List Of Vegetables
- Absinthe Interesting Facts

- Ahipa Nutritional Values

- Akudjura Various Uses

- Amaranth Health Benefits

- American Pokeweed

- Aniseed Myrtle Properties

- Aonori Summary

- Apple Mint Uses

- Arame Medicinal Uses

- Arracacha Nutritional Value

- Artichoke Nutrition Values

 Arugula Health Summary
Arugula Health Summary- Asarabacca Various Uses

- Asparagus Healthy Eating

- Avocado Nutrition Benefits

- Bamboo shoots

- Basil Nutrition Guide

- Beans Beneficial Properties

- Bean sprouts

- Beet Greens Nutrition Facts

- Beets Health Benefits
- Bishop’s weed Various Uses

- Bitter Gourd Nutritional Value

- Black Beans Benefits

- Blue Fenugreek Various Uses

- Boldo Medicinal Values

- Bok Choy Health Benefits

- Borage Greens Medicinal Purposes

- Bottle Guard Aspects

- Broccoli Health Properties

- Broccoflower Nutrition Guide

- Broccoli Raab Nutrition Values

- Broadleaf Arrowhead Health Benefits

- Brussel sprouts Nutrition Summary

- Burdock Health Benefits

- Cabbage Health Facts

- Camas Health Benefits

- Cantaloupe Nutrition Guide

- Canella Uses

- Carrots Health Properties

- Cardoon Nutritional Value

- Carola Summary

- Cassava Health Properties

- Catnip Oil Benefits

- Catsear Flower Uses

- Celeriac Nutritional Value

- Celery Health Benefits

- Chard(Swiss & red)Nutrition Values

- Chaya Nutrition Facts

- Chervil Properties

- Good King Henry

- Chickweed Health Benefits

- Chickpeas Nutrition Summary

- Chile peppers Health Benefits

- Chinese Artichoke Uses

- Chinese Broccoli Nutritional Valu

- Chinese cabbage Nutrition Values

- Chinese Mallow Aspects

- Chives Nutrition Guide

- Chrysanthemum Leaves Uses

- Cicely Unknown Benefits

- Cinnamon Myrtle Medicinal Value

- Collards Nutrition Facts

- Common Purslane Benefits

- Corn Health Values

- Corn Salad Interesting Facts

- Cress Medicinal Values

- Cucumber Health Benefits

- Culantro Leaves

- Curry Leaf Tree Origin

- Collard Greens Nutrition Facts

- Dabberlocks Interesting Facts

- Dandelion Health Benefits

- Dill Health requirements

- Drumstick Nutritional Value

- Dulse Health Benefits

- Earthnut Pea Properties

- Eggplant Nutrition Guide

- Elephant Foot yam Health Benefits

- Elephant Garlic Uses

- Endive Medicinal Properties

- Ensete Health Benefits

- Epazote Properties

- Fat Hen Interesting Facts

- Fingerroot Uses

- French Sorrel Health Facts

- Garlic Nutrition Values

- Gim seaweed Uses

- Ginger Flower Properties

- Ginger Medicinal Values

- Golden Samphire Aspects

- Greater Plantain Medicinal Uses

- Green onions Health Facts

- Green peas Nutrition Values

- Hijiki Nutritional Aspects

- Holy Basil Leaves

- Horseradish Health Benefits

- Onions Nutrition Guide

- Sea Beet Aspects

- Sea Lettuce Health Benefits

- Yam Nutritional Value

- Yarrow Medicinal Uses

- Zucchini Health Guide

- Veggies by seasons

- Veggies did you know??

- Comparison of veggies!!!

