List Of Vegetables
- Absinthe Interesting Facts

- Ahipa Nutritional Values

- Akudjura Various Uses

- Amaranth Health Benefits

- American Pokeweed

- Aniseed Myrtle Properties

- Aonori Summary

- Apple Mint Uses

- Arame Medicinal Uses

- Arracacha Nutritional Value

- Artichoke Nutrition Values

 Arugula Health Summary
Arugula Health Summary- Asarabacca Various Uses

- Asparagus Healthy Eating

- Avocado Nutrition Benefits

- Bamboo shoots

- Basil Nutrition Guide

- Beans Beneficial Properties

- Bean sprouts

- Beet Greens Nutrition Facts

- Beets Health Benefits
- Bishop’s weed Various Uses

- Bitter Gourd Nutritional Value

- Black Beans Benefits

- Blue Fenugreek Various Uses

- Boldo Medicinal Values

- Bok Choy Health Benefits

- Borage Greens Medicinal Purposes

- Bottle Guard Aspects

- Broccoli Health Properties

- Broccoflower Nutrition Guide

- Broccoli Raab Nutrition Values

- Broadleaf Arrowhead Health Benefits

- Brussel sprouts Nutrition Summary

- Burdock Health Benefits

- Cabbage Health Facts

- Camas Health Benefits

- Cantaloupe Nutrition Guide

- Canella Uses

- Carrots Health Properties

- Cardoon Nutritional Value

- Carola Summary

- Cassava Health Properties

- Catnip Oil Benefits

- Catsear Flower Uses

- Celeriac Nutritional Value

- Celery Health Benefits

- Chard(Swiss & red)Nutrition Values

- Chaya Nutrition Facts

- Chervil Properties

- Good King Henry

- Chickweed Health Benefits

- Chickpeas Nutrition Summary

- Chile peppers Health Benefits

- Chinese Artichoke Uses

- Chinese Broccoli Nutritional Valu

- Chinese cabbage Nutrition Values

- Chinese Mallow Aspects

- Chives Nutrition Guide

- Chrysanthemum Leaves Uses

- Cicely Unknown Benefits

- Cinnamon Myrtle Medicinal Value

- Collards Nutrition Facts

- Common Purslane Benefits

- Corn Health Values

- Corn Salad Interesting Facts

- Cress Medicinal Values

- Cucumber Health Benefits

- Culantro Leaves

- Curry Leaf Tree Origin

- Collard Greens Nutrition Facts

- Dabberlocks Interesting Facts

- Dandelion Health Benefits

- Dill Health requirements

- Drumstick Nutritional Value

- Dulse Health Benefits

- Earthnut Pea Properties

- Eggplant Nutrition Guide

- Elephant Foot yam Health Benefits

- Elephant Garlic Uses

- Endive Medicinal Properties

- Ensete Health Benefits

- Epazote Properties

- Fat Hen Interesting Facts

- Fingerroot Uses

- French Sorrel Health Facts

- Garlic Nutrition Values

- Gim seaweed Uses

- Ginger Flower Properties

- Ginger Medicinal Values

- Golden Samphire Aspects

- Greater Plantain Medicinal Uses

- Green onions Health Facts

- Green peas Nutrition Values

- Hijiki Nutritional Aspects

- Holy Basil Leaves

- Horseradish Health Benefits

- Onions Nutrition Guide

- Sea Beet Aspects

- Sea Lettuce Health Benefits

- Yam Nutritional Value

- Yarrow Medicinal Uses

- Zucchini Health Guide

- Veggies by seasons

- Veggies did you know??

- Comparison of veggies!!!

