List Of Vegetables
- Absinthe Interesting Facts

- Ahipa Nutritional Values

- Akudjura Various Uses

- Amaranth Health Benefits

- American Pokeweed

- Aniseed Myrtle Properties

- Aonori Summary

- Apple Mint Uses

- Arame Medicinal Uses

- Arracacha Nutritional Value

- Artichoke Nutrition Values

 Arugula Health Summary
Arugula Health Summary- Asarabacca Various Uses

- Asparagus Healthy Eating

- Avocado Nutrition Benefits

- Bamboo shoots

- Basil Nutrition Guide

- Beans Beneficial Properties

- Bean sprouts

- Beet Greens Nutrition Facts

- Beets Health Benefits
- Bishop’s weed Various Uses

- Bitter Gourd Nutritional Value

- Black Beans Benefits

- Blue Fenugreek Various Uses

- Boldo Medicinal Values

- Bok Choy Health Benefits

- Borage Greens Medicinal Purposes

- Bottle Guard Aspects

- Broccoli Health Properties

- Broccoflower Nutrition Guide

- Broccoli Raab Nutrition Values

- Broadleaf Arrowhead Health Benefits

- Brussel sprouts Nutrition Summary

- Burdock Health Benefits

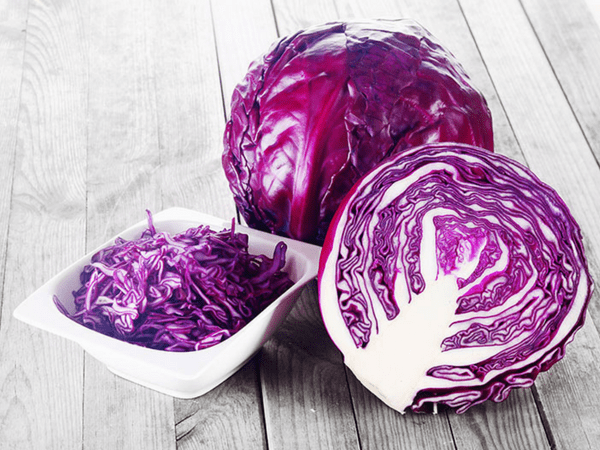
- Cabbage Health Facts

- Camas Health Benefits

- Cantaloupe Nutrition Guide

- Canella Uses

- Carrots Health Properties

- Cardoon Nutritional Value

- Carola Summary

- Cassava Health Properties

- Catnip Oil Benefits

- Catsear Flower Uses

- Celeriac Nutritional Value

- Celery Health Benefits

- Chard(Swiss & red)Nutrition Values

- Chaya Nutrition Facts

- Chervil Properties

- Good King Henry

- Chickweed Health Benefits

- Chickpeas Nutrition Summary

- Chile peppers Health Benefits

- Chinese Artichoke Uses

- Chinese Broccoli Nutritional Valu

- Chinese cabbage Nutrition Values

- Chinese Mallow Aspects

- Chives Nutrition Guide

- Chrysanthemum Leaves Uses

- Cicely Unknown Benefits

- Cinnamon Myrtle Medicinal Value

- Collards Nutrition Facts

- Common Purslane Benefits

- Corn Health Values

- Corn Salad Interesting Facts

- Cress Medicinal Values

- Cucumber Health Benefits

- Culantro Leaves

- Curry Leaf Tree Origin

- Collard Greens Nutrition Facts

- Dabberlocks Interesting Facts

- Dandelion Health Benefits

- Dill Health requirements

- Drumstick Nutritional Value

- Dulse Health Benefits

- Earthnut Pea Properties

- Eggplant Nutrition Guide

- Elephant Foot yam Health Benefits

- Elephant Garlic Uses

- Endive Medicinal Properties

- Ensete Health Benefits

- Epazote Properties

- Fat Hen Interesting Facts

- Fingerroot Uses

- French Sorrel Health Facts

- Garlic Nutrition Values

- Gim seaweed Uses

- Ginger Flower Properties

- Ginger Medicinal Values

- Golden Samphire Aspects

- Greater Plantain Medicinal Uses

- Green onions Health Facts

- Green peas Nutrition Values

- Hijiki Nutritional Aspects

- Holy Basil Leaves

- Horseradish Health Benefits

- Onions Nutrition Guide

- Sea Beet Aspects

- Sea Lettuce Health Benefits

- Yam Nutritional Value

- Yarrow Medicinal Uses

- Zucchini Health Guide

- Veggies by seasons

- Veggies did you know??

- Comparison of veggies!!!