- Veggies and it's origin

- Comical View of Veggiess

- Categories of veggies

- Top Veggiess 100 To 91

- Top Veggiess 90 To 81

- Top Veggiess 80 To 71

- Top Veggiess 70 To 61

- Top Veggiess 60 To 51

- Top Veggiess 50 To 41

- Top Veggiess 40 To 31

- Top Veggiess 30 To 21

- Top Veggiess 20 To 11

- Top Veggiess 10 To 01

Veggie Picks
Top Veggiess 80 To 71 For Health Benefits
80. Soybean
Soya beans belong to the legume family that is widely grown for its edible beans. It is a light cream color bean with grassy and bitter flavor. Soya beans are processed into soy flour, soy protein, tofu, soy milk, soy sauce and oil. It is an excellent source of protein and has good amounts of carbohydrates, fiber and fat. It contains nutrients such as molybdenum, vitamin K1, folate, copper, manganese, phosphorus and thiamine. Consuming soy products helps in reducing cancer risk. Soybeans are effective to treat menopause symptoms and benefit our bone health.
- Soybeans are very rich in nutritive components.
- Very High Protein Content.
- It contains a lot of fibre Rich in calcium, magnesium.
- Helps in preventing digestive disorders.
- Soy beans plays a major role in enabling the blood cells to carry oxygen from the lungs to the other vital parts of the body such as brain, heart and spinal cord.
Soy beans are legumes that rich in vital nutrients. One cup of soy beans consists of 446 calories and 20g of fat content. Soy beans are rich in cholesterol lowering fibre which helps in activating radicals in the blood and aids in lowering cholesterol. It also helps majorly in regulating the secretion of insulin from the pancreas thus keeping the blood sugar levels under control. Legumes are the leading source of proteins and fibre one has ever known; this fibre rich food are highly beneficiary to the body as it contains both soluble and insoluble fibre that aids in smooth metabolism.People who eat legumes more often have lesser risk of falling prey to heart diseases; this is proven by many studies conducted on men from different age groups. The risk is lowered by the presence of magnesium and folate in these beans. Folate helps in lowering the levels of homocysteine an amino acid responsible to bring in the risk of heart attacks. Soy bean houses iron in itself; containing 24% or required iron for daily intake, this food should be added to every aging adult and adolescents diet plan. Containing 72% of protein, soy beans are a rich source of this vital nutrient that the vegetarians miss on fish eggs and other meat.
Soy beans contain oxalate; a compound found and derived from plants. Increase in intake of oxalate will lead to accumulation of uric acid which is a by product of oxalate. Excessive accumulation will lead to the formation of a condition called gout in the kidney also known kidney stones. One needs to monitor their intake and take extra attention to double check on what is the required amount of soy bean needed by the body.
| Principle | Nutrient Value | Percentage of RDA |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamins | ||
| Betaine | 2.1 mg | |
| Choline | 115.9 mg | |
| Folate | 375.00 mcg | |
| Folic acid | 0.00 mcg | |
| Niacin | 1.623 mg | 8% |
| Pantothenic acid | 0.793 mg | 8 % |
| Riboflavin | 0.870 mg | 51 % |
| Thiamin | 0.874 mg | 58 % |
| Vitamin A | 22.00 IU | 0 % |
| Vitamin A, RAE | 1.00 mcg | |
| Carotene, alpha | 0.00 mcg | |
| Carotene, beta | 13.00 mcg | |
| Cryptoxanthin, beta | 0.00 mcg | |
| Lutein + zeaxanthin | 0.00 mcg | |
| Lycopene | 0.00 mcg | |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.00 mcg | 0 % |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.377 mg | 19 % |
| Vitamin C | 6.0 mg | 10 % |
| Vitamin D | 0.00 IU | 0 % |
| Vitamin E | 0.85 mg | 3 % |
| Tocopherol, alpha | 0.85 mg | |
| Vitamin K | 47.0 mcg | 59 % |
| Minerals | ||
| Calcium, Ca | 277.00 mg | 28 % |
| Copper, Cu | 1.658 mg | 83 % |
| Iron, Fe | 15.70 mg | 87 % |
| Magnesium, Mg | 280.00 mg | 70 % |
| Manganese, Mn | 2.517 mg | 126 % |
| Phosphorus, P | 704.00 mg | 70 % |
| Potassium, K | 1797.00 mg | 38 % |
| Selenium, Se | 17.8 mcg | 25 % |
| Sodium, Na | 2.00 mg | 0 % |
| Zinc, Zn | 4.89 mg | 33 % |
| Proteins and Aminoacids | ||
| Protein | 36.49 g | 73 % |
| Alanine | 1.915 g | |
| Arginine | 3.153 g | |
| Aspartic acid | 5.112 g | |
| Cystine | 0.655 g | |
| Glutamic acid | 7.874 g | |
| Glycine | 1.880 g | |
| Histidine | 1.097 g | |
| Isoleucine | 1.971 g | 141 % |
| Leucine | 3.309 g | 121 % |
| Lysine | 2.706 g | 129 % |
| Methionine | 0.547 g | 52 % |
| Phenylalanine | 2.122 g | 121 % |
| Proline | 2.379 g | |
| Serine | 2.357 g | |
| Threonine | 1.766 g | 168 % |
| Tryptophan | 0.591 g | 211 % |
| Tyrosine | 1.539 g | 88 % |
| Valine | 2.029 g | 111 % |

79. Snow pea
Snow peas are wide and flat peas with pale green pods and thin pod walls. It has a tender and crisp texture with mild sweetness. The versatile flavor allows it to incorporate in soups, stews, curries, meat and made into healthy snacks. It is loaded with nutrients similar to sugar pea, that includes vitamin C, iron, vitamin K, vitamin B5, thiamine, vitamin B6, manganese and folate. It protects your heart from certain diseases and regulates blood pressure. It increases bone mineral density and promotes healthy vision. It improves better digestion and helps in weight management. It also reduces the risk of certain cancer, diabetes, anemia and osteoporosis. It nourishes the growth of the fetus and benefits the pregnant woman.
Scientifically known as Pisum sativum; snow peas is a legume which is consumed when it is not ripe and the pea pods are yet to arrive. Snow peas are also known as mangetout in French which translates to 'eat all' in English. Also known as Chinese pea pods these pea pods are edible and taste a little milder and sweeter when compared to the normal garden pea. It is believed that the name snow peas was coined because of the whitish tint present on the pea pod that gives an imaginary snowy effect. On the other side there are possibilities for it to carry the tint as it is harvested right after spring freeze. Initially used as a dry vegetable, it eventually over a period of time became tender and tastier as it evolved. These peas were also considered holy and royal by the Egyptians as according to the archaeological evidence peas were found inside tombs of pharaohs.
- It has High fiber content.
- Contains carbohydrates,protein, vitamins A and C, healthy fats, iron, potassium, magnesium, folic acid and antioxidants.
- Snow pea is Low in Saturated Fat.
- Prevent eye diseases.
- Benefits from eating snow peas are those who suffer from asthma, autoimmune disease, arthritis, IBS.
- Resolve digestive issues naturally.
Snow Peas were Only Seen in Chinese Restaurants, But now they are available everywhere.