- Veggies and it's origin

- Comical View of Veggiess

- Categories of veggies

- Top Veggiess 100 To 91

- Top Veggiess 90 To 81

- Top Veggiess 80 To 71

- Top Veggiess 70 To 61

- Top Veggiess 60 To 51

- Top Veggiess 50 To 41

- Top Veggiess 40 To 31

- Top Veggiess 30 To 21

- Top Veggiess 20 To 11

- Top Veggiess 10 To 01

Veggie Picks
Top Veggiess 100 To 91 For Health Benefits
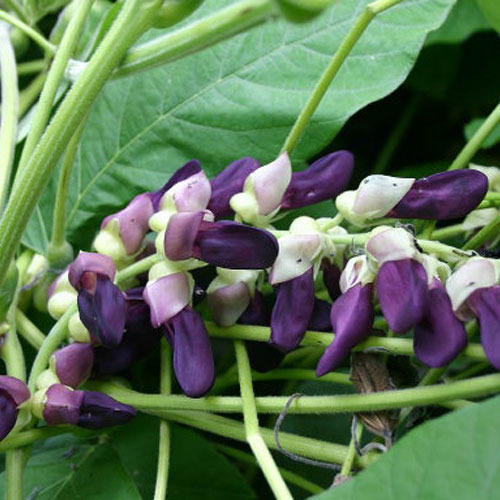
100. Velvet Bean
Velvet beans are the exotic legume with purplish flowers and dense hair pods. Velvet beans are elliptical purple beans that are effectively used in ayurvedic treatments. It is a good source of protein and fiber. It contains minerals like potassium, calcium, sodium, magnesium, phosphorus, iron, copper, zinc and manganese. Velvet beans highly benefit male to enhance sperm count. It is used to treat diseases like parkinson disease and diabetes. It promotes our brain health and helps to reduce stress.
- The plants and its leaves have certain medicinal effects.
- The Ayurvedic experts squeeze the leaves and apply it on the snake bitten area.
- Ayurvedic experts also use these plants for curing Parkinson's disease.
- Siddha doctors also use this plant for treating certain diseases.
- These beans have L-Dopa a precursor to the neurotransmitter dopamine. So these beans help in improving brain function.
The full grown plant has medicinal properties which will be dealt in later part of this topic. These plants are annual climbing shrub that can reach over 15 m in length. When young these plants have fuzzy hair and these hairs disappear when they grow fully. The length of the flowers reaches up to 32 cm and the length of the leaves are approximately 2.5 mm to 5 mm. The size of the fruit is 4 to 13 cm. The dried plants are used as a fodder for animals.These beans are used as a coffee substitute and many consume these beans after boiling it for an hour.
- The people will suffer from extreme itchiness if they touch the young foliage and the seed pods.
- The beans may be harmful if it is eaten uncooked.

99. Okinawan purple sweet potato
The sweet potato has a vibrant purplish flesh and brown papery skin in the exterior. It is an exotic vegetable with a rich flavor. It is a good source of nutrients such as vitamin A, vitamin C, manganese, copper, dietary fiber, vitamin B6, potassium and iron. It may regulate insulin production and improve blood circulation. They have antibacterial and antifungal properties to treat infections. It can be eaten like regular sweet potato or boiled, smashed, steamed and mashed to enjoy its flavor.
- Calories: 140
- Carbs: 27 g
- Protein: 1 g
- Fat: 0.1 g
- Fiber: 4 g
- Sodium: 0.83% of the Daily Value (DV)
- Potassium: 13.5% of the DV
- Calcium: 2% of the DV
- Iron: 4% of the DV
- Vitamin C: 40% of the DV
- Vitamin A: 4% of the DV