- Veggies and it's origin

- Comical View of Veggiess

- Categories of veggies

- Top Veggiess 100 To 91

- Top Veggiess 90 To 81

- Top Veggiess 80 To 71

- Top Veggiess 70 To 61

- Top Veggiess 60 To 51

- Top Veggiess 50 To 41

- Top Veggiess 40 To 31

- Top Veggiess 30 To 21

- Top Veggiess 20 To 11

- Top Veggiess 10 To 01

Veggie Picks
Top Veggiess 70 To 61 For Health Benefits
70. Habanero pepper
Habanero pepper is known to be the hottest variety in a chilly family. The pepper is green when immature and turns to orange to bright red when fully ripe. They have thin and waxy flesh that can be added into a wide range of recipes for its heat and flavor. Habanero pepper is an excellent source of vitamin C than any other citrus fruit that helps in promoting your immune system and prevents the risk of cancer and heart diseases. It contains vitamin A that enhances night vision and improves your skin health. Potassium and capsaicin present in this pepper may benefit your bone health and helps in weight management
Habanero contains a number of nutrients which gives many health benefits. They contain a high concentration of vitamins, minerals and dietary fiber. As same as most of the chili pepper family, habanero also contain capsaicin. This compound gives many health benefits for people.
- The released energy was coming from fat burning therefore, it helps to reduce weight.
- Habanero has anti-inflammatory effect. The capsaicin acting as an anti-inflammatory by slow down the production of substance. So that the inflammatory effect can be reduced, such as swelling and pain associated.
- This will work maximize in overweight person, which mostly get risk of diabetes type 2. By consuming habanero, this can help blood glucose control. The blood glucose will reduce significant and avoid people getting diabetes.
- This help the blood cholesterol level to lower down. So that any type of the cardiovascular disease can be avoid.
- In a research by Yucatan University mentioned that hot peppers including Habanero are known to be a good source of phenolic compounds such aspolyphenols, carotenoids and ascorbic acid. These phytochemicals exhibit high antioxidant activity, and their consumption has been linked to a decreased risk of developing chronic diseases including cancer.
- Having habanero as a pain relief has been proven to be effective.Capsaicin lower the amount of substance P, a chemical that helps transmit pain signals to the brain, when applied directly to the skin.
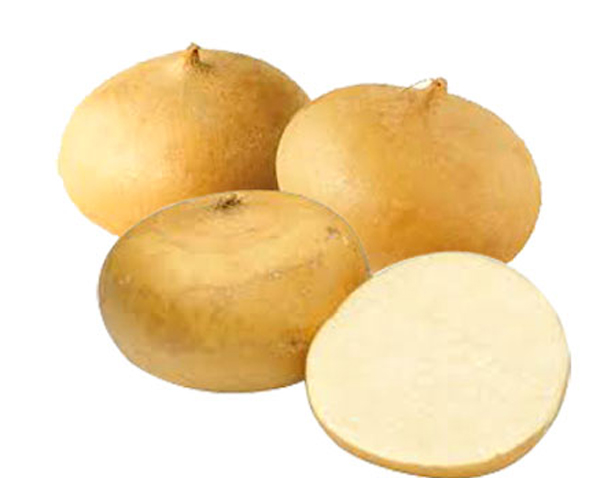
69. Jicama
Jicama is a tuberous root vegetable and has the similar appearance of potato. It has a papery brown skin and juicy, crunchy flesh as in apple and pear. The sweet and nutty flavor gives an option to use in wide variety of dishes. It can be eaten raw or cooked into fries, stews and soups. Jicama is loaded with vitamin C and packed with nutrients like folate, iron, magnesium, potassium, manganese and fiber. Jicama is rich in inulin, the prebiotic fiber that reduce the risk of obesity, diabetes, heart disease and kidney problems. It may also protects against certain type of cancer. The rich carbohydrate vegetables give you fullness and help to reduce weight.
- Full health-boosting vitamins and minerals.
- Helps to stabilize blood sugar levels and boosts digestive health.
- Helps to synthesize antibodies that Fight Foreign Viruses and bacteria in our body.
- Excellent source of fiber and vitamin C.
- Reduces the risk of capillary damage.
- Lowers the homocysteine levels.
- Boosts the immune system.
Jicama is a lesser known vegetable but that doesn't defy the fact that it is nutritious enough for consumption. It can be eaten raw as a vegetable, add it to char grilled vegetables, enjoy any fish or steaks with accompaniments of jicama fried with parsley and garlic. The starch derived from jicama is used to prepare crepes and soups.
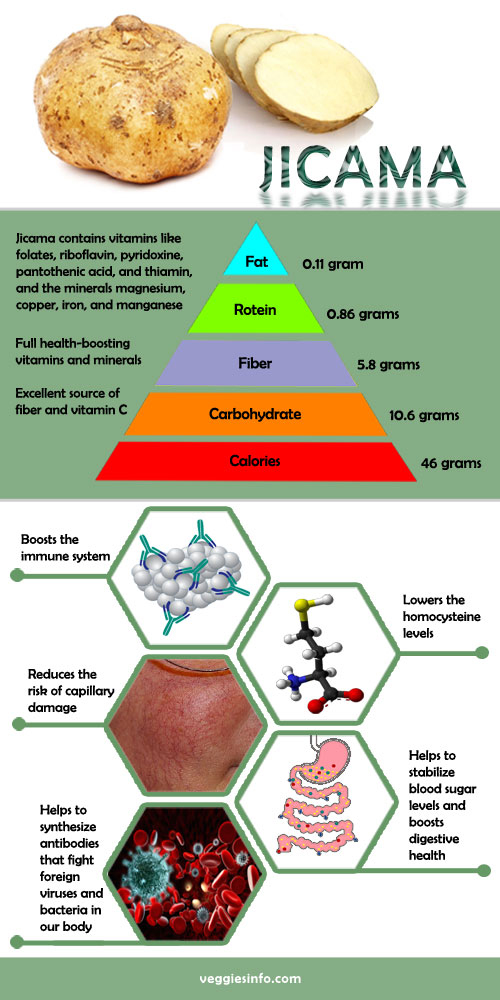
- Jicama contains vitamins like folates, riboflavin, pyridoxine, pantothenic acid, thiamin.
- Minerals magnesium, copper, iron, and manganese.
- Fiber – 5.8 grams.
- Calories – 46 ,Carbohydrate – 10.6 grams.
- Protein – 0.86 ,grams Total fat – 0.11 grams.