One cup of snow peas constitutes of 117 calories; that is 6% of the daily intake recommended for everyone. also has very less quantity of sodium and cholesterol. Vitamin K rich food such as green peas contains 21% of recommended vitamin for daily intake for a healthy body but what beat this is the fact that snow peas that contains double the amount of vitamins present in garden green peas. It is required to take care of smooth functioning of the bones as well as prevents osteoporosis, a condition where bones begin to break. Fractures can be kept at bay by incorporating Snow peas in daily diet. Snow peas are also a good source of vitamin A which is essential for a good and healthy eye sight. A healthy skin and membrane are the other benefits that one gets on consumption of peas. The absorbic acid and anti oxidant properties of peas develops resistance against diseases and boost the immunity of the body. Folate is recommended to be included in the diet of new mothers as it reduces the risk for the new born to get any spine deformities. Peas consist of 16% of daily recommended levels of folate that one should be consuming.
Snow peas are extremely healthy to munch on due to the potent healthy nutrients in them that are nourishing to our bodies and protective of our health. The nutrients in snow peas are fiber, carbohydrates, protein, vitamins A and C, healthy fats, iron, potassium, magnesium, folic acid and antioxidants. These nutrients have the ability to relieve and prevent inflammation, cancers, eye diseases, scurvies and digestive issues naturally.
Snow peas should be crisp and thin when bought from the market and needs to be stored in refrigeration or low and dry temperature. Snow peas taste great if one chooses to eat them in a raw form which is the healthiest form of eating them. They taste even better and sweeter when cooked. Snow peas can be boiled, simmered or even sautéed in olive oil with other vegetables to give it a nice crunchy texture to a dish. Snow peas go well with shiitake mushrooms and risotto. The can also be served as a salad alongside a grilled steak or fish. Vegetable quiche can be an interesting dish with snow peas in it.