98. Romanesco cauliflower
Romanesco cauliflower is a leafy greens with a bunch of crunchy florets. It belongs to the family of cauliflower and broccoli. They have a delicate and nutty flavor and serve a good nutrition profile. It contains vitamin C, sodium, vitamin B6, vitamin B5 and manganese. It improves blood circulation and promotes heart health. It improves your vision and boosts digestive health. It reduces the risk of cancer and high fiber content may benefit the digestive system. It can be boiled, steamed and stir fried to add in your favorite dishes.
- Broccoli is one of the very low calorie vegetables; provides just 34 calories per 100 g.
- It is rich in dietary fiber, minerals, vitamins, and anti-oxidants that have proven health benefits.
- Total antioxidant strength measured in terms of Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity (ORAC) of broccoli is 1632 µmol TE/100 g.
- Fresh Broccoli is a storehouse of many phyto-nutrients such as thiocyanates, indoles, sulforaphane, isothiocyanates and flavonoids like beta-carotene cryptoxanthin, lutein, and zea-xanthin.
- Improves Eyesight.
- Supports Vision.
- Helps fight viral infections.
- Protects from free radicals.
- Improves Blood Sugar Levels.
- Lowers Risk of many cancers.
- Improves healing.
- Supports Muscles.
- Helps protect from cold and flu.
- Helps protect from infections.
- Improves Lung health.
- Supports red cell health.
- Improves Bone health.
- Improves Brain function.
- Reduces Depression.
- Reduces Constipation.
- Supports Nerves.
- Supports Heart Health.
| Principle | Nutrient Value | Percentage of RDA |
|---|---|---|
| Energy | 25 Kcal | 1% |
| Carbohydrates | 4.97 g | 4% |
| Protein | 1.92 g | 4% |
| Total Fat | 0.28 g | 1% |
| Cholesterol | 0 mg | 0% |
| Dietary Fiber | 2.0 g | 5% |
| Vitamins | ||
| Folates | 57 µg | 14% |
| Niacin | 0.507 mg | 3% |
| Pantothenic acid | 0.667 mg | 13% |
| Pyridoxine | 0.184 mg | 14% |
| Riboflavin | 0.060 mg | 4.5% |
| Thiamin | 0.050 mg | 4% |
| Vitamin A | 0 IU | 0% |
| Vitamin C | 48.2 mg | 80% |
| Vitamin E | 0.08 mg | 0.5% |
| Vitamin K | 15.5 µg | 13% |
| Electrolytes | ||
| Sodium | 30 mg | 2% |
| Potassium | 299 mg | 6% |
| Minerals | ||
| Calcium | 22 mg | 2% |
| Copper | 0.039 mg | 4.5% |
| Iron | 0.42 mg | 5% |
| Magnesium | 15 mg | 3.5% |
| Manganese | 0.155 mg | 7% |
| Zinc | 0.27 mg | 2.5% |
| Phyto-nutrients | ||
| Carotene-ß | 0 µg | — |
| Lutein-zeaxanthin | 1 µg | — |
97.Napa cabbage
Napa cabbage is an elongated cabbage that looks more like a lettuce. It contains white to pale green leaves that are firmly packed in its rigid head. It is loaded with antioxidants and provides us with other essential nutrients including folates, vitamin C, vitamin K and fiber. It helps to reduce the risk of asthma and promotes healthy bones and teeth. It is used to treat conditions like arthritis, common cold and premenstrual symptoms.it reduce the risk of diabetes and improves brain health and heart health. Napa cabbages are easily incorporated in many dishes like wraps, stir fries, chicken salads and made into kimchi.
- Food for pregnant women.
- Keeps your bones and teeth strong with the help of calcium and vitamin K.
- Chinese cabbage is also Rich in Anti-oxidants.
- Helps regulate blood pressure.
- Fights anemia and fatigue.
- Rich in antioxidants.
- Keeps eyes healthy.
- Great for weight loss.
- Supports youthful and healthy skin.
- Boosts the immune system.
- Fights off bad bacteria.
- Cabbage helps dry up oily and acne skin.
- Relieves the pain of a headache.
| Principle | Nutrient Value | Percentage of RDA |
| Energy | 25kcal | 1% |
| Carbohydrates | 5.8g | 4% |
| Protein | 1.3g | 2% |
| Total Fat | 0.1g | 0.5% |
| Cholesterol | 0 mg | 0% |
| Dietary Fibre | 2.50 mg | 6% |
| Vitamins | ||
| Folates | 53 µg | 13% |
| Niacin | 0.234 mg | 1.5% |
| Pantothenic acid | 0.212 mg | 4% |
| Pyridoxine | 0.124 mg | 10% |
| Riboflavin | 0.040 mg | 3% |
| Thiamin | 0.061 mg | 5% |
| Vitamin A | 98 IU | 3% |
| Vitamin C | 36.6 mg | 61% |
| Vitamin K | 76 µg | 63% |
| Electrolytes | ||
| Sodium | 18 mg | 1% |
| Potassium | 170 mg | 3.5% |
| Minerals | ||
| Calcium | 40 mg | 4% |
| Iron | 0.47 mg | 6% |
| Magnesium | 12 mg | 3% |
| Manganese | 0.160 mg | 7% |
| Phosphorus | 26 mg | 3.5% |
| Zinc | 0.18 mg | 1.5% |
| Phyto-nutrients | ||
| Carotene-a | 33 µg | — |
| Carotene-ß | 42 µg | — |
| Lutein-zeaxanthin | 30 µg | — |
This cabbage has longer leaves that are tightly wrapped up. It forms a core ingredient of oriental and pan Asian cooking styles. Use the leaves of Napa cabbage to make wraps; fill it with fun stuffing of meat or any vegetables and steam them.
Cabbage soup comes with a crunchy texture and is a whole new innovation to the world of creamy rich soups. Coleslaw made out of cabbage is crunch zesty and overall a healthy sandwich spread. Hot dogs wouldn't taste that good if they weren't topped with sauerkraut (pickled cabbage). All in all Chinese cabbage blends well with food and taste great without being unhealthy.

