List Of Vegetables
- Absinthe Interesting Facts

- Ahipa Nutritional Values

- Akudjura Various Uses

- Amaranth Health Benefits

- American Pokeweed

- Aniseed Myrtle Properties

- Aonori Summary

- Apple Mint Uses

- Arame Medicinal Uses

- Arracacha Nutritional Value

- Artichoke Nutrition Values

 Arugula Health Summary
Arugula Health Summary- Asarabacca Various Uses

- Asparagus Healthy Eating

- Avocado Nutrition Benefits

- Bamboo shoots

- Basil Nutrition Guide

- Beans Beneficial Properties

- Bean sprouts

- Beet Greens Nutrition Facts

- Beets Health Benefits
- Bishop’s weed Various Uses

- Bitter Gourd Nutritional Value

- Black Beans Benefits

- Blue Fenugreek Various Uses

- Boldo Medicinal Values

- Bok Choy Health Benefits

- Borage Greens Medicinal Purposes

- Bottle Guard Aspects

- Broccoli Health Properties

- Broccoflower Nutrition Guide

- Broccoli Raab Nutrition Values

- Broadleaf Arrowhead Health Benefits

- Brussel sprouts Nutrition Summary

- Burdock Health Benefits

- Cabbage Health Facts

- Camas Health Benefits

- Cantaloupe Nutrition Guide

- Canella Uses

- Carrots Health Properties

- Cardoon Nutritional Value

- Carola Summary

- Cassava Health Properties

- Catnip Oil Benefits

- Catsear Flower Uses

- Celeriac Nutritional Value

- Celery Health Benefits

- Chard(Swiss & red)Nutrition Values

- Chaya Nutrition Facts

- Chervil Properties

- Good King Henry

- Chickweed Health Benefits

- Chickpeas Nutrition Summary

- Chile peppers Health Benefits

- Chinese Artichoke Uses

- Chinese Broccoli Nutritional Valu

- Chinese cabbage Nutrition Values

- Chinese Mallow Aspects

- Chives Nutrition Guide

- Chrysanthemum Leaves Uses

- Cicely Unknown Benefits

- Cinnamon Myrtle Medicinal Value

- Collards Nutrition Facts

- Common Purslane Benefits

- Corn Health Values

- Corn Salad Interesting Facts

- Cress Medicinal Values

- Cucumber Health Benefits

- Culantro Leaves

- Curry Leaf Tree Origin

- Collard Greens Nutrition Facts

- Dabberlocks Interesting Facts

- Dandelion Health Benefits

- Dill Health requirements

- Drumstick Nutritional Value

- Dulse Health Benefits

- Earthnut Pea Properties

- Eggplant Nutrition Guide

- Elephant Foot yam Health Benefits

- Elephant Garlic Uses

- Endive Medicinal Properties

- Ensete Health Benefits

- Epazote Properties

- Fat Hen Interesting Facts

- Fingerroot Uses

- French Sorrel Health Facts

- Garlic Nutrition Values

- Gim seaweed Uses

- Ginger Flower Properties

- Ginger Medicinal Values

- Golden Samphire Aspects

- Greater Plantain Medicinal Uses

- Green onions Health Facts

- Green peas Nutrition Values

- Hijiki Nutritional Aspects

- Holy Basil Leaves

- Horseradish Health Benefits

- Onions Nutrition Guide

- Sea Beet Aspects

- Sea Lettuce Health Benefits

- Yam Nutritional Value

- Yarrow Medicinal Uses

- Zucchini Health Guide

- Veggies by seasons

- Veggies did you know??

- Comparison of veggies!!!