| Principle | Nutrient Value | Percentage Of RDA |
| Energy | 81 Kcal | 4% |
| Carbohydrates | 14.45 g | 11% |
| Protein | 5.42 g | 10% |
| Total Fat | 0.40 g | 2% |
| Cholesterol | 0 mg | 0% |
| Dietary Fiber | 5.1 g | 13% |
| Vitamins | ||
| Folates | 65 µg | 16% |
| Niacin | 2.090 mg | 13% |
| Pantothenic acid | 0.104 mg | 2% |
| Pyridoxine | 0.169 mg | 13% |
| Riboflavin | 0.132 mg | 10% |
| Thiamin | 0.266 mg | 22% |
| Vitamin A | 765 IU | 25.5% |
| Vitamin C | 40 mg | 67% |
| Vitamin E | 0.13 mg | 1% |
| Vitamin K | 24.8 µg | 21% |
| Electrolytes | ||
| Sodium | 5 mg | <1% |
| Potassium | 244 mg | 5% |
| Minerals | ||
| Calcium | 25 mg | 2.5% |
| Copper | 0.176 mg | 20% |
| Iron | 1.47 mg | 18% |
| Magnesium | 33 mg | 8% |
| Manganese | 0.410 mg | 18% |
| Selenium | 1.8 µg | 3% |
| Zinc | 1.24 mg | 11% |
| Phyto-nutrients | ||
| Carotene-ß | 449 µg | — |
| Crypto-xanthin-ß | 0 µg | — |
| Lutein-zeaxanthin | 2477 µg | — |
78. Sorrel
Sorrel is a leafy green vegetable or a small edible plant. These leaves have a tangy and sour flavor that is highly used in all cuisines. It serves a better replacement for spinach for its unique flavor. It is a nutritional powerhouse, providing a significant amount of micro nutrients including vitamin A, vitamin C, folate, riboflavin, niacin, vitamin B6 and pantothenic acid. It promotes healthy ete, skin, immune system, growth and reproductive health. It may also help to treat certain health conditions like cancer, obesity and type 2 diabetes. It may also be used to treat infections, fluid retention and sinuses.
Plants and trees are exemplary creatures which communicate and whispers many things wonderfully within their family members. They absorb water, sunlight, nutrients and other important ingredients from the nature and prepare food on their own. The leaves which are nothing but a food factory prepare food and distribute it to other parts of the plant beautifully. No one in this world teaches any lessons about the art of living but these divine species does everything meticulously without interruption. This topic will deal about the plant Sorrel is a perennial herb which belongs to the family polyganaceae and is cultivated as garden herb or leaf vegetable in many parts of the world. The botanical name of this plant is Rumex acetosa. The other common names of this plant are spinach dock and narrow-leaved dock.
This plant is abundantly found in grassland habitats throughout Europe from the northern Mediterranean coast to the north of Scandinavia and in parts of Central Asia. It is also found in some parts of North America and native of British Isles.
These plants are also found in meadows, near streams and also open woodlands. Sorrel grows to a height of 0.6 m by 0.3 m. It is in leaf during the month of January and in flower from May to June. The flowers are dioecious and pollinated by wind. This plant grows normally in sandy and heavy clay soils but prefers moist soil.
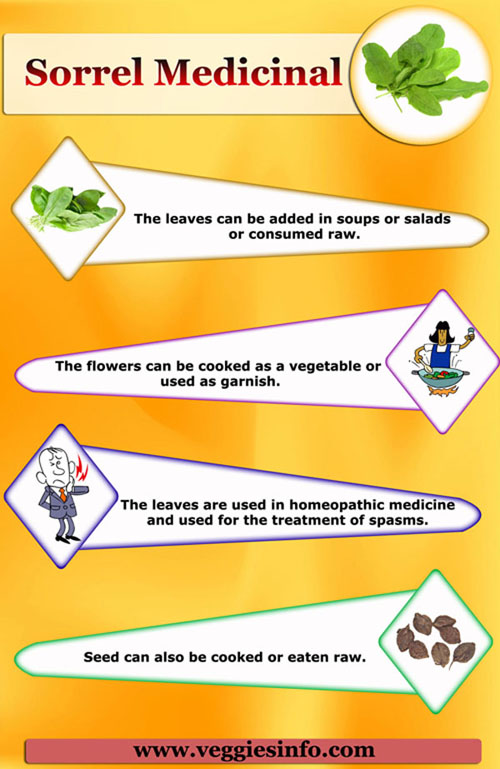
- The leaves can be added in soups or salads or consumed raw.
- Many people like lemon-like flavor and that is the reason this leaves are added as a flavor in salads.
- The flowers can be cooked as a vegetable or used as garnish.
- Root can be cooked or grounded into a powder.
- Seed can also be cooked or eaten raw.
- The leaves have many medicinal effects and are astringent, diuretic, laxative and refrigerant.
- The leaves are used in homeopathic medicine and used for the treatment of spasms.
| Principle | Nutrient Value | Percentage of RDA |
|---|---|---|
| Energy | 22 Kcal | 1% |
| Carbohydrates | 3.20 g | 2.50% |
| Protein | 2.00 g | 3.50% |
| Total Fat | 0.7 g | 3% |
| Cholesterol | 0 mg | 0% |
| Dietary Fiber | 2.9 g | 7.50% |
| Vitamins | ||
| Folates | 13 µg | 4% |
| Niacin | 0.500 mg | 3% |
| Pantothenic acid | 0.041 mg | 1% |
| Pyridoxine | 0.122 mg | 9% |