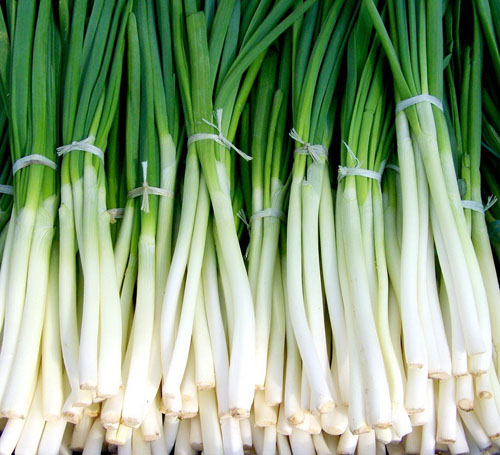
96. Green onion
Green onion is a slim, tender and baby plant of the onion. It is commonly known as scallions in many parts of the world. It has a leafy stem and white bulb that has a mild taste of onions. It is a rich source of vitamin K, sulphur, vitamin C and vitamin A. Including scallions in our diet may help to reduce the risk of cancer and lower the blood sugar. It promotes healthy digestion and good vision. It is used to treat viral diseases like flu and cold. It is added with other vegetables, sandwiches, salads, stews and makes an excellent garnish.
- Immune System Health.
- Healthy eye and healthy bones.
- Protects your cells from damage and Fights Mascular Degeneration.
- Exerts heart-healthy effect.
- Improves your bone density.
- Reduces risk of cancer.
- Lowers blood sugar levels.
- Prevents stomach complications.
- Protects against infection.
- Green Onions are very low in calories.
- 100 g of fresh leaves provide just 31 calories.
- 100 g fresh leaves provide 64 µg of folates.
- Aids in respiratory function.
- Maintains normal vision.
| Principle | Nutrient Value | Percentage of RDA |
|---|---|---|
| Energy | 32 Kcal | 1% |
| Carbohydrates | 7.34 g | 6% |
| Protein | 1.83 g | 3% |
| Total Fat | 0.30 g | 1% |
| Cholesterol | 0 mg | 0% |
| Dietary Fiber | 2.6 g | 7% |
| Vitamins | ||
| Folates | 64 µg | 16% |
| Niacin | 0.525 mg | 3% |
| Pantothenic acid | 0.075 mg | 1.5% |
| Pyridoxine | 0.61 mg | 5% |
| Riboflavin | 0.080 mg | 6% |
| Thiamin | 0.055 mg | 5% |
| Vitamin A | 997 IU | 33% |
| Vitamin C | 18.8 mg | 31% |
| Vitamin E | 0.55 mg | 4% |
| Vitamin K | 207 µg | 172% |
| Electrolytes | ||
| Sodium | 16 mg | 1% |
| Potassium | 276 mg | 6% |
| Minerals | ||
| Calcium | 72 mg | 7 % |
| Copper | 0.083 mg | 9% |
| Iron | 1.48 mg | 18.5% |
| Magnesium | 20 mg | 5% |
| Manganese | 0.160 mg | 7% |
| Phosphorus | 37 mg | 5% |
| Selenium | 0.6 µg | 1% |
| Zinc | 0.39 mg | 3.5% |
| Phyto-nutrients | ||
| Carotene-ß | 598 µg | — |
| Crypto-xanthin-ß | 0 µg | — |
| Lutein-zeaxanthin | 1137 µg | — |
95. Artichoke
Artichoke is the immature flower buds of the artichoke plants. It may be purple or green in color and has mild and earthy flavor. Artichokes are low in fat but rich in nutrients such as vitamin C, vitamin K, potassium, vitamin B6, magnesium, phosphorus, folate, iron, calcium and zinc. It may lower bad cholesterol levels, blood sugar level and regulate blood pressure. It protects your liver from damage and promotes growth of new cells. It may improve digestive health and helps to treat irritable bowel syndrome. It may also have anticancer effects that inhibit the growth of cancer cells.
- Good remedy for providing relief from hangover.
- Reducing the presence of toxins.
- Improve bone health and density.
- Stimulates production secretion of gastric juices and bile juices.
- Preventing neural tube defects in new born.
- Improving Brain Health and metabolic processes.
- Reduces levels of bad cholesterol and increases levels of good cholesterol.
Interesting Facts
The highest amount of vitamins and nutrients are contained within the vegetable's skin and the layer directly underneath it.
How To Enjoy Artichoke
