Broccoli Nutrition Guide and Health Summary
About Broccoli
Broccoli is a flowering vegetable that is otherwise scientifically belongs to the Brassica oleracea species. This vegetable grows into a luscious green edible flower with stalks that can be consumed and it belongs to the cabbage family. Its name is derived from the Latin word brocco which means an arm a shoot or a branch.It is an Italian vegetable and was first found in France during 1560 long after which it gained popularity in other parts of the European countries. Cultivation of broccoli started in U.S in 1920’s which was much later after it was found. Broccoli was also known as the Italian Asparagus in England as its stems were edible and the flower seemed like that of the cauliflower. The cross between broccoli and cauliflower is known as broccoflower and the cross that is consumed is a cross hybrid of broccoli and kale. Baby broccoli is known as broccolini which is budded off during its early stages of growth. Broccoli like cauliflower is a winter vegetable and it cannot thrive in hot summers. The largest producer of broccoli is China, producing for about 9,500,000 tons annually. India and Italy also fairly contribute to the broccoli market.
Broccoli is a dark green vegetable belonging to the cruciferous family. It is a versatile vegetable that can be eaten raw, steamed, grilled, roasted, or boiled. It is an excellent source of vitamins and minerals including vitamins A, C, and K, as well as folate, iron, and calcium. Broccoli is also high in dietary fiber, which helps to regulate digestion and promote a healthy digestive tract. Broccoli is a popular choice for many home cooks due to its mild flavor and versatility. It can be added to a variety of dishes, from stir-fries and salads to soups and casseroles. The vegetable has a slightly bitter taste when eaten raw, but when cooked, it takes on a sweet flavor. This makes it a great addition to both savory and sweet dishes. Broccoli contains a high amount of antioxidants, which help to fight harmful free radicals in the body. Free radicals can cause damage to cells, leading to the development of chronic diseases such as cancer. The antioxidants in broccoli can also help to reduce inflammation in the body.
Additionally, broccoli is a great source of dietary fiber. Fiber helps to slow down digestion, which can help to keep you fuller for a longer period of time. This can be beneficial for those looking to control their weight or maintain a healthy diet. Overall, broccoli is an incredibly nutritious vegetable that can be enjoyed in a variety of dishes. It is packed with essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants and is high in dietary fiber. Eating broccoli regularly can help to promote a healthy digestive tract, reduce inflammation, and support overall health.
Broccoli Nutrition Value
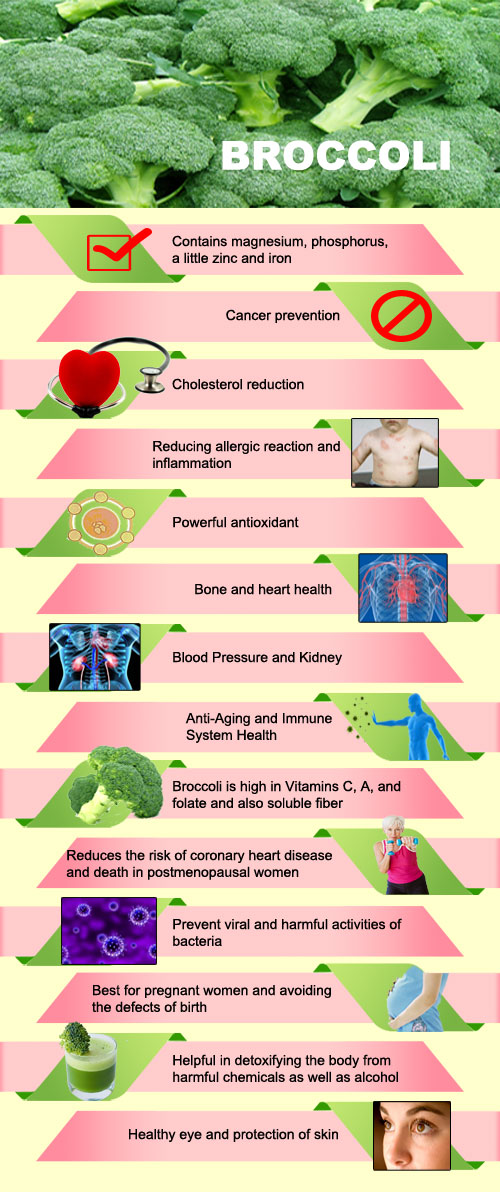
- Contains magnesium, phosphorus, a little zinc and iron.