A cup of jicama that 130g of serving contains on 49 calories. One can definitely include it in their average 2000 daily calorie diet. Low in calories but it is definitely high in other vital nutrients such as proteins, vitamins, fibre, potassium and oxidants. It is high in phto nutrients , it is a compound derived only from plants and helps in nourishing the body. Jicama is a good source of dietary fibre, they also have diuretic properties that act as a laxative and ensuring smooth bowel movements. The anti oxidants present in this vegetable helps in reviving radical free components for free flow of blood and also has anti cancer property that keeps cancer such as breast cancer, prostate cancer and colon cancer at bay. Jicama contains 80% of water content and it helps in keeping the body hydrated; consumption of this tuberous vegetable during summers is a refreshing experience as it restores the replenished water from the body. Rich in vitamin A jicama is a recommended add on to the diet as it is essential for a healthy vision and clear eye sight for the aging adults. Vitamin C is known to ensure good bone health and promotes bone growth consumption of jicama is believed to useful in prevention of osteoporosis and arthritis. The carbohydrates of this plant are all derived from the sugar content of the vegetable.
| Principle | Nutrient Value | Percentage of RDA |
|---|---|---|
| Energy | 38 Kcal | 2% |
| Carbohydrates | 8.82 g | 7% |
| Protein | 0.72 g | 1% |
| Total Fat | 0.19 g | <1% |
| Cholesterol | 0 mg | 0% |
| Dietary Fiber | 4.9 g | 13% |
| Vitamins | ||
| Folates | 12 µg | 3% |
| Niacin | 0.200 mg | 1.5% |
| Pantothenic acid | 0.135 mg | 3% |
| Pyridoxine | 0.042 mg | 3% |
| Riboflavin | 0.029 mg | 2% |
| Thiamin | 0.020 mg | 2% |
| Vitamin A | 21 IU | 1% |
| Vitamin C | 20.2 mg | 34% |
| Vitamin E | 0.46 mg | 3% |
| Vitamin K | 0.3 µg | <1% |
| Electrolytes | ||
| Sodium | 4 mg | <1% |
| Potassium | 150 mg | 3% |
| Minerals | ||
| Calcium | 12 mg | 1% |
| Copper | 0.048 mg | 5% |
| Iron | 0.60 mg | 7% |
| Magnesium | 12 mg | 3% |
| Manganese | 0.60 mg | 3% |
| Zinc | 0.16 mg | 1% |
| Phyto-nutrients | ||
| Carotene-ß | 13 µg | — |
| Carotene-a | 0 µg | — |
| Lutein-zeaxanthin | 0 µg | — |
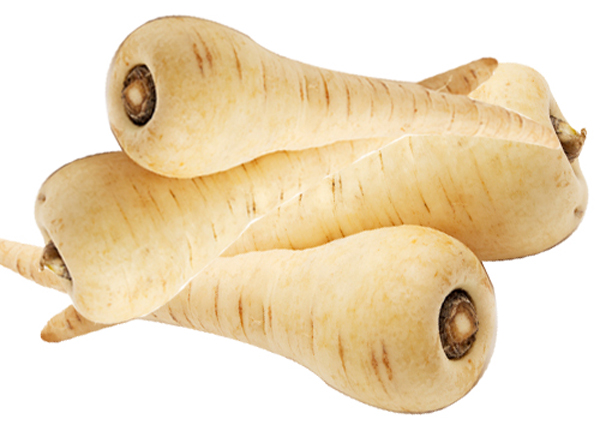
68. Parsnip
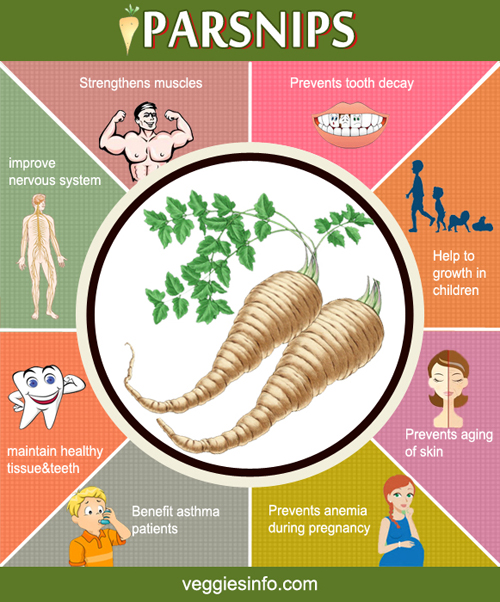
Parsnip is a root vegetable which belongs to the carrot family. It looks like a white carrot with nutty and earthy flavor while some describe it as a spicy carrot. Parsnips are a good source of vitamins C, K and E. It also has folate, magnesium, thiamine, phosphorus, zinc and vitamin B6. The antioxidant present in parsnip prevents oxidative stress and helps to treat chronic conditions like cancer, diabetes and heart diseases. The soluble and insoluble fiber improves your digestive system and regulates blood sugar level. It is a low calorie vegetable that helps you promote weight loss. Parsnip has the potential to improve heart health and immune system. Parsnip can be easily added to your diet by replacing carrot and incorporated in many dishes.
- Parsnips help to improve the digestive and nervous system.
- Prevent problems such as gum disease and tooth decay.
- Reducing the number of harmful free radicals in the body.
- Parsnip tea can be drunk to promote Elimination Of Toxins through urination.
- Benefit asthma patients.
- Strengthens muscles.
- Prevents aging of skin.
- Help to avoid the condition of anemia during pregnancy.
- 100 g root provides 4.9 mg or 13% of fiber.
- 1-cup serving of parsnips offers 499 milligrams of potassium.
- Eating parsnips can stimulate growth in children.
 Prevents and treats kidney stones
Prevents and treats kidney stones
The ultimate food for good health is turnips, high source of nutrients and minerals they are rightly known as power house of energy. One serving of chopped turnips will provide 75 calories, 4.8 grams of sugar, 18g grams of carbohydrates and 1 gram of proteins. Turnips are rich in beta- carotene a phyto-nutrient that is derived from the plants. Anti oxidants such as Vitamin c is found in abundance in parsnips and helps the body to prevent cancer. It is justified in many studies and medical examinations conducted that carrot juice inhibits the growth of cancer cells and also prevents colon cancer. One of the most popular known health benefits is consuming carrots for good vision. People consuming carrots regularly are lesser prone to glaucoma as proven by medical research. Way to a good heart is a good diet rich in anti oxidant properties; carrots are known for their antioxidant property that aids in unclogging of the arteries thus promoting good cardiovascular functioning.Parsnip is abundant with foliate as well as vitamin B9. It will help ladies who have problems with the condition of loss of blood or even anemia. Additionally it is abundant with RNA that benefits ladies in pregnancy. It may also help to avoid the condition of anemia during pregnancy.Since parsnip is abundant with vitamin C, it will help to keep a youthful looking skin. By consuming parsnip juice, one can possibly avoid aging of skin. Vitamin C likewise helps to fix skin cells. Parsnip likewise helps to enhance the immunity of the body.