Artichokes are the best winter vegetables and popular across the Mediterranean regions like Europe. Baby artichokes can be readily consumed with the pine where as the globe artichoke will need some scaling off of the prickly pines. All these hassles can be put to rest, thanks to the supermarket where fresh buds are readily available for consumption. Artichokes can be mixed with vegetables, can be barbequed or char grilled or can even be stuffed with meat and sea food. Many people shed off the stem and eat only the bud, the stem can also be consumed as it taste just like the heart of Artichoke. This vegetable is very well treated and does not manifest any allergic reaction to the general population.
| Principle | Nutrient Value | Percentage of RDA |
|---|---|---|
| Energy | 47 Kcal | 2% |
| Carbohydrates | 10.51 g | 8% |
| Protein | 3.27 g | 6% |
| Total Fat | 0.15 g | 0.5% |
| Cholesterol | 0 mg | 0% |
| Dietary Fiber | 5.4 g | 14% |
| Vitamins | ||
| Folates | 68 µg | 17% |
| Niacin | 1.046 mg | 6.5% |
| Pantothenic acid | 0.338 mg | 7% |
| Pyridoxine | 0.116 mg | 9% |
| Riboflavin | 0.066 mg | 5% |
| Thiamin | 0.072 mg | 6% |
| Vitamin C | 11.7 mg | 20% |
| Vitamin A | 13 IU | 0.5% |
| Vitamin E | 0.19 mg | 1% |
| Vitamin K | 14.8 µg | 12% |
| Electrolytes | ||
| Sodium | 94 mg | 6% |
| Potassium | 370 mg | 8% |
| Minerals | ||
| Calcium | 44 mg | 4% |
| Copper | 0.231 mg | 27% |
| Iron | 1.28 mg | 16% |
| Magnesium | 60 mg | 15% |
| Manganese | 0.256 mg | 11% |
| Phosphorus | 90 mg | 13% |
| Selenium | 0.2 µg | <0.5% |
| Zinc | 0.49 mg | 4.5% |
| Phyto-nutrients | ||
| Carotene-alpha | 8 µg | |
| Crypto-xanthin | 0 µg | |
| Lutein-zeaxanthin | 464 µg |
94. Yam
Yam is a tuberous vegetable that is often confused with sweet potatoes. They have brown bark-like exterior and varied color flesh including white, yellow, purple or pink. Yam contains essential nutrients including vitamin C, vitamin B5, manganese, magnesium, potassium, thiamine, copper and folate. It supports bone health and promotes a healthy heart. It contains a unique compound called diosgenin that enhances brain function. It may promote blood sugar level and digestive system. The carb content may reduce your appetite and manage your weight. It may also have anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory effects. It can be boiled, baked, steamed, roasted and fried to add in our diet.
There are different types of yam which are found throughout the humid tropics. Some of the known varieties under dioscorea are rotundata, alata, polystachya, bulbifera,cayenensis, esculenta, dumetorum and trifida.
- D. rotundata
D. rotundata is also callsed white yam. The most prevalent yam in many countries is d.rotundata and d. cayenensis. The rotundata is generally called as white yam and cayenensis is called yellow yam. Both are classifed as same species and there are more than two hundreds cultivated varieties between them. White yam's tuber is cylindrical in shape and has a brown skin and white flesh. Yellow yam has yellow flesh and color caused by the presence of carotenoids. The variety named kokoro is used for making yam chips. Yellow has a longer period of vegetation compared to white yam. The vines of these plants grow as long as 39 ft and the tubers weight about 5 kg. The tubers are generally harvested after 7 to 12 months. "Pounded yam" dish is very famous in Africa.
- D. alata
The next important variety which is grown by many countries are D. alata which is also called winged yam and purple yam is cultivated lavishly in southeast Asia and has the largest distribution throughout the world. This is grown in in Asia, the Pacific islands, Africa, and the West Indies.
- D. Polystachya