| Riboflavin | 0.100 mg | 8% |
| Thiamin | 0.040 mg | 3% |
| Vitamin A | 4000 IU | 133% |
| Vitamin C | 48 mg | 80% |
| Electrolytes | ||
| Sodium | 4 mg | <1% |
| Potassium | 390 mg | 8% |
| Minerals | ||
| Calcium | 44 mg | 4% |
| Copper | 0.131 mg | 14% |
| Iron | 2.40 mg | 30% |
| Magnesium | 103 mg | 26% |
| Manganese | 0.349 mg | 21% |
| Zinc | 0.20 mg | 2% |
| Phyto-nutrients | ||
| Kaempferol | 10.3 mg | — |
| Myrcetin | 5.7 mg | — |
| Quercetin | 86.2 µg | — |
77. Shallots
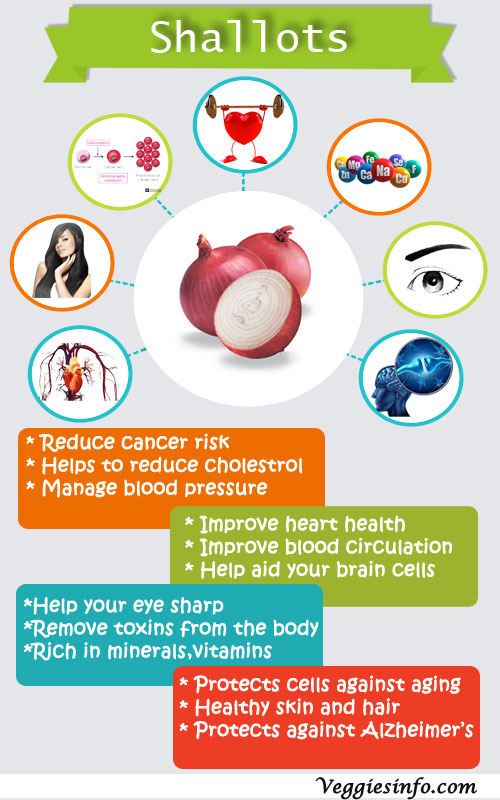
Shallots are a small elongated onion with reddish copper papery skin. They have a sweet flavor with a hint of sharpness and intense heat. It serves as the best substitute of an onion but can also be eaten raw. When compared to onions, shallots are rich in protein and nutrients including calcium, iron, phosphorus, potassium, zinc, copper and folate. It serves as a best antiseptic agent for wounds and allergies. It supports heart health and blood circulation. It helps to maintain healthy weight and lower the blood sugar. Shallots help to lower the blood pressure and cholesterol level. It makes an excellent addition in soups, stews, salads and many other recipes.
- Rich in minerals, vitamins and trace elements.
- Contain phosphorus, potassium, magnesium, manganese, iron and copper.
- Shallots hold several fold more concentration of vitamins and minerals than in onions, especially vitamin A, pyridoxine, folates, thiamin, vitamin C etc.
- Pyridoxine (B-6) raises GABA chemical level inside the human brain that help soothe nervous irritability.
- 100 g fresh shallots carry 1190 IU (35% RDA) of vitamin A. Vitamin A is a powerful antioxidant that helps protect from lung and oral cavity cancers.
- Reduce cancer risk.
- Helps to reduce cholesterol.
- Manage blood pressure.
- Improve heart health.
- Improve blood circulation.
- Help aid your brain cells performing better.
- Help your eye sharp and healthy.
- It helps to Remove Toxins from the body.
Shallot is healthier than onion. It can prevent formation of blood cloths and development of coronary arterial diseases, heart attack and strokes.
Shallots belong to the onion family and like the other members of its family its nutrition value is very high. This food is also very low in saturated fats and carbohydrates. Shallots are rich source of Vitamin A, Vitamin C, calcium, iron, manganese, folate and magnesium. Being rich in vitamin C and K shallot onions needs to be incorporated in ones daily diet for healthy bone and bone health. The wear and tear of muscles and tissues is prevented and also largely prevents bone fracture. The anti oxidant properties in shallots because of vitamin A and C helps in preventing heart diseases. It prevents tissue damage by releasing radical free compounds lowering the risk of blood pressure and promoting a healthy cardiovascular functioning. The food for the retina is rhodospin; a compound produced by vitamin A. This compound helps in promoting good eyesight and healthy vision. Shallots onions are known boost up body's immune system and protect the body from choric diseases. Apart from these nutrients it is also rich in thiamine which is vitamin B2, riboflavin, niacin and pantothenic acid.
Shallots are enjoyed in a lot of delicacies many Indian delicacies where it is used as a staple ingredient for their day to day cooking. Sambhar a gravy made out of lentils makes use of these shallots as they infuse a lot of flavours and taste in the food. Sambhar is usually used as an accompaniment to rice, idly or dosa which forms a part of the staple south Indian diet. Pickled shallots in vinegar are given as an appetiser in many Indian restaurants as they are believed to enhance the taste of rich Indian cuisine. Famous momos made in Nepal makes use of shallots as a core ingredient of the dish. Shallots are used in making Wazwan Kashmiri cuisine which is used in making rich meat gravies. The Iranian use shallots in dense yoghurt and serve it as an accompaniment with kebabs and other grills. Buddhist vegetarians avoid pungent vegetables in their food which also includes shallots, onions and garlic. Chinese use shallots along with other vegetables to make stews and pan seared vegetables used as an accompaniment with flavoured rice and noodles. Shallots are used in making chips in south china where it is enjoyed as an afternoon snack.