| Principle | Nutrient Value | Percentage of RDA |
|---|---|---|
| Energy | 75 Kcal | 4% |
| Carbohydrates | 17.99 g | 14% |
| Protein | 1.20 g | 2% |
| Total Fat | 0.30 g | 1% |
| Cholesterol | 0 mg | 0% |
| Dietary Fiber | 4.9 g | 13% |
| Vitamins | ||
| Folates | 67 µg | 17% |
| Niacin | 0.700 mg | 4% |
| Pantothenic acid | 0.600 mg | 12% |
| Pyridoxine | 0.90 mg | 7% |
| Riboflavin | 0.050 mg | 4% |
| Thiamin | 0.090 mg | 7.5% |
| Vitamin A | 0 IU | 0% |
| Vitamin C | 17 mg | 29% |
| Vitamin K | 22.5 µg | 19% |
| Electrolytes | ||
| Sodium | 10 mg | <1% |
| Potassium | 375 mg | 8% |
| Minerals | ||
| Calcium | 36 mg | 3.5% |
| Copper | 0.120 mg | 13% |
| Iron | 0.59 mg | 7.5% |
| Magnesium | 29 mg | 7% |
| Manganese | 0.560 mg | 24% |
| Phosphorus | 71 mg | 10% |
| Selenium | 1.8 µg | 3% |
| Zinc | 0.59 mg | 5% |
| Phyto-nutrients | ||
| Carotene-a | 0 µg | — |
| Carotene-ß | 0 µg | — |
| Crypto-xanthin-ß | 0 µg | — |
| Lutein-zeaxanthin | 0 µg | — |
Parsnips can be enjoyed in multiple ways such as parsnips can be grated to make parsnip harsh browns that are a healthier substitute to potato harsh brown. Pureed parsnips can be used to make soups spiced with condiments and hand grounded herbs. Parsnips can be used to make a crunchy Italian starter of bruchesttas with melting cheese on top of it. A twist in the regular desserts would be caramelized parsnips served at the end of the meal with cinnamon sprinkled on top of it and it will be over in a jiffy. Substitute the classic old potato mash with an interesting twist of parsnip mash with herbs served alongside with dinner.
Parsnip can also be used to make the extra ordinary pilaf that is made up of basmati rice and rich condiments that add mouth watering flavours. Sweet parsnips can be used to make cake just like its relative vegetable carrot. A spongy cake made out of parsnips and maple syrup is something one cannot miss on. Parsnip is a versatile root and can be incorporated in breakfast, dinner and even desserts. One needs to incorporate parsnip in its daily diet to enjoy the best of both worlds of good food and great health benefits.
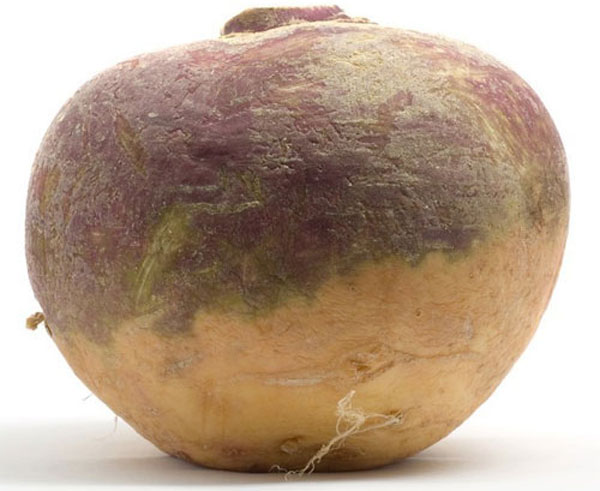
67. Rutabaga
Rutabaga is a root vegetable and has a brownish white pulp similar to turnip. It is known as the hybrid of cabbage and turnip and has a flavor of their combination. Rutabagas are an excellent source of vitamin C, calcium, magnesium, potassium and vitamin E. It also has the trace amount of folate, phosphorus and selenium. The antioxidant present in rutabaga neutralizes the free radical and promotes the immune system. It has the potential to reduce risk of chronic disease and benefits your digestive system. It helps to promote weight loss and reduce the risk of premature aging.
It was a part of the royal gardens since 1669 and in 1800s got widely introduced to Britain. During the 19th century rutabaga was found growing in a part of North America called as Illinois. Rutabaga is also very prominent during Halloween as people living on the British Isles carved on turnips during this festival to wade of evil spirits. This food is also used in a championship named 'The International Rutabaga Curling Championship' conducted in New York city where rutabaga is thrown at people participating in it and the completion takes places between 3 teams in 3 arenas.
- High levels of manganese, potassium, phosphorous, magnesium, calcium, iron, and zinc, as well as vitamins like vitamin C, E, K, and members of the B-family.
- Stimulate the healthy regeneration of cells throughout our organs and tissues.
- High In Antioxidants.
- Improve your digestive health.
- Boost your immune system.
- Improve your metabolic function.
- Lowers blood pressure.
- Prevents certain forms of cancer.
- Lowers cholesterol levels.
- Builds strong bones.
- Help you Lose Weight.
- Reduce the growth of cancerous tumors in the body.
- Effectively prevent premature aging.
- Improve eyesight.
Rutabaga is believed to be a Cross between the Turnips and Cabbage, and to have Originated During the Middle Ages in Europe.