D. Polystachya is a well known variety in China and the Chinese yam is very famous in this country. This plant is small compared to African vines. The plants grow up to 3m long. The Chinese yams are frost tolerant and can be cultivated in cooler condition. This yam was introduced in Europe during 19th century and has become very famous in many countries in Europe including France. These tubers are harvested after 6 months from the date of planting.
- D. bulbifera
The Chinese use these yams as ingredients in noodles and for other dishes. The next popular yam is d. bulbifera which is also called air potato is famous in Africa and Asia. The vines reach 6 m or more in length the bulbils which grow at the base are used as edible ones. The weight of the potato is around 2 kg. Some varieties can be eaten raw while some require boiling or cooking.
- D. esculent
D. esculent is a will bitter yam vines which is a native of Southeast Asia and it is the third most cultivated species. It is very famous throughout the world. The vines reach a 3 m in length and the tubers are very small. The tubers are eaten raw or cooked. D. Dumetorum is also called as bitter yam which is very popular in West Africa. This yam can be cultivated easily without any difficulty and requires very less labor.
- D. trifida
The next variety is D. trifida which is also called cush-cush yam which is found in Guyana region of South America. Yams occupy 5 million hectares in about 47 countries. In West and Central Africa the plants are intercropped with cereals and vegetables. Yams are often attacked by various pests and require good maintenance. The production will be wonderful when the annual rainfall is over 1500 mm. White, yellow and water yams produce a single large tuber per year which will weighs 5 to 10 kgs. The production levels of yams are very low. Labor charges for cultivation are very high. The production throughout the world during 2010 was 48.7 million tons of Yam. The biggest reap was in 2008 where the world produced 54 million metric ton.
Different Names Of D. alata:
The tubers are cylindrical and have white flesh which is extremely watery. The Philippine people call this yam as "ube" and use this yam as an ingredient in sweet desserts. Indonesians call this as ubi. Vietnamese call this as khoai mo and they use it in the soup. Indians call this yam as ratalu or violet yam. Hawaiians call this yam as uhi and Japanese call it as daijo or beniimo.
- Yam, like other root crops, is not a good source of essential amino acids.
- It is rich in phenylalanine and threonine but limiting in the sulphur amino-acids, cystine and methionine and in tryptophan.
- Yam consuming areas of Africa have a high incidence of kwashiorkor, a serious medical condition in children caused by protein deficiency.
- Experts emphasize the need to supplement a yam-driven diet with more protein-rich foods in order to support active and healthy growth in infants.
- But the tubers are rich in vitamin B6 and vitamin c.
- It has valuable nutrients and minerals which are essential to maintain good health.
| Principle | Nutrient Value | Percentage of RDA |
|---|---|---|
| Energy | 108 Kcal | 5% |
| Carbohydrates | 27.88 g | 21% |
| Protein | 1.53 g | 3% |
| Total Fat | 0.17 g | 0.50% |
| Cholesterol | 0 mg | 0% |
| Dietary Fiber | 4.1 g | 11% |
| Vitamins | ||
| Folates | 23 µg | 6% |
| Niacin | 0.552 mg | 3.50% |
| Pantothenic acid | 0.314 mg | 7% |
| Pyridoxine | 0.293 mg | 23% |
| Riboflavin | 0.032 mg | 2.50% |