| Principle | Nutrient Value | Percentage of RDA |
|---|---|---|
| Energy | 72 Kcal | 3.6% |
| Carbohydrates | 16.80 g | 13% |
| Protein | 2.50 g | 5% |
| Total Fat | 0.10 g | 0.5% |
| Cholesterol | 0 mg | 0% |
| Vitamins | ||
| Folates | 34 µg | 9% |
| Niacin | 0.200 mg | 1.5% |
| Pantothenic acid | 0.290 mg | 6% |
| Pyridoxine | 0.345 mg | 26.5% |
| Riboflavin | 0.020 mg | 2% |
| Thiamin | 0.060 mg | 5% |
| Vitamin A | 1190 IU | 35% |
| Vitamin C | 8 mg | 13% |
| Electrolytes | ||
| Sodium | 12 mg | 1% |
| Potassium | 334 mg | 7% |
| Minerals | ||
| Calcium | 37 mg | 4% |
| Copper | 0.088 mg | 10% |
| Iron | 1.20 mg | 15% |
| Magnesium | 21 mg | 5% |
| Manganese | 0.292 mg | 13% |
| Phosphorus | 60 mg | 8.5% |
| Selenium | 1.2 µg | 2% |
| Zinc | 0.40 mg | 4% |
76. Palm heart
Palm heart is the inner core of a certain palm tree. It is a delicious and crunchy white vegetable with a nutty and creamy center. The Heart of palms are loaded with potassium and vitamin B6. It is packed with other nutrients like vitamin C, iron, calcium, magnesium, vitamin A, fiber and protein. It contains plant compounds that have the potential to inhibit the risk of cancer, diabetes and heart diseases. The essential nutrients maintain blood pressure, cholesterol and blood sugar level. The low calorie vegetable helps to promote weight loss and benefits our digestive system. Palm hearts are added in vegetable or grain salad and can also be cooked into stir fries and casseroles.
- Promotes Heart Health
- Helps Prevent Iron-Deficiency Anemia
- Supports Weight Loss
- Improves Blood Sugar Control
- May Enhance Brain Function in Seniors
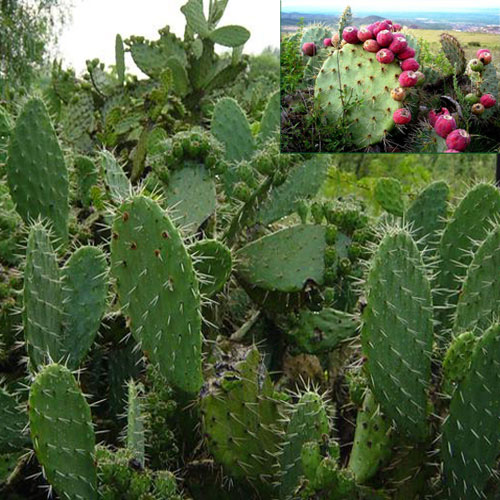
75. Nopal
Nopal is an opuntia cacti or a prickly pear cactus. The pads of the cactus are the edible part to have high health benefits. It has a crunchy and slimy texture with tart and citrusy taste. Nopalesare usually sauteed and added in a wide range of dishes including tacos, eggs and jams. Nopales are particularly rich in fiber and protein. I also contain vitamin C, calcium, vitamins K and A. Nopales have antiviral, neuroprotective properties and have high antioxidants that help to reduce oxidative stress. It may regulate blood sugar and cholesterol level.
Nopal cactus is a plant which is the common ingredient in foods in some parts of Mexico. There are hundred and fourteen species endemic in Mexico where Nopal pads are used as the ingredients of Mexican dishes. Nopal pads can be eaten raw or cooked.
This topic will deal with a plant named Nopal Cactus which is also called as Prickly Pear. The botanical name of this plant is OPUNTIA FICUS-INDICA .The other common names of this plant are Prickly Pear, Tuna , Sabra or Paddle Cactus .
- This plant is found abundantly in South Western regions of United States and Mexico.
- The origin of this plant is South Central Mexico.
- This plant grows well in Spring seasons.
- There are number of medicinal uses for this plant.So, this plant is used as major food ingredients in many parts of mexico.
- It is used to control Diabetes, High Cholesterol, Obesity and Hangovers
- It is used as Antiviral and Anti-inflammatory properties.
- It helps in decreasing the blood sugar level for the diabetes people.
- It also helps in improving Skin health, Protect heart health and also improves and regulates the immune system.