- Veggies and it's origin

- Comical View of Veggiess

- Categories of veggies

- Top Veggiess 100 To 91

- Top Veggiess 90 To 81

- Top Veggiess 80 To 71

- Top Veggiess 70 To 61

- Top Veggiess 60 To 51

- Top Veggiess 50 To 41

- Top Veggiess 40 To 31
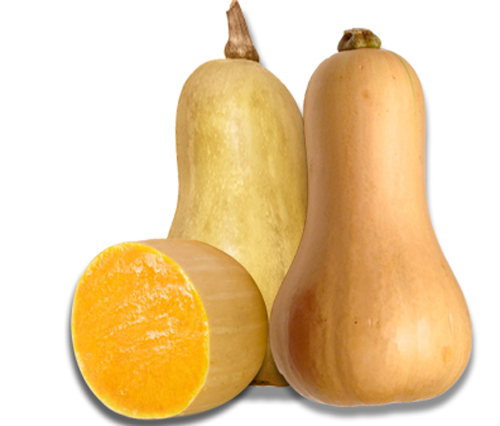

- Top Veggiess 30 To 21
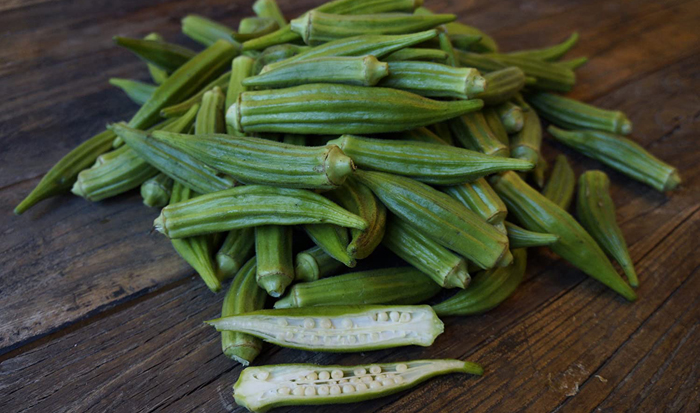

- Top Veggiess 20 To 11
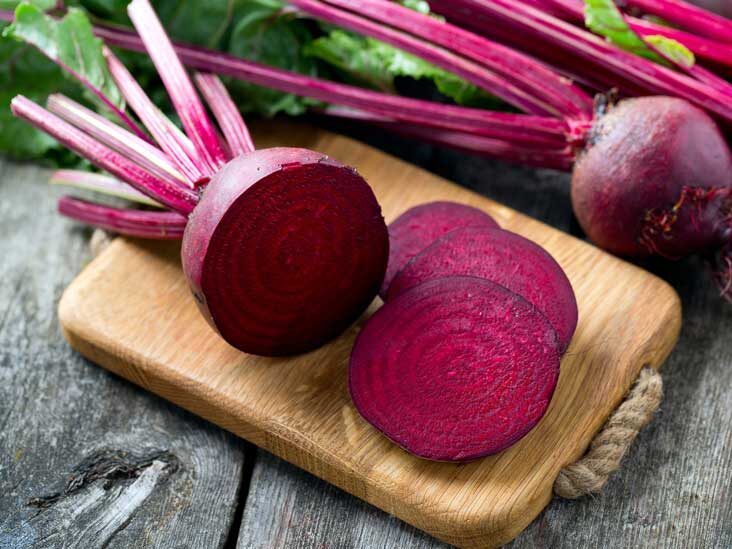

- Top Veggiess 10 To 01
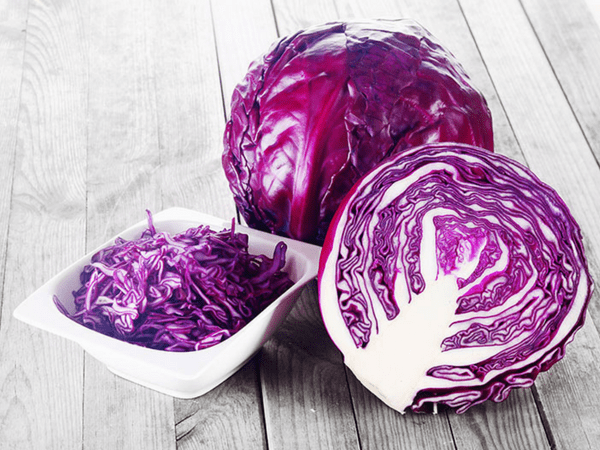

Veggie Picks
Top Veggiess 50 To 41 For Health Benefits
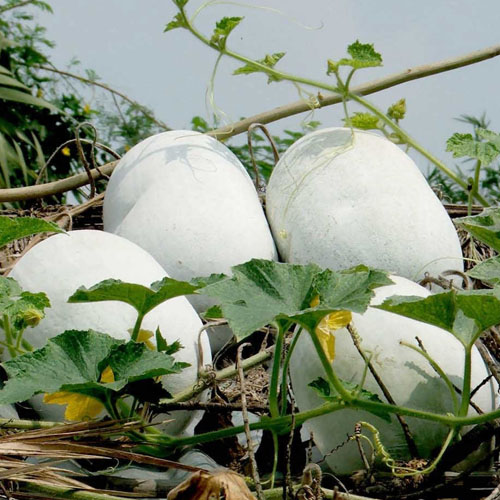
50. Wax gourd
Wax gourd also known as winter melon is a winter squash that has green skin and white waxy coating. It has a subtle or mild taste and has a texture similar to watermelon. It comprises nutrients like Vitamin C, iron, calcium, phosphorus, dietary fiber and magnesium. It may prevent ulcer, reduce inflammation and protect against type 2 diabetes. Wax gourd helps to reduce weight and improves digestion.
Wax gourd is a versatile vegetable that can be added in stews, soups, salads or it can be processed into jam and ketchups.
- The fruit is fuzzy and the young ones have a thick white flesh which is sweet when eaten.
- During the process of maturity the fruit loses its hair and is replaced by a waxy coating giving rise to the name wax gourd. This plant reaches a height of 80 cm.
- This plant is native to South Asia and Southeast Asia. Fully grown fruit will not be sweet.
- So melon is only used as suffix. These melons grow well in warmer weather and they can be stored for many months like winter squash.
- This plant has many medicinal properties. It is used in Ayurvedic system of medicine for the treatment of certain diseases.
- It is used as an ingredient in the soups and helps produce more milk for breastfeeding.
- The melons are used in pork soups and other meat items.
- Taiwanese and Chinese use melons as filler in moon cakes.