Marked as one of the rare vegetable that is highly nutritious and on the other hand is filling to stomach as it satisfies hunger and keeps you full for a longer period. One cup of raw rutabaga contains 66 calories which is quite low for diet enthusiast. Being a good source of dietary fibre rutabaga helps is healing digestive disorders and has diuretic quality that leads to smooth bowel movements. It is a rich source of vitamin C; this vitamin promotes good hair and skin and also purifies blood and aids in smooth functioning of cardiovascular muscles. Rutabaga like other plants of its genre is a cruciferous plant that is rich in anti cancer properties. It prevents the body from various types of cancer such as breast cancer, colon cancer and prostate cancer. The phosphorus content present in rutabaga helps in instigating compounds that manage blood pressure levels. The anti oxidant properties present in rutabaga makes it an ailment for asthma and lung related problems. Apart from these vital nutrients rutabaga takes on board many other nutrients as well as minerals.Rutabaga additionally helps prevent spot baldness (alopecia).It relieves the premenstrual syndrome (pms).The chance of type 2 diabetes is reduced by consuming it.It safeguards from heart diseases as well as brittle bones.Rutabaga repairs as well as safeguards DNA.Rutabaga raises endurance, milk manufacturing as well as digestion.Frequencies of migraines may also be decreased by rutabaga.Regular usage of rutabaga helps prevent stroke as well as epileptic seizures.Due to the high-content of fibre, rutabaga manage blood levels of cholesterol.
| Principle | Nutrient Value | Percentage of RDA |
|---|---|---|
| Energy | 28 Kcal | 1.5% |
| Carbohydrates | 6.43 g | 5% |
| Protein | 0.90 g | 1.5% |
| Total Fat | 0.10 g | <1% |
| Cholesterol | 0 mg | 0% |
| Dietary Fiber | 1.8 g | 5% |
| Vitamins | ||
| Folates | 15 µg | 4% |
| Niacin | 0.400 mg | 2.5% |
| Pantothenic acid | 0.200 mg | 4% |
| Pyridoxine | 0.090 mg | 7% |
| Riboflavin | 0.030 mg | 2.5% |
| Thiamin | 0.040 mg | 4% |
| Vitamin A | 0 IU | 0% |
| Vitamin C | 21 mg | 35% |
| Vitamin E | 0.03 mg | <1% |
| Vitamin K | 0.1 µg | <1% |
| Electrolytes | ||
| Sodium | 39 mg | 2.5% |
| Potassium | 233 mg | 5% |
| Minerals | ||
| Calcium | 30 mg | 3% |
| Copper | 0.085 mg | 9% |
| Iron | 0.30 mg | 4% |
| Magnesium | 11 mg | 2.5% |
| Manganese | 0.134 mg | 6% |
| Zinc | 0.27 mg | 2% |
| Phyto-nutrients | ||
| Carotene-ß | 0 µg | — |
| Carotene-a | 0 µg | — |
| Lutein-zeaxanthin | 0 µg | — |
Rutabaga is a new addition to the vegetable kingdom and has very low acceptance and awareness in all the parts of the world. This veggie can be consumed using the method of char grilling, roasting or even baking it to eat it with butter or sour cream that gives a very nice punch of flavour. Rutabaga is also consumed in soups and added to baked delicacies such as pie and quiches.