Nutrient content increases as the plant matures.
| Nutrients | Nutrition Value |
|---|---|
| Protein | 1.4 g |
| Total Fat | 0.1 g |
| Carbohydrate | 3.3 g |
| Total dietary Fiber | 2 g |
| Minerals | |
| Calcium, Ca | 16 g |
| Iron, Fe | 2 g |
| Potasium, K | 195 mg |
| Manganese, Mn | 11 g |
| Sodium, Na | 20 mg |
| Vitamins | |
| Vitamin A | 8 g |
| Vitamin B6 | 5 g |
| Vitamin C | 8 g |
74. Gongura
Gongura is a plant that is grown for edible leaves in southern parts of India. The small and immature leaves have a mild sour flavor while mature leaves turn bitter. Gongura contains multiple essential nutrients thatinclude iron, vitamin C, vitamin A, calcium, potassium, magnesium, thiamine, folic acid and riboflavin. It also contains beneficial amino acids. It had the potential to treat urinary infections and sexually transmitted diseases. It highly benefits hair and bone health. It promotes healthy digestion, immune system and prevents cancer. They can be used in various foods and beverages. Gongura seeds, pods and stems are used in pharmaceutical industries to benefit our body.
- Gongura leaves contain anti-oxidants benefits which reduce the cancer, and heart disease.
- It contains high dietary fiber which helps in improving digestive health.
- It contains potassium and magnesium which helps in regulating blood pressure level.
- These leaves contain antioxidant compounds like polyphenolic compounds, anthocyanins, and flavonoids which reduce the chances of cancer.
- The leaves contain various vitamins that benefit for the body health.
- Gongura leaves also rich with various minerals that needed for the body development. Therefore, frequent consume of this leave will lead to optimum body health and body growth.
- It can improve the intestinal bowel movement in produce some fasten digest inside the body, no more afraid of the possibility experience digestive problems, including to avoid an upset stomach or slower digestive metabolism.
- Improve the body metabolic rate in converting food into needed energy, it can produce a fasten metabolic system and bring more energy source for daily activities.
- It can help to avoid the fat formation inside the body and and important nutrient can absorbed by the body.
- The leaves contain vitamin C that can help to increase the body immunity. Therefore, it will help the body to prevent diseases and bacteria or virus infection.
73. Guar bean
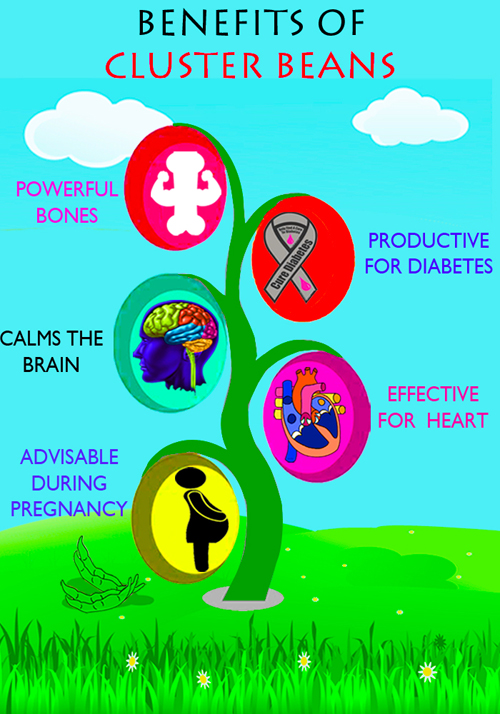
Guar bean or cluster bean is a long and narrow body with tiny pods. It has a slight and similar flavor to broad beans. Guar beans are full of nutrients including vitamins K, C and A, foliates, calcium, iron, potassium and have abundant amounts of carbohydrates. Guar is a vital source of iron that helps to resolve anemia. It is great for diabetics and beneficial for cardio health. Guar beans benefit our bones and enhance better blood circulation. It helps to regulate blood pressure, regulate proper bowel movement and it is highly beneficial for pregnant women. This popular Indian vegetable makes a good side dish and is enjoyed with Indian spices.
- This plant is found abundantly in India and Pakistan and these countries cultivate this plant for many centuries.
- The origin of this plant is unknown since it is not found in the wild.
- This plant grows well in semiarid areas but needs rainfall.
- The gelling agent from the seeds which is popularly called guar gum is used in many industries.
- Cluster beans grow erect and reach a maximum height of 2-3 m.
- This plant can access soil moisture since it has tap roots.
- The oval shaped leaves measures 5-10 cm length. The white to bluish colored flowers grow in the axil.
- The pods contain 5 to 12 small oval seeds which measures 5 mm length.
- The color of the mature seeds is white or gray but they will turn into black in case there is excess moisture.
- The kernel consists of a protein-rich germ and large endosperms containing galacomannan.
- Cluster beans are drought-tolerant and grow well under the sun.
- It grows wonderfully when the soil is rich in moisture.
- It grows well in fertile, medium-textured and sandy-loam soils that are well-drained.
- During cultivation process water-logging should be avoided.
India and Pakistan are the main producers of this plant and these countries produce approximately 80% of world production.
This plant is grown in north-western India like Kutch in Gujarat and in Pakistan. Cluster beans are also cultivated in USA, Australia and Africa.
| Nutrients | Nutrition Value | % DV of RDA |
|---|---|---|
| Water | 82 g | N/D |
| Protein | 4 g | 8.00% |
| Total Fat (lipid) | 0.2 g | 0.57% |
| Ash | 1.5 g | N/D |
| Carbohydrate | 10 g | 7.69% |
| Total dietary Fiber | 2.5 g | 6.58% |
| Minerals | ||
| Calcium, Ca | 100 mg | 10.00% |
| Iron, Fe | 6 mg | 75.00% |
| Phosphorus, P | 250 mg | 35.71% |
| Vitamins | ||
| Vitamin C (Ascorbic acid) | 50 mg | 55.56% |
| Vitamin A, IU | 330 IU | N/D |
72. Banana flower
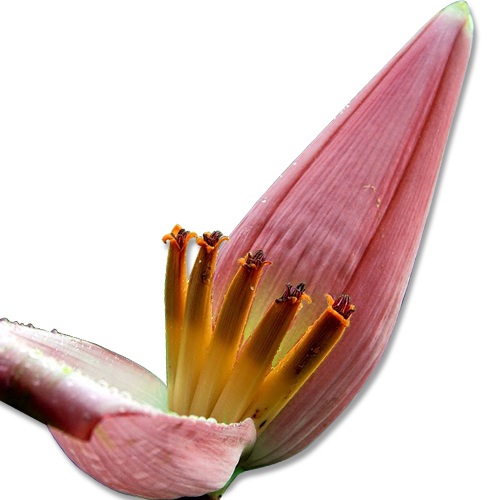
Banana flowers are a large tapered cone. They have deep orange to deep purple and consist of tightly compacted petals that have white tubular flowers. Banana flower is treated as a vegetable and serves as an excellent side dish. The flower has a slightly bitter taste with earthy flavor. It is an excellent source of vitamins C and E. It also contains manganese, copper, iron, dietary fiber and potassium. Banana flowers help to cure the infection and prevent diabetes and anemia. It highly benefits breastfeeding females as it improves lactation and helps to treat menstrual problems. It promotes weight loss, anti-aging effects and gastrointestinal health.
- Widely used in South Asian and Southeast Asian cuisines, the flavor of banana flower will remind you of artichoke.
- As with artichokes, the plump part of the bracts and the flower are suitable for eating; banana flower are used either raw or steamed and is used with dips or cooked in soups, curries, and fried foods. Cleaning this vegetable is no easy thing, so is cooking them.
- Banana flower in the hands of an amateurish cook is not going to come out with flying colors and the issue with this vegetable is if you don't cook it well, it will turn out bitter, consequently affecting other dishes that you are planning to combine it with, so the best way to get rid of it is to cook it discretely.
- Well-cooked banana flower is said to give out a subtle creamy flavor.
- Apart from that, this giant purplish-crimson bud, when dried, the sterile yellow flower is used as an aromatic and earthy spice.
Along with dietary fibers, proteins, and unsaturated fatty acids, it is rich in vitamin E, flavonoids and 100g of banana flower is said to have the following nutrition:
- This plant grows wonderfully in well-drained, semi-shaded areas.
- 51 kcal
- 1.6g of Protein
- 0.6g of Fat
- 9.9g Carbs
- 5.7fgof Fiber
- 56mg of Calcium
- 73.3mg of Phosphorous
- 56.4mg of Iron
- 13mg of Copper
- 553.3 mg of Potassium
- 48.7mg of Magnesium
- 1.07mg of Vitamin E
- Manages anemia
- Reduces free radical activity
- Wards off infections
- Boosts mood and reduces anxiety
- Reduces menstrual bleeding