| Thiamin | 0.112 mg | 9.50% |
| Vitamin C | 17.1 mg | 28.50% |
| Vitamin A | 138 IU | 5% |
| Vitamin E | 0.35 mg | 2% |
| Vitamin K | 2.3 µg | 2% |
| Electrolytes | ||
| Sodium | 9 mg | 0.50% |
| Potassium | 816 mg | 17% |
| Minerals | ||
| Calcium | 17 mg | 2% |
| Copper | 0.178 mg | 20% |
| Iron | 0.54 mg | 7% |
| Magnesium | 21 mg | 5% |
| Manganese | 0.397 mg | 17% |
| Phosphorus | 55 mg | 8% |
| Selenium | 0.7 µg | 0.50% |
| Zinc | 0.24 mg | 2% |
| Phyto-nutrients | ||
| Carotene-β | 83 µg | — |
| Crypto-xanthin | 0 µg | — |
| Lutein-zeaxanthin | 0 µg | — |
93. Mint
Mint is a perennial herb with ovate leaves and rich aroma. The distinctive taste and aroma allows it to incorporate in beverages and rice or processed into candies and many other eatables. It is a good source of vitamin A, iron, manganese and folate. It is loaded with antioxidants when compared to other herbs. It may help to treat irritable bowel syndrome and digestive problems. Inhaling the aroma of mint benefits our brain health and decreases frustration, anxiety and fatigue. It is also effectively used to treat cold and flu.
- This plant is native to Southern and Eastern Africa, from South Africa and Swaziland to Angola and Mozambique and north to Kenya and Tanzania.
- This plant is used as an ornamental and decorative plant in many houses in south India.
- This large aromatic plant has hairs with smelling leaves.
- The fleshy stems measures 90 cm with long hairs.
- The undivided and oval-shaped leaves have aromatic smell.
- The pale purplish flowers are on a short stem.
- This plant grows wonderfully in well-drained, semi-shaded areas.
- The natural antioxidant properties are found in this plant's leaves, fruits, seeds, roots and bark.
- The leaves act as a free radical quenchers since it has rich antioxidant properties.
- The leaves acts are anti-inflammatory, antimutagenic, hypocholestemic and antiplatelent aggregation properties.
- The leaves are also used as a decoction for treating many chronic diseases.
- The leaves are used a flavor in meat and poultry stuffing.
- The leaves are administered as juice to lactating women to improve milk production.
- The leaves are also used as a vegetable in many countries.
The leaves are used for treating coughs, throats, nasal congestion, infections, rheumatism, malaria, asthma, renal diseases, vesical calculi, epilepsy, and flatulence, hiccup, long infections skin ulcerations, diarrhea, skin allergy, liver diseases and other diseases.
- Skin Care
- Help's for Digestion
- Treats Asthma
- Cures Common Cold
- Cures Headache
- Improves Brain Power
- Help Ease Symptoms Of Morning sickness
- Help to cure stress and depression
92. Coriander
Coriander leaves and seeds are the staple food in Indian cuisine used for its unique flavor and health benefits. The curly leaves are commonly called cilantro. The leaves are an excellent source of vitamin C, vitamin K, calcium, phosphorus,potassium, thiamine, niacin and protein. It may lower blood sugar, cholesterol level and benefits our immune system. It promotes our heart and brain health. The coriander seeds may promote digestion and gut health. It helps to treat infections and protect your skin. The fresh leaves are used to make many Indian dishes like salads, salsas , chutneys and many other dishes.
- Plants have the capacity to grow from the ashes and become gigantic trees after few years. The leaves and the fruits grow once again from the same place where it is cut or harvested.