- This melon is used during New Year festivals. Philippines call this melon as kundol, kondol or gondol.
- It is also used in savory soups and stir-fries. North Indians prepare a candy named Petha.
- Juice of the melon is used for the treatment of dysentery. Winter melon tea is very famous drink in Southeast Asia.
- This wonderful plant has high amounts of Vitamins such as B1, B3 and C.
- It also has calcium in high amounts.
- Ash gourd contains 96% of water and can reduce high blood pressure.
- The ayurvedic experts prescribed wax gourd for the treatment of nervous problems, epilepsy and other brain problems.
- The seeds can be used to expel stomach worms.
- Wax gourd is beneficial in dealing with various respiratory ailments such as asthma, bronchitis and chest congestion.
- It has lots of curative properties and can be used for treating stomach ailments.
| Nutrients | Amount Value | % DV of RDA |
|---|---|---|
| Energy | 71 kJ | N/D |
| Protein | 0.53 g | 1.06% |
| Total Fat | 0.26 g | 0.74% |
| Ash | 0.4 g | N/D |
| Carbohydrate | 3.96 g | 3.05% |
| Dietary Fiber | 3.8 g | 10.00% |
| Vitamins | ||
| Vitamin C | 17.2 mg | 19.11% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.145 mg | 11.15% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.053 mg | 4.42% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.046 mg | 3.54% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.176 mg | 3.52% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.528 mg | 3.30% |
| Minerals | ||
| Sodium | 147 mg | 9.80% |
| Zinc | 0.81 mg | 7.36% |
| Iron | 0.53 mg | 6.63% |
| Phosphorus | 25 mg | 3.57% |
| Manganese | 0.077 mg | 3.35% |
| Copper | 0.03 mg | 3.33% |
| Others | ||
| Tryptophan | 0.003 g | 0.68% |
| Lysine | 0.012 g | 0.36% |
| Methionine | 0.0047 g | 0.28% |
| Palmitic acid | 0.015 g | N/D |
| Stearic acid | 0.007 g | N/D |
| Oleic acid | 0.049 g | N/D |
| Linoleic acid | 0.115 g | N/D |