66. Lotus root
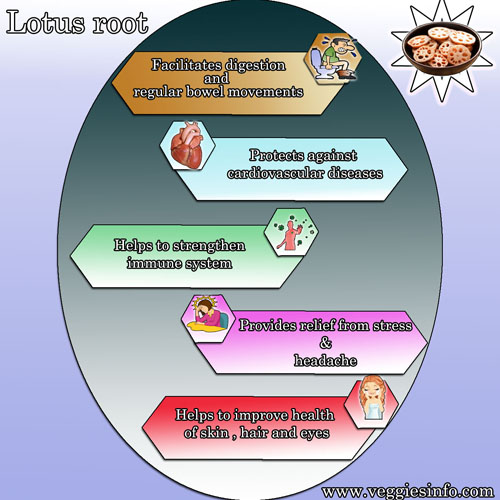
Lotus root or kamalkakdi is the edible root of the lotus plant. It has a crunchy texture with mild sweet flavor. It is advisable to eat cooked lotus root, as raw root may cause stomach infection. Lotus root is rich in potassium and also contains other nutrients including calcium, magnesium, iron, phosphorus, folate and choline. Lotus root supports our digestive system, regulates blood sugar and promotes your hair and skin health. It has low calories which helps in weight management. It may support heart health and regulate the cholesterol level. The excess amount of potassium in the lotus root prevents water retention.
The roots are planted at the bottom of the river and the leaves float on top of the river. The flowers grow on the stem which is found above the river. The plants grow to height of 150 cm and horizontally spread up to 3 m. The lotus has the remarkable ability to regulate the temperature of it flowers to within a narrow range just as humans and other creatures.
The legend goes that Goddess Lakshmi, Hindu God of Wealth bestows her blessings sitting on this beautiful flower. The devotees of India also place the Lotus flower bud as an offering to many gods and goddesses.This plant is also considered as holy plant like holy basil (Tulasi leaves).
- The leaves, flowers, stem are all edible.
- The lotus root has a wide range of health benefits owing to its rich nutritional composition.
- Some of the healing properties including its ability to improve digestion, reduce cholesterol, lower blood pressure, boost the immune system, prevent cancer, and reduces the stress.
- The lotus root is a long is a long woody object that is found on the bottom of the pad.
- The lotus root is very rich in minerals and supplement.
- The lotus roots can be fried, deep-fried, stir-fried and consumed in many ways.
- The lotus roots are included in many Indian and international cuisines.
- The taste of the lotus root is somewhat tasty and sugary.
| Principle | Nutrient Value | Percentage of RDA |
|---|---|---|
| Energy | 74 Kcal | 3.70% |
| Carbohydrates | 17.23 g | 13% |
| Protein | 2.60 g | 5% |
| Total Fat | 0.10 g | 0.50% |
| Cholesterol | 0 mg | 0% |
| Dietary Fiber | 4.9 g | 13% |
| Vitamins | ||
| Folates | 13 µg | 3% |
| Niacin | 0.400 mg | 2.50% |
| Pantothenic acid | 0.377 mg | 7.50% |
| Pyridoxine | 0.258 mg | 20% |
| Riboflavin | 0.220 mg | 17% |
| Thiamin | 0.160 mg | 13% |
| Vitamin A | 0 IU | 0% |
| Vitamin C | 44 mg | 73% |
| Electrolytes | ||
| Sodium | 40 mg | 3% |
| Potassium | 556 mg | 12% |
| Minerals | ||
| Calcium | 45 mg | 4.50% |
| Copper | 0.257 mg | 29% |
| Iron | 1.16 mg | 14% |
| Magnesium | 23 mg | 6% |
| Manganese | 0.261 mg | 1% |
| Selenium | 0.7 µg | 1% |
| Zinc | 0.39 mg | 3.50% |
| Phyto-nutrients | ||
| Carotene-ß | 0 µg | — |
| Carotene-α | 0 µg | — |
| Cryptoxanthin-ß | 0 µg | — |
| Lutein-zeaxanthin | 0 µg | — |
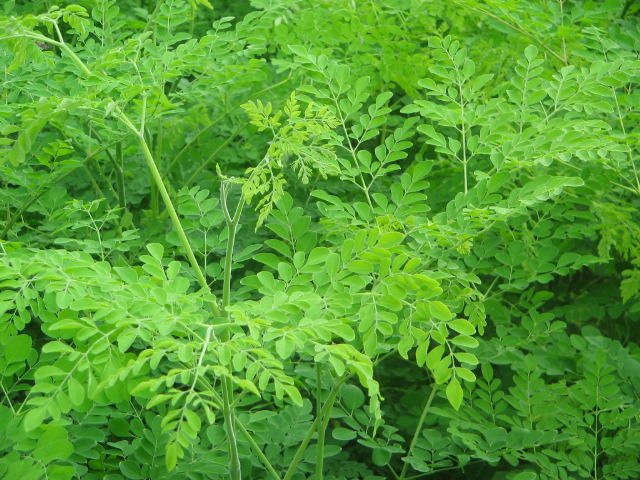
65. Moringa leaves
Moringa leaves are small, oval shaped leaves with wax coating. They have a slightly bitter taste with fresh and grassy aroma. Moringais known as a miracle tree, as every part of the plant benefits our health. Moringa leaves are more nutritious when compared to drumstick pods. They are high in vitamin B6, riboflavin, iron, vitamin C, beta-carotene and magnesium. Moringa leaves lower the blood sugar and cholesterol level. It promotes our nervous system, bone, skin and hair health. It helps in weight management and protects the liver. It also helps to improve our digestive system. Moringa leaves are added into soup, stew or processed into powder.
- Lower Blood Sugar Levels
- Rich in Vitamins and Minerals
- Protects the Liver
- Antiseptic
- Rich in Antioxidants
- Rich in Amino Acids
- Fight Inflammation
- Lowers Cholesterol
- Protects Against Arsenic Toxicity
- Improves Bone health
- Good for Detoxification
- Improve Lactation
- Good for Skin and Hair
- Good for Nervous System
- Helps in Weight Management
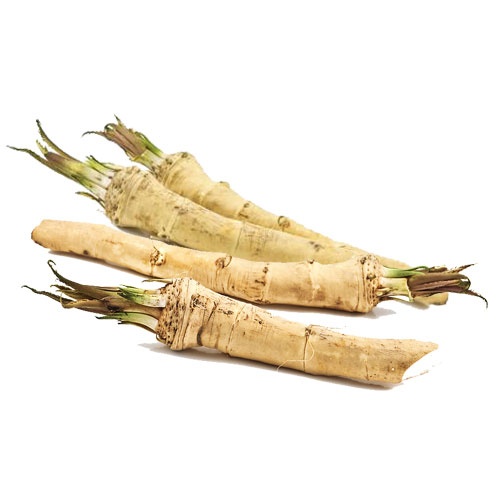
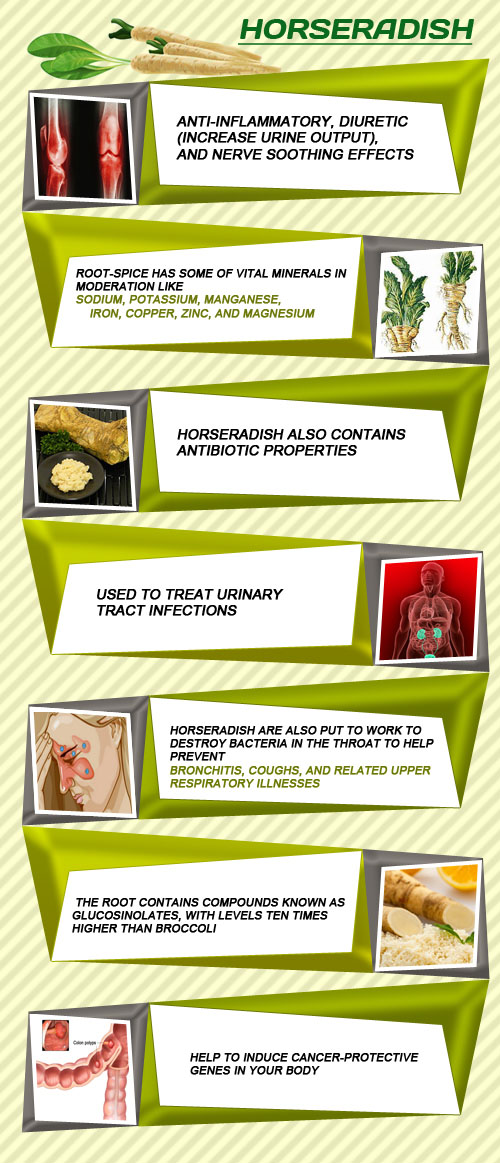
64. Horseradish
Horseradish is a hard perennial root vegetable from the mustard family. It is well known for its hot pungent taste, odor and spicy flavor. It has a long white root with flaky skin and green leaves.
It can be processed into sauce and often used as a replacement for wasabi. It contains several nutrients and plant compounds including calcium, potassium, magnesium, folate, protein and other micronutrients. The antioxidant in horseradish helps to inhibit the growth of the cancer cells. It has antibacterial and inflammatory properties. It may also support your respiratory system.
- Horseradish also contains Antibiotic Properties.
- Used to treat urinary tract infections.
- Root-spice has some of vital minerals in moderation like sodium, potassium, manganese, iron, copper, zinc, and magnesium.
- Horseradish are also put to work to destroy bacteria in the throat to help prevent bronchitis, coughs, and related upper respiratory illnesses.
- The root contains compounds known as glucosinolates, with levels ten times higher than broccoli.
- Help to induce cancer-protective genes in your body.