- Powerful antioxidant.
- This is high in Vitamins C, A, and folate and also soluble fiber.
- Helpful in detoxifying the body from harmful chemicals as well as alcohol
Health Benefits of Broccoli
- Cancer prevention.
- Cholesterol reduction.
- Reducing allergic reaction and inflammation.
- Bone and heart health.
- Blood Pressure and Kidney Health.
- Anti-Aging and Immune System Health.
- Reduces the risk of coronary heart disease and death in postmenopausal women.
- Prevent viral and harmful activities of bacteria.
- Best for pregnant women and Avoiding the Defects Of Birth.
- Healthy eye and protection of skin.
Interesting Facts
Broccoli originated in Italy off of the Mediterranean. It has been eaten there since the time of the ancient Romans in the 6th Century BC.
Broccoli for Healthy Bones
It gives you healthy bones because it contains calcium in a high amount which is more than any other vegetables. As we know calcium is helpful to build bone mass.
| Principle | Nutrient Value | Percentage of RDA |
|---|---|---|
| Energy | 34 Kcal | 1.5% |
| Carbohydrates | 6.64 g | 5% |
| Protein | 2.82 g | 5% |
| Total Fat | 0.37 g | 1% |
| Cholesterol | 0 mg | 0% |
| Dietary Fiber | 2.60 g | 7% |
| Vitamins | ||
| Folates | 63 µg | 16% |
| Niacin | 0.639 mg | 4% |
| Pantothenic acid | 0.573 mg | 12% |
| Pyridoxine | 0.175 mg | 13% |
| Riboflavin | 0.117 mg | 9% |
| Thiamin | 0.071 mg | 6% |
| Vitamin A | 623 IU | 21% |
| Vitamin C | 89.2 mg | 149% |
| Vitamin E | 0.17 mg | 1.5% |
| Vitamin K | 101.6 µg | 85% |
| Electrolytes | ||
| Sodium | 33 mg | 2% |
| Potassium | 316 mg | 7% |
| Minerals | ||
| Calcium | 47 mg | 5% |
| Copper | 0.049 mg | 5.5% |
| Iron | 0.73 mg | 9% |
| Magnesium | 21 mg | 5% |
| Manganese | 0.210 mg | 9% |
| Selenium | 2.5 µg | 5% |
| Zinc | 0.41 mg | 4% |
| Phyto-nutrients | ||
| Carotene-ß | 361 µg | — |
| Crypto-xanthin-ß | 1 µg | — |
| Lutein-zeaxanthin | 1403 µg | — |
Great tasting nutrition, that’s what broccoli is known for Broccoli lovers are all over the world. This cruciferous vegetable has the following nutrients. It is a great source of vitamin K it is essential for blood clotting in the body and also helps in getting stronger bones preventing osteoporosis. It is a known fact that eating non starchy vegetables leads to cancer prevention and it is a proven fact that eating broccoli can help you prevent and fight cancer. Breast cancer, ovarian cancer, bladder cancer and colon cancer are said to be prevented when one consumes broccoli. Keeping true to its dietary fibre this veggie helps in digestive support and relives the body of any digestive disorder. The dietary fibre protects the lining on the stomach and prevents and bacterial growth inside the stomach.It supports a healthy heart and a healthy hearts simply indicates a good lifestyle. The anti inflammatory property present in cruciferous plants makes it heart friendly and thus avoids absorption of bad cholesterol and thinning of arteries thus preventing cardiovascular disease and keeping heart attacks at bay. Apart from the ones mentioned above broccoli also forms a good source of vitamin A that helps treating sun burnt skin. All in all this food has no fat, low in sodium and contains only 31 calories per serving.
How To Enjoy Broccoli
A cup of broccoli is equal to the proteins gained from a cup of rice with half the amount of calories. This way substituting broccoli with rice can be a good option for all weight watchers. Boiling broccoli will drain up to 90% of all the nutrients so instead of boiling it one should opt for microwaving, steaming or even stir frying. Eating broccoli raw is very nutritious, add broccoli to your salad and make it a healthy meal. Broccoli is often added to Chinese soups and gravies as it is a vegetable highly consumed in China. Italian pasta and casseroles also feature broccoli as they are not only flavoursome but highly nutritious.
This cabbage relative is a power house of nutrition infused with flavour. Eating tasty is new eating healthy.