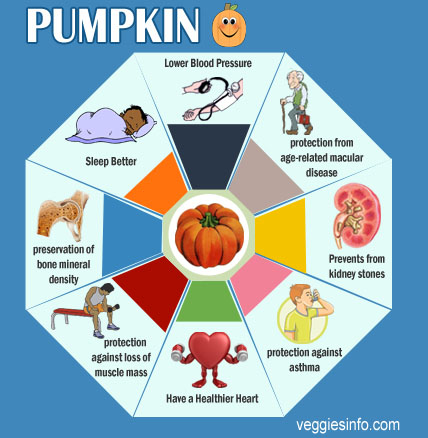
49. Pumpkin
pumpkin is a winter squash having round and smooth exterior with longitudinal ridges. It has a deep yellow to orange flesh and earthy sweet flavor. Pumpkin is scientifically considered to be a fruit, but is treated as a vegetable. It has a lavish amount of Vitamin A, exceeding the daily intake value. Pumpkin contains a fair amount of Vitamin C, potassium, copper, manganese, Vitamin B2, Vitamin E and iron. Pumpkins can neutralize free radicals and prevent the risk of chronic disease such as heart disease and cancer. It may boost the immune system, promote weight loss and eye health. Pumpkin protects skin from sun damage.
Pumpkins are easy to incorporate in dishes like pies, custard and pancakes or it enjoyed raw.
- protection against loss of muscle mass.
- preservation of bone mineral density.
- protection from "Age-Related Muscular Disease" (ARMD).
- Feel Fuller.
- Boost Vision.
- Lower Blood Pressure.
- Sleep Better.
- Have a Healthier Heart.
- protection against asthma.
- Reduction in the formation of kidney stones.
- Reduced risk of stroke.
Pumpkin comes in different shapes sizes and sometimes in an array of colours but what makes it stand apart from the rest of the vegetables is its nutrition value. Pumpkin has the property that transforms good health to fit health. This vegetable has vital vitamins such as Vitamin A which forms a substance called alpha carotene an anti aging property good for freckled skin as it produces collagen that makes your skin look youthful and smooth. Speaking of good skin vitamin E also contributes to great skin as it protects the skin against skin damage. Vitamin C found in pumpkin is popular for its ability to boost the immunity of your body and strengthening bones in order to give a good frame to the body. Apart from these nutrients pumpkin consisting many minerals that meet the daily needs of the body.Pumpkin seed oil is rich in natural phytoestrogens and studies suggest it may lead to a significant increase in good "HDL" cholesterol along with decreases in blood pressure, hot flashes, headaches, joint pains and other menopausal symptoms in postmenopausal women.Pumpkin seeds are a rich source of tryptophan, an amino acid (protein building block) that your body converts into serotonin, which in turn is converted into melatonin, the "sleep hormone." Eating pumpkin seeds a few hours before bed, along with a carbohydrate like a small piece of fruit, may be especially beneficial for providing your body the tryptophan needed for your melatonin and serotonin production to help promote a restful night's sleep
| Principle | Nutrient Value | Percentage of RDA |
|---|---|---|
| Energy | 26 Kcal | 1% |
| Carbohydrates | 6.50 g | 5% |
| Protein | 1.0 g | 2% |
| Total Fat | 0.1 g | 0.5% |
| Cholesterol | 0 mg | 0% |
| Dietary Fiber | 0.5 g | 2% |
| Vitamins | ||
| Folates | 16 mcg | 4% |
| Niacin | 0.600 mg | 4% |
| Pantothenic acid | 0.298 mg | 6% |
| Pyridoxine | 0.061 mg | 5% |
| Riboflavin | 0.110 mg | 8.5% |
| Thiamin | 0.050 mg | 4% |
| Vitamin A | 7384 IU | 246% |
| Vitamin C | 9.0 mg | 15% |
| Vitamin E | 1.06 mg | 7% |
| Vitamin K | 1.1 mcg | 1% |
| Electrolytes | ||
| Sodium | 1 mg | 0.5% |
| Potassium | 340 mg | 7% |
| Minerals | ||
| Calcium | 21 mg | 2% |
| Copper | 0.127 mg | 14% |
| Iron | 0.80 mg | 10% |
| Magnesium | 12 mg | 3% |
| Manganese | 0.125 mg | 0.5% |
| Phosphorus | 44mg | 5% |
| Selenium | 0.3 mcg | <0.5% |
| Zinc | 0.32 mg | 3% |
| Phyto-nutrients | ||
| Carotene-a | 515 mcg | — |
| Carotene-ß | 3100 mcg | — |
| Crypto-xanthin-ß | 2145 mcg | — |
| Lutein-zeaxanthin | 1500 mcg | — |
Pumpkin is a vegetable that goes good with every form of cooking such as baking, simmering, and grilling or sometimes even for food carving. Pumpkin soup is a delicacy that can be enjoyed as a hot soups during winter and cold soups during summer times.
Pumpkin pies are a favourite amongst vegetarian food lovers. Pumpkin seeds are also of great importance one cannot afford to discard the seeds as they are edible too.
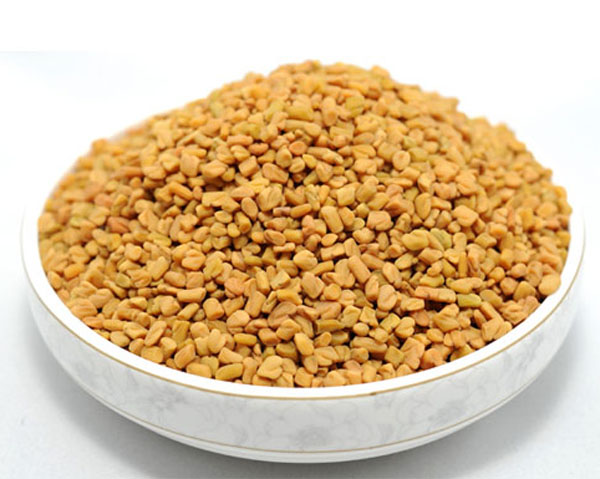
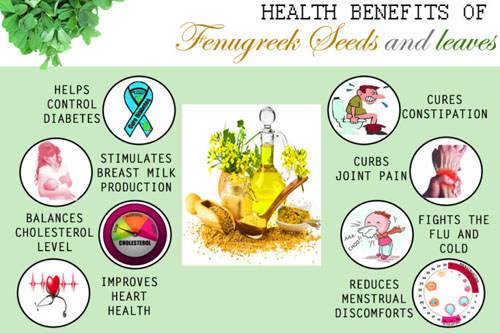
48. Fenugreek
Fenugreek is a herb whose leaves and seeds are commonly known for its health benefits. The seeds of the fenugreek have a taste and flavor similar to maple syrup. Iron, magnesium, manganese, protein and fat are the key nutrients in fenugreek seeds. Fenugreek boosts the production of breast milk and promotes weight gain in newborn babies. It helps increase testosterone level in men. Fenugreek seeds may maintain diabetes and blood sugar level. It may also help to treat ulcerative cancer and skin problems.
Fenugreek is an annual plant which comes under the family Fabaceae and grows up to 2ft by 1.4 ft at a fast rate. Fenugreek finds its place in Indian dishes since Indians use fenugreek lavishly in their cuisines. The leaves have three small obviate to oblong leaflets. It is cultivated in semiarid crop in many parts of India. The Archealogists have recovered fenugreek from Iraq which dates back to 4000 BC. They have also found bronze age seeds from the tomb of Tutankhamen.
Fenugreek was grown food staple during the 1st century CE. The name of this plant in Hebrew is tiltan and finds a place in a book named Mishnah which was compiled during 2nd century. The major producers of fenugreek are Afghanistan, Pakistan, India, Iran, Nepal, Bangladesh, Argentina, Egypt, France, Spain, Turkey, and Morocco. The state of Rajasthan tops the chart in fenugreek production followed by other Indian states such as Gujarat, Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Haryana, and Punjab. Rajasthan produces 80% of overall production in India.
- Dried or fresh leaves are used as an herb, spice and also as vegetable.
- There is a component named sotolon which is responsible for the aromatic smell of fenugreek.
- The powder is used in many Indian dishes.
- The Indians use it in various continental dishes, daals and sambar.
- The leaves with roots attaches in it are sold in many Indian markets.
- Its leaves are very famous in Turkey, Persia, Iran, Egypt, Eritrean and Ethiopia.
- These countries use fenugreek in their cuisines and relish its taste.
- It is rich in minerals, vitamins and supplements and should be consumed regularly to improve the overall health.
- Lactating mothers can improve the milk production when they consume fenugreek.
- Though there is no sufficient proof or evidence researchers have found that it helps in effective weight management.
- Fenugreek improves digestion, upset stomach, constipation and inflammation of stomach.
- It reduces hardening of the arteries, cholesterol and triglycerides.
- It improves kidney function, reduces mouth ulcers, fights a disease named beriberi, reduces chronic coughs, chapped lips, improve hair growth, fights cancer, reduced blood sugar in the people suffering from diabetes.
- It improves sexual performance since it improves erectile dysfunction and other male problems.
- It is also used in the treatment of inflammation, muscle pain, breast enlargement, swelling of lymph nodes, leg ulcers and eczema.
- Fenugreek extracts are also used in manufacturing soaps and cosmetics.
- It cures hear burn, acid reflux, increases libido and improves the texture of the skin.
| Principle | Amount Value | % DV of RDA |
|---|---|---|
| Energy | 323 Kcal | 16% |
| Carbohydrates | 58.35 g | 45% |
| Protein | 23 g | 41% |
| Total Fat | 6.41 g | 21% |
| Cholesterol | 0 mg | 0% |
| Dietary Fiber | 24.6 g | 65% |
| Vitamins | ||
| Folates | 57 µg | 14% |
| Niacin | 1.640 mg | 7% |
| Pyridoxine | 0.600 mg | 46% |
| Riboflavin | 0.366 mg | 28% |
| Thiamin | 0.322 mg | 27% |
| Vitamin A | 60 IU | 2% |
| Vitamin C | 3 mg | 5% |
| Electrolytes | ||
| Sodium | 67 mg | 4.50% |
| Potassium | 770 mg | 16% |
| Minerals | ||
| Calcium | 176 mg | 18% |
| Copper | 1.110 mg | 123% |
| Iron | 33.53 mg | 419% |
| Magnesium | 191 mg | 48% |
| Manganese | 1.228 mg | 53% |
| Phosphorus | 296 mg | 42% |