Horseradish is known for its fiery taste but there is more to it; this food that is usually used as condiment has health benefits that many foods lack in. Like other cruciferous Horseradish has anti cancer properties in it. Glucosinolate a compound present in horseradish is used to fight cancer cells and horseradish is considered to have 10 times more glucosinolate when compared to broccoli and other cruciferous vegetables. Horseradish has been used as an age old remedy for sinus, horseradish consumed as a sauce or powdered form creates a sensation in the body and thus clearing sinus formed in form of sweating or tearing. Owing to its anti bacterial properties it is also known for its remedial properties of treating urinal infections.
| Principle | Nutrient Value | Percentage of RDA |
| Energy | 48 cal | 2% |
| Carbohydrates | 11.29 g | 9% |
| Protein | 1.18 g | 2% |
| Total Fat | 0.69 g | 3% |
| Cholesterol | 0 mg | 0% |
| Dietary Fiber | 3.3 g | 9% |
| Vitamins | ||
| Folates | 57 µg | 14% |
| Niacin | 0.386 mg | 2.5% |
| Pantothenic acid | 0.093 mg | 2% |
| Pyridoxine | 0.073 mg | 6% |
| Riboflavin | 0.024 mg | 2% |
| Thiamin | 0.008 mg | <1% |
| Vitamin A | 2 IU | <1% |
| Vitamin C | 24.9 mg | 41% |
| Electrolytes | ||
| Sodium | 314 mg | 21% |
| Potassium | 246 mg | 5% |
| Minerals | ||
| Calcium | 56 mg | 6% |
| Copper | 0.058 mg | 6% |
| Iron | 0.42 mg | 5% |
| Magnesium | 27 mg | 7% |
| Manganese | 0.126 mg | 5.5% |
| Phosphorus | 31 mg | 4.5% |
| Zinc | 0.83 mg | 8% |
| Phyto-nutrients | ||
| Carotene-ß | 1 µg | — |
| Crypto-xanthin-ß | 0 µg | — |
| Lutein-zeaxanthin | 10 µg | — |
Horseradish is sold in small jars in supermarket and sometimes alsoin flavoured sauces such as dips, mayonnaise and hot sauces.There are numerous possibilities with horseradish it is served as a accompaniment to beef steaks and it is a classic combination. Grating a horseradish can be a tough task as it has so much heat in it that it emits fumes when you peel the outer skin of it and leaves with irritated eyes and nose. Care should be taken while peeling this tap root.
Horseradish is one of the traditional spices that is relished even today in the countryside. Fresh root grated directly on the recipes to add special jest.The root is used in many preparations, including dips, dressings, salads, and sauces as an accompaniment with meat, chicken, and seafood.Horseradish sauce with cream is a perfect accompaniment to steak, venison, and fish like mackerel, tuna, and smoked trout.
Horseradish can be enjoyed by mixing it with some freshly pureed beet and sugar as it not only reduces the heat but fuses to give an interesting flavour. This is known for its rustic flavours so it is often paired with subtle fish such as tuna or mackerel. It is also a key ingredient in making tartar dips as it gives a pungent flavour to it.
This aids in bringing zing to the food while incubating good health benefits in it.
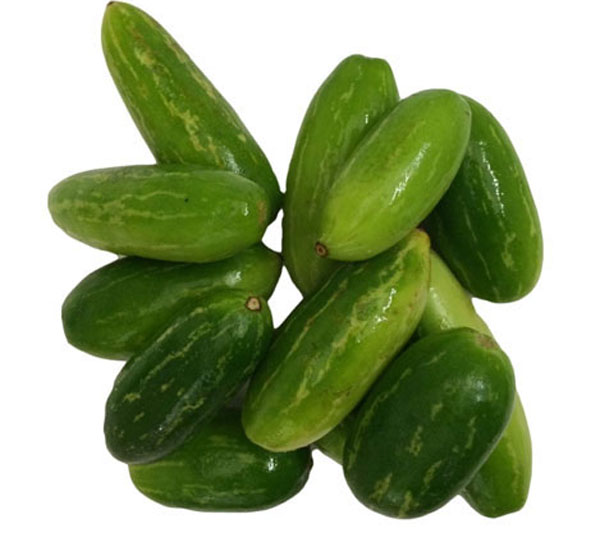
63. Ivy gourd
Ivy gourd is a tropical vine with small melon shaped vegetables. It has a polished green exterior with longitudinal light green stripings and white to red flesh. It is a good source of protein, calcium, fiber, vitamin A and beta carotene. It helps to regulate blood sugar level and body temperature. It reduces the risk of type 2 diabetes, chronic sinuses and fever. Ivy gourd supports our digestive system and promotes better health. The roots and leaves of the plant are used to treat skin infection and wounds. It makes an excellent side dish and it is also enjoyed in gravies.
This plant resembles watermelon plant and grows throughout the year. The other names of this plant are baby watermelon, little gourd, gentleman's toes, tindora or gherkin. This plant is found abundantly in many countries such as Africa to Asia, Philippines, Cambodia, China, Indonesia, Malaysia, Myanmar, Thailand, Papua New Guinea and Australia.
The seeds are dispersed throughout the world through various means which includes pig, bird, human and rats and it grows rapidly where it is dispersed. This plant is generally regarded as very invasive plant and the vines spread across the areas extremely vast. Farmer or the people who grow this plant generally find it difficult to control the growth of the plant and take various steps to control the growth. The plants are deciduous in nature, growing as long as 30m.
They are climbers with long tendrils, tuberous rootstock and their broad leaves are arranged in alternate fashion. They bear flowers that shaped like stars which transform into fruits. The length of the vegetable varies from 2 to 2 ½ inches. The colour of this vegetable is light green and attains red when it ripens. The shape of this plant is oval or elongated. This plant prefers well-drained or humus soils, but grows.
- This plant is used as a free radical quencher and it protects the heart from further damage.
- This plant has lots of medicinal properties and should be consumed regularly by everyone.
- It wonderfully controls the sugar level in the blood, improves immunity and body's defence mechanism, has beta-carotene, improves the function of thyroid, cures leprosy and other skin diseases, cures jaundice, reduces tongue sores, cures psoriasis and stabilizes blood pressure.
- This plant is extremely invasive climbers which invade the nearby plants quickly and it prefers maximum sunlight.
- It is listed in Hawaii state Noxious Weed list. It also obstructs the growth of the plants under it.
| Principle | Nutrient Value | Percentage of RDA |
|---|---|---|
| Water | 93.5 g | N/D |
| Energy | 18 Kcal | N/D |
| Energy | 75 kJ | N/D |
| Protein | 1.2 g | 2.40% |
| Total Fat (lipid) | 0.1 g | 0.29% |
| Carbohydrate | 3.1 g | 2.38% |
| Total dietary Fiber | 1.6 g | 4.21% |
| Minerals | ||
| Iron, Fe | 1.4 mg | 17.50% |
| Calcium, Ca | 40 mg | 4.00% |
| Potassium, K | 30 mg | 0.64% |
| Vitamins | ||
| Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) | 0.08 mg | 6.15% |
| Vitamin B1 (Thiamin) | 0.07 mg | 5.83% |
