3.5% |
| Zinc | 0.18 mg | 1.5% |
| Phyto-nutrients | ||
| Carotene-a | 33 µg | — |
| Carotene-ß | 42 µg | — |
| Lutein- zeaxanthin | 30 µg | — |
A leafy cabbage is very nutritious and is very low in fat and calories. A serving of 100grams of cabbage leaves consist of only 25 calories. Deficiency of vitamin C can lead to scurvy; which is normally indicated by bleeding gums, bad immune system leading to frequent infections and cracked lips. This is an abundant source of vitamin C that will prevent the body from being a prey to such a chronic disease. Premature aging can also be an effect of vitamin c deficiency. It consists of sulphur that helps the body from microbial infections and reduces the severity of wounds and ulcers in the body. Its family is known for its cruciferous property that helps in prevention of cancer. Its anti oxidant trait kills cancer cells and also has shown proven results in reduction of breast cancer. Anti inflammatory properties of cabbage prevents the body from being affected by irritations, skin infections allergies, joint fever etc. The popular cabbage soup diet is recommended by many dieticians to ensure weight loss while enjoying healthy cabbage soups. Since cabbage houses so many nutrients and minerals one need not worry about lacking in any of the vital intakes while consuming cabbage soup. Diseases like Alzheimer are known to be treated and prevented by adding cabbage to your diet. This in the medieval days was used to treat headaches and digestive disorders and was well known for its medicinal properties.
How to Enjoy Your Cabbage
This is a key ingredient to many Chinese dishes and thus the younger looking radiant skin of Chinese people can be explained. Cabbage soups, or Manchurian, add them to your noodles or just stir fry them with other vegetables cabbage goes well with everything. It is added to salads to bring in freshness and add nutrition to the meal. Cooking always leads to the loss of vital nutrients in the food so in order to make the best out of all the nutrition it has offer it is recommended to eat cabbage raw.
It has an extended family and all its relatives are equally nutritious! This truly becomes a superhero plant.