- A new sapling will sprout from the place where the tree is uprooted. The plants and trees are magicians at work which throws different magical spells.
- Only few insects like lizards, cockroaches have the capacity to grow its own parts when someone cuts it.
- Coriander is used in various cuisines throughout the world.
- The leaves of this plant have a very different taste with citrus overtones.
- South Asians use coriander in many dishes.
- Chinese, Thailand, Mexicans and Russians also use corander leaves lavishly in their foods items.
- The Indians chop the leaves and mix it with dal.
- The coriander seeds are used as a spice. The seeds emit lemon flavor when crushed since it has linalool and pinene.
- The diameter of the fruit is 0.12-0.20 in.
- Large-fruited types are grown in tropic and subtropical contries and smaller ones are used in temperate regions.
- This plant is native to Europe, Asia and Africa.
- This wonderful soft plant reaches a height of 50 cm.
- The leaves have different shapes and white or pale pink flowers are found in small umbels.
- The globular fruit measures 3-5mm in diameter.
- The seeds are used as spice or an added ingredient in foos or recipes.
- The word coriander derives from the French word coriandre which comes from Latin.
- Several mericarps were found in the Pre-pottery Neolithic B level of the Nahal Hemar Cave in Israel.
- As per the archeological evidences this plant was cultivated by ancient Egyptians.
- Coriander was brought to the British colonies in North America during 1670 and was the first spice that was cultivated by early settlers.
- Though all parts of the plants are edible the fresh leaves and dried seeds are most used in cooking.
| Nutrients | Nutrition Value | % DV of RDA |
|---|---|---|
| Energy | 23 Kcal | 1% |
| Carbohydrates | 3.67 g | 3% |
| Protein | 2.13 g | 4% |
| Total Fat | 0.52 g | 2% |
| Cholesterol | 0 mg | 0% |
| Dietary Fiber | 2.80 g | 6.50% |
| Vitamins | ||
| Folates | 62 µg | 15.50% |
| Niacin | 1.114 mg | 7% |
| Pantothenic acid | 0.570 mg | 11% |
| Pyridoxine | 0.149 mg | 11% |
| Riboflavin | 0.162 mg | 12% |
| Thiamin | 0.067 mg | 5.50% |
| Vitamin A | 6748 IU | 225% |
| Vitamin C | 27 mg | 45% |
| Vitamin E | 2.50 mg | 17% |
| Vitamin K | 310 mcg | 258% |
| Electrolytes | ||
| Sodium | 46 mg | 3% |
| Potassium | 521 mg | 11% |
| Minerals | ||
| Calcium | 67 mg | 7% |
| Iron | 1.77 mg | 22% |
| Magnesium | 26 mg | 6.50% |
| Manganese | 0.426 mg | 18.50% |
| Phosphorus | 48 mg | 7% |
| Selenium | 0.9 mg | 2% |
| Zinc | 0.50 mg | 4.50% |
| Phyto-nutrients | ||
| Carotene-α | 36 µg | — |
| Carotene-ß | 3930 µg | — |
| Crypto-xanthin-ß | 202 µg | — |
| Lutein-zeaxanthin | 865 µg | — |
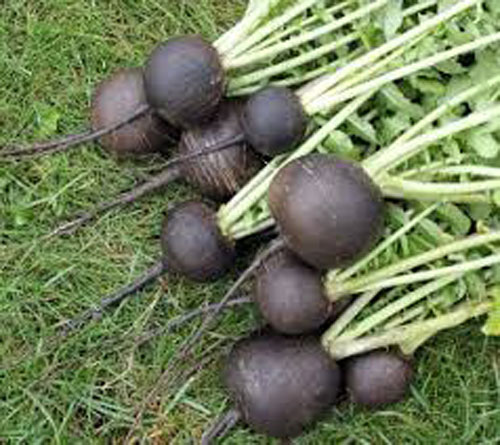
91. Black radish
Black radish is a type of radish with black skin and crunchy white flesh. Black radish is high in dietary fiber that fights cholesterol and promotes weight loss. It comprises essential nutrients including vitamins A, C and E, magnesium, potassium and selenium. The fiber content may improve your gut health and can prevent hyperthyroidism. It supports mental health and helps to remove toxins from our body. It improves blood circulation and hair growth. It is effectively used to treat cold and bronchitis.
- Black radish control cholesterol
- Black radish has plenty of vitamin C
- High amounts of immunity
- Important for a healthy liver
- Help for weight loss
- Improve hair growth
- Detoxification
- Support great brain