71. Fluted pumpkin
Fluted pumpkin is a creeping vine with incredible nutritional content. The plant has a edible long green leaves and hard seeds with best health benefits. The leafy green vegetable can be boiled and cooked with foods or can be eaten in vegetable salad or as juice. It is a good source of calcium, iron, potassium, manganese, vitamins C, A, B2 and E. It helps to maintain healthy digestive system and body tissues. It has an anti-diabetic effect and balances the hormone. It improves blood production and promotes healthy bone and teeth. Fluted pumpkin leaves helps in the treatment of infertility issues in both men and women.
- In Southern part of Nigeria and in some parts of West Africa, Fluted gourd is found abundantly.
- The origin of this plant is Nigeria.
- Fluted Gourd is a Tropical vine that grows well in West Africa as a leafy vegetable.
- The fruits of this plant is not edible but seeds produced by this plant is edible and rich in protein and fat.
- The Fluted pumpkin's leaf is primarily used in soups and herbal medicines Which is high in nutrition.
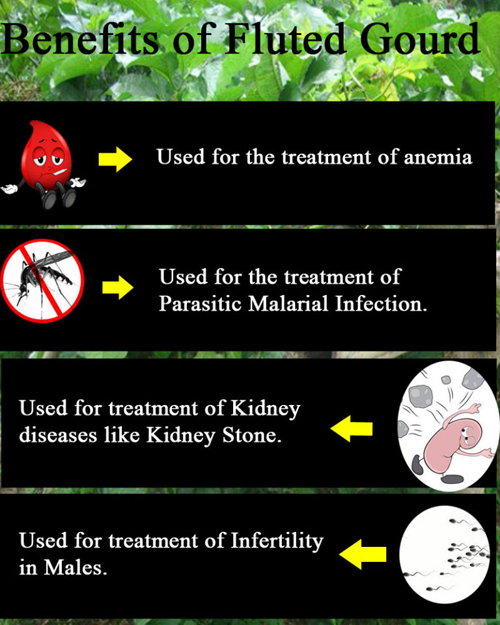
- The liquid extracts of the leaves are used for the treatment of anemia .
- The presence of anti plasmodia and schizonticidal in the root of the plant helps in treating parasitic malarial infections.
- It useful for treating kidney diseases like kidney stone.
- The presence of anti-oxidative properties like oleic acid, alkaloids, tannins and linoleic acids which is helpful in treating infertility in males by boosting the functionality of testicles for an increased sperm count.
The seeds of this plant is rich in Protein and Fat and also contains significant level of Vitamin A and Vitamin C .
| Nutrients | Nutrition Value |
|---|---|
| Protein | 27 g |
| Total Fat | 53 g |
| Carbohydrate | 53.3 g |
| Minerals | |
| Calcium, Ca | 280 mg |
| Iron, Fe | 69 mg |
| Magnesium, Mg | 700 mg |
| Vitamins | |
| Vitamin A | 9.18 mg |
| Vitamin C | 74.44 mg |