| Vitamin C (Ascorbic acid) | 1.4 mg | 1.56% |
| Vitamin B3 (Niacin) | 0.07 mg | 0.44% |
62. Earthnut
Earthnut or peanut is a small, oval shaped, pale pink seed or legume. They have a crunchy and grain texture with rich aroma. Peanut has a high oil content, which plays a major role in Indian cuisine. Groundnuts are an excellent source of protein, healthy fats and fiber. It also has potassium, folate, calcium, iron, magnesium and vitamin B. Groundnuts are served as a healthy snack, processed into peanut butter, oil and added in many dishes to add flavor. It may prevent the risk of diabetes, cancer and promotes weight loss. It benefits oru skin and hair health. The rich source of protein helps in children's growth and boosts their memory.
These plants grow throughout the year and the tubers grow up to 3 to 5 cm which is attached to the roots. The stem of these plants grow up to 30 to 80 cm and is sprawling, wingless and nearly hairless. The leaf blades are pinnate with a single pair of broad lanceolate leaflets with blunt tips, entire margins and a terminal tendril. The inflorescence has long stem and two to seven pinkish-red flowers, each 12 to 20 mm long. These have five sepals and five petals and are irregular, with a standard, two wings and a fused keel. There are ten stamens and a single carpel. The fruit is a flat brown pod containing up to six seeds.
- The oleic and linoleic acid present in the earthnut comprises about 44-56% of the mono and polyunsaturated fat that is used to make peanut oils. The groundnut oil will help to promote weight loss and improve the healthy fat content, but it is better to not consume everyday.
- Peanuts highly benefit the diabatic patient as they have low glycemic index. The earthnuts have only 13-16% carbohydrate content of the total weight of the peanut, so it quickly enters your bloodstream after a meal. Despite having the high calorie content peanut will not add extra pounds to you, therefore it is used in a supplementary drink. The observational studies state that the consumption helps to maintain healthy weight and lowers the chance of obesity. The peanut gives you stomach filling food even when consumed in small amounts. Therefore, people who are trying to lose weight can take this nut without any doubt.
- All nuts including earthnut may reduce the risk of heart disease. The frequent consumption of peanuts help to prevent gallstone as it has the effect of lowering cholesterol level. The components like thiamine and niacin help to reduce the risk of heart diseases and provide the essential components for the function of muscle and the nervous system.
- The high protein content in peanuts can cause allergy in some people. Peanuts may be contaminated with a species that produces aflatoxin, which may lead to liver failure. Peanuts should not be taken in excess amounts to prevent peanut allergies.
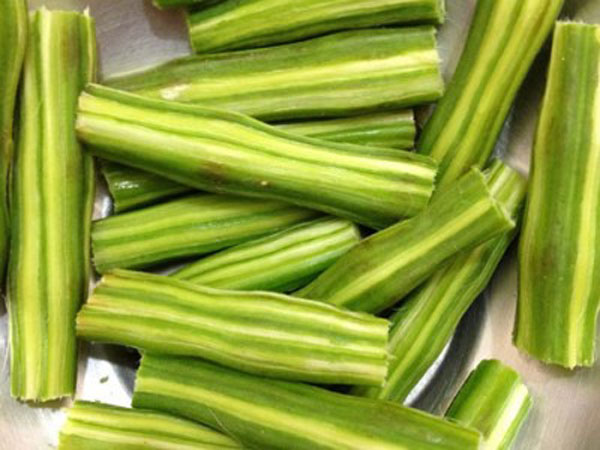
61. Drumstick
Drumstick or moringa is a long green vegetable with tapering ends. It had bulgy seeds with thin white covering. The flesh becomes tender when cooked and has a mixed flavor. It is enriched with vitamins C, A and B1 and also provides us with magnesium, phosphorus, potassium and fiber. Drumstick has the potential to regulate blood sugar level and helps to purify blood. It helps to boost your digestive system, immune system and develops strong bones. It has blood-purifying compounds and supports better blood circulation. It is also used to treat respiratory problems. It is mainly used in Indian dishes like sambar and curries.
It is imperative to note that these plants grow rapidly when planted. This plant can reach a height of 10-12 m and the trunk can reach a diameter of 45 cm. The bark has a whitish-grey colour and is surrounded by thick cork. Young shoots have purplish or greenish-white, hairy bark. The tree has an open crown of drooping, fragile branches and the leaves build up feathery foliage of tripinnate leaves. The flowers are rich in fragrance and bisexual.
- The leaves are very rich in nutritional contents since they have vitamins, minerals, fat, energy and water.
- The mature seed yields 40% edible oil called ben oil and has behenic acid in it.
- The seed cake which remains after oil extraction is used as a fertilizer or flocculent to purify water.
- The seed oil is also used as biofuel.
- The drum stick plants are used to treat malnutrition among infants and nursing mothers.
- Indians use both leaves and green pods in several foot items.
- Many parts of the plant are used as traditional medicine.
- The leaves are used as forage for livestock.
- Drum stick leave powder is used as soap for hand washing.
It is worth to note that India is the largest producer of drumstick with an annual production of 1.3 million tons. Andhra Pradesh tops the list in production followed by Tamil Nadu and Karnataka. These plants are also found in wild and grown as a garden plant in hundreds of houses all over the world including Philippines and Thailand.
| Principle | Nutrient Value | Percentage of RDA |
|---|---|---|
| Energy | 37 Kcal (2%) | 64 Kcal (3%) |
| Carbohydrates | 8.53 g (6.5%) | 8.28% (6%) |
| Protein | 2.10 g (4%) | 9.40 g (17%) |
| Total Fat | 0.20 g (1%) | 1.40% (7%) |
| Cholesterol | 0 mg (0%) | 0 mg (0%) |
| Dietary Fiber | 3.2 g (8%) | 2.0 g (5%) | Vitamins |
| Folates | 44 µg (11%) | 40 µg (10%) |
| Niacin | 0.680 mg (4%) | 2.220 mg (14%) |
| Pyridoxine | 0.120 mg (9%) | 1.200 mg (92%) |
| Riboflavin | 0.074 mg (6%) | 0.660 mg (51%) |
| Thiamin | 0.053 mg (4.5%) | 0.257 mg (21.5%) |
| Vitamin A | 74 IU (2.5%) | 7564 IU (252%) |
| Vitamin C | 141mg (235%) | 51.7 mg (86%) | Electrolytes |
| Sodium | 42 mg (3%) | 9 mg (0.5%) |
| Potassium | 461 mg (10%) | 337 mg (7%) | Minerals |
| Calcium | 30 mg (3%) | 185 mg (18.5%) |
| Iron | 0.36 mg (4.5%) | 4.00 mg (50%) |
| Magnesium | 45 mg (11%) | 147 mg (37%) |
| Phosphorus | 50 mg (9%) | 112 mg (20%) |
| Selenium | 8.2 µg (15%) | 0.9 µg (1.5%) |
| Zinc | 0.45 mg (4%) | 0.60 mg (5%) |