| Selenium | 6.3 µg | 11% |
| Zinc | 2.50 mg | 23% |
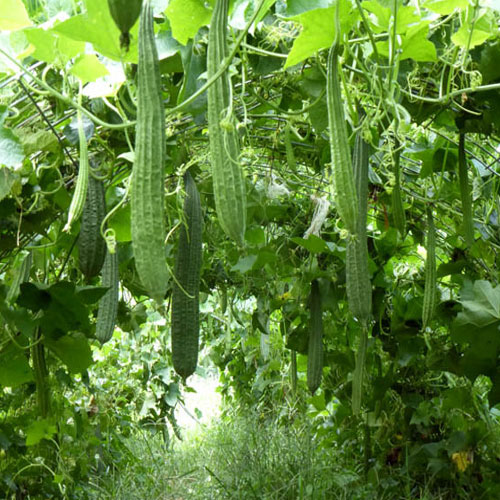
47. Ridge gourd
Ridge gourd is a long vegetable with rigid dark green skin and spongy white flesh that has more number of seeds. It is generally consumed as a side dish in India. Ridge gourd is enriched with dietary fiber and contains all other essential nutrients including Vitamin C, iron, zinc, riboflavin, magnesium, thiamine and other minerals. It aids weight loss, constipation and heals jaundice. It promotes your eye health, liver health and strengthens your immune system. Ridge gourd may also be used to purify blood and acts as a cooling agent.
The fruits are consumed as vegetables by the people all over the world. The other common names of this plant are angled luffa, Chinese okra, dish cloth gourd, ridged gourd, sponge gourd, vegetable gourd, strainer vine, ribbed loofah, silky gourd, ridged gourd, silk gourd, and sinkwa towelsponge. This ridge gourd is used in India lavishly and plays an important part in Indian cuisines. Mainly South Indians consume this vegetable every day.
The native place of this plant is India and is now grown in many parts of the world. These plants are planted in spring seasons grown up and across a head-high trellis. The fruits can be harvested easily since the gourds hang below the foliage. The single-vines will produce up to 25 large fruits which can be handpicked easily.
The male and female organs are found on the same plant. This tropical running vine plant has yellow flowers and rounded leaves. Pollination is done by bees. The leaves are covered with short hairs and the fruits are ribbed. The length of the fruit is 1-2 ft. The young fruit is used as a cooked vegetable. But the farmers also grow for the fibrous interiors.
- This plant contains calcium, phosphorous, iron and other micronutrients.
- The leaves of this plant are lots of nutrients, minerals, vitamins, antioxidant, anti microbial and anti-inflammatory properties.
- The fibrous netting is an excellent sponge but they are also used in water filters.
- The leaves are used for curing amenorrhea and hemorrhoids.
| Principle | Nutrient Value | Percentage of RDA |
|---|---|---|
| Calcium, Ca | 20 mg | 2 % |
| Copper, Cu | 0.04 mg | 1.75 % |
| Iron, Fe | 0.36 mg | 2 % |
| Magnesium, Mg | 14 mg | 3.5 % |
| Manganese, Mn | 0.09 mg | 4.6 % |
| Phosphorus, P | 32 mg | 3.2 % |
| Potassium, K | 139 mg | 3.97 % |
| Selenium, Se | 0.2 mcg | 0.29 % |
| Sodium, Na | 3 mg | 0.12 % |
| Zinc, Zn | 0.07 mg | 0.47 % |
| Vitamin A | 410 IU | 8.2 % |
| Vitamin C | 12 mg | 20 % |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.04 mg | 2.15 % |
| Vitamin E | 0.1 mg | 0.33 % |
| Vitamin K | 0.7 mcg | 0.87 % |
| Riboflavin | 0.06 mg | 3.53 % |
| Thiamin | 0.05 mg | 3.33 % |
| Folate, DFE | 7 mcg | 1.75 % |
| Niacin | 0.4 mg | 2 % |
| Sugars | 2.02 g | |
| Fiber | 1.1 g | 4.4 % |
| Cholesterol | 0 mg | 0% |
| Water | 93.85 g | |
| Carotene, alpha | ~ | |
| Carotene, beta | ~ | |
| Choline | ~ | |
| Lycopene | ~ |
- Juice of the fresh leaves is used for the treatment of conjunctivitis in children.
- The leaves are also used to prevent the lids from adhering at night from excessive meibomian secretion.
- Juice of leaves are also used externally for sores and various animal bites.
- Pulp of the fruit is used internally, like calocynth, to cause vomiting and purging.
- Powdered dried is used for patients afflicted with jaundice.
- Seed oil is used for dermatitis.
- The roots are used as a purge.
- The infused seeds are used as purgative and emetic, dropsy and as laxative.
- The leaf decoction is used for uremia and amenorrhea.
- The pounded leaves are used for hemorrhoids, splenitis and leprosy.
- The leaf extract of ridged gourd is applied to sores caused by guinea worms.
- The fruits and seeds are used in herbal preparations for treatment of venereal diseases.
- The seeds are eaten to expel intestinal worms.
- This plant is classified as herb since it has lots of medicinal properties.

46. Bitter gourd
Bitter gourd or bitter melon is a long pale green vegetable with soft protruded extension on the exterior. It is commonly hated by children due to its strong and distinctive bitter flavor. Bitter gourd is particularly rich in Vitamin C and packed with many other nutrients including Vitamin A, folate, potassium, zinc, iron and fiber. Bitter gourd is proven to reduce the blood sugar level and cholesterol level. It aids weight loss and has cancer fighting properties. Bitter gourd promotes skin and eye health.
It can be eaten raw or baked, steamed or pan fried according to your choice.
Plants and trees occupy most parts of the planet and grow lavishly in nooks and corners of the earth. The plants give healthy flowers, fruits and nuts which are consumed by the animals and human being. Human beings have chopped off hundreds of trees to satisfy their desire and are still chopping off number of trees for timber which is a dangerous signal. Most of the plants and trees are harmless creatures. This topic will deal with the plant named Bitter gourd which is very popular in India. The botanical name of this plant is Momordica charantia.
The other names of these plants are bitter melon, Patrick or balsam-pear. This tropical and sub-tropical plant comes under the family cucurbitacea. Bitter guard plant is cultivated in Asia, Africa and the Caribbean Islands. These plants originated in India and were introduced into China during 14th century. The taste of this gourd is bitter. This plant grows up to 5 m in length. The size of the leaves is approximately 12 cm. It is imperative to note that each plant bears separate yellow and female flowers. The flowering occurs during the months of June to July and fruits sprout during the months of September to November. Bitter gourd is the most sought after vegetable in south India since the people living in this zone use it during "No moon day". Many people around the world hate the bitter taste and so it did not gain much popularity.
- Indians use these gourds in the soups and dishes.
- Some even fry this gourd along with cooking oil and consume it immediately.
- Bitter gourd has many curative properties.
- Medical practitioner's advise the diabetic patients to consume this guard every day.
- This gourd is gaining popularity worldwide due to its medicinal effects.
- This plant is very rich in vitamins and supplements.
| Principle | Nutrient Value | Percentage of RDA |
|---|---|---|
| Energy | 17 Kcal | <1% |
| Carbohydrates | 3.70 g | 3% |
| Protein | 1.00 g | 2% |
| Total Fat | 0.17 g | 0.50% |
| Cholesterol | 0 mg | 0% |
| Dietary Fiber | 2.80 g | 7% |
| Vitamins | ||
| Folates | 72 µg | 18% |
| Niacin | 0.400 mg | 2.50% |
| Pantothenic acid | 0.212 mg | 4% |
| Pyridoxine | 0.043 mg | 3% |
| Riboflavin | 0.040 mg | 3% |
| Thiamin | 0.040 mg | 3.50% |
| Vitamin A | 471 IU | 16% |
| Vitamin C | 84 mg | 140% |
| Electrolytes | ||
| Sodium | 5 mg | <1% |
| Potassium | 296 mg | 6% |
| Minerals | ||
| Calcium | 19 mg | 2% |
| Copper | 0.034 mg | 4% |
| Iron | 0.43 mg | 5% |
| Magnesium | 17 mg | 4% |
| Manganese | 0.089 mg | 4% |
| Zinc | 0.80 mg | 7% |
| Phyto-nutrients | ||
| Carotene-β | 190 µg | — |
| Carotene-α | 185 µg | — |
| Lutein-zeaxanthin | 170 µg | — |
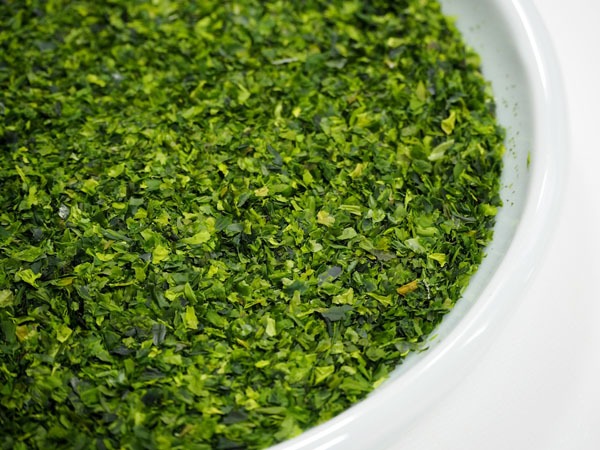
45. Aonori
Aonori is a dried and powdered green seaweed or green laver. It is mainly used in japanese dishes due to their distinctive aroma. Aonori may look unattractive but is attracted by its nutritional value. It is loaded with calcium, sodium, potassium, magnesium, phosphorus, iron, manganese, zinc, copper and selenium. It also contains omega-3 fatty acids that maintain cholesterol level. It benefits our digestive system and immune system. Aonori helps to reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular diseases.
| Nutrients | Amount Value | % DV of RDA |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamins | ||
| Vitamin A Retinol Equivalent | 35μg | 221μgRE |
| Vitamin E Alpha Tocopherol | 0.06mg | 2.2mg |
| Vitamin K | 0.08μg | 17μg |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.02mg | 0.32mg |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.04mg | 0.36mg |
| Niacin | 0.15mg | 3.48mgNE |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.01mg | 0.35mg |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.8μg | 0.8μg |
| Folate | 6.5μg | 80μg |
| Pantothenic Acid | 0.01mg | 1.5mg |
| Biotin | 1.84μg | 17μg |
| Vitamin C | 1mg | 33mg |
| Mierals | ||
| Sodium | 85mg | ~1000mg |
| Potassium | 19.25mg | 833mg |
| Calcium | 18mg | 221mg |
| Magnesium | 32.5mg | 91.8mg |
| Phosphorus | 9.5mg | 381mg |
| Iron | 1.87mg | 3.49mg |
| Zinc | 0.07mg | 3mg |
| Copper | 0.02mg | 0.24mg |
| Manganese | 0.33mg | 1.17mg |
| Iodine | 70μg | 43.8μg |
| Selenium | 0.18μg | 8.3μg |
| Chromium | 1.03μg | 10μg |
| Molybdenum | 0.48μg | 6.7μg |
| Other | ||
| Total Dietary Fiber | 0.96g | 5.7g~ |
| Sodium Chloride Equivalent | 0.22g | ~2.5g |
These plants are also found in America and other parts of the world. For the purpose of cultivation the spores are collected on rope nets by submerging the nets in the areas where natural Monostroma grow.
The nets are harvested 3-4 weeks. The other common names of these weeds are green laver and blue seaweed. Japanese use these weeds lavishly in their food items. They add these in soups, tempura and sprinkle it in hot food items.
44. Amaranth
Amaranth is considered to be a pseudo cereal that produces seeds and fruits that are eaten as grains. There are more than 60 different species of amaranth present all over the world. Amaranth has a high nutrient profile benefiting our health. Amaranth is particularly blessed with manganese. It is also a good source of magnesium, phosphorus, iron, selenium, copper, carbohydrate and protein. It helps to benefit our brain function and prevent certain neurological conditions. Antioxidants present in amaranth helps in damaging the cells causing chronic diseases and protects against heart disease and cancer. It has the potential to reduce cholesterol level and inflammations. It is gluten free grain that aids weight loss.
- Amaranth oil is very famous and the oil is extracted from its grains.
- This oil has many commercial values.
- Raw amaranth is unfit for human consumption.
- So these grains have to be properly cooked and like other grains.
- Cooked amaranth grain is much better than wheat bread.
- These grains have lysine which is a powerful amino acid.
- These grains are totally free of gluten.
- These grains are rich in various supplements such as riboflavin, zinc, potassium, folate, thiamin and niacin.
- It is imperative to note that one plant produce up to 600, 000 seeds.
- Amaranth is rich in protein and calcium. These plants are also cultivated in Thailand, Nigeria, Russia, Mexico, Nepal and African continent.
- Many consume these grains as porridge in the morning time.
- These beans are rich in fiber.
- The leaves of these plants are also edible.
43. Alfalfa sprouts
Alfalfa sprouts are the baby plants or immature shoots of the alfalfa plants. They are harvested early, as the mature leaves tend to be more bitter. The crunchy texture of the sprouts makes it delicious when added in sandwich, soup and stir-fries. Alfalfa sprouts are loaded with Vitamin K and packed with other nutrients such as Vitamin C, thiamine, copper, manganese, iron, riboflavin and magnesium. The powerful antioxidant present in these sprouts helps to reduce cell death and damage caused by free radicals.
It helps to maintain cholesterol level and relieves menopause symptoms.

- Vitamin K: 13%.
- Vitamin C: 5%.
- Copper: 3%.
- Manganese: 3%.
- Folate: 3%.
- Thiamin: 2%.
- Riboflavin: 2%.
- Magnesium: 2%.
- Iron: 2%.
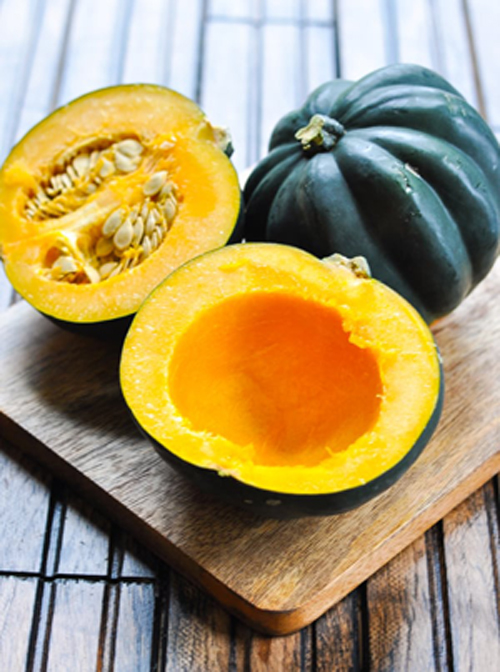
42. Acorn squash
Acorn squash is a winter squash with longitudinal green to white ridges on the exterior resembling pumpkin. It has a sweet, yellow flesh with impressive health benefits. Acorn squash is enriched with Vitamin C, thiamine and Vitamin B6. The high carbohydrate vegetable also contains a fair amount of fiber, provitamin A, folate, potassium, magnesium, iron and manganese. Acorn squash is loaded with antioxidants that have the potential to reduce the risk of chronic conditions like heart diseases, diabetes and various types of cancer. It promotes a healthy immune and skeletal system and helps to maintain cholesterol level.
It makes a great side dish when baked, roasted or microwaved and can be added to sweet and savory dishes.
- Builds Strong Bones.
- Boosts Immunity.
- Regulates Blood Pressure.
- Improves Vision.
- Controls Diabetes.
- Skin Care.
- Calories: 115
- Fat: 0.3g
- Sodium: 8.2mg
- Carbohydrates: 30g
- Fiber: 9g
- Sugar: 0g
- Protein: 2.3g
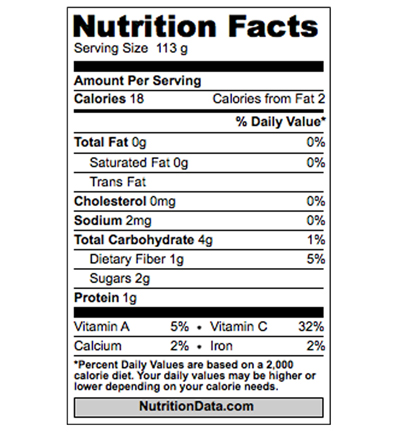
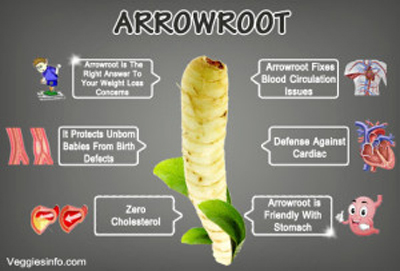
41. Arrowroot
Arrowroot is a starchy root vegetable and a tropical tuber. It is usually processed into a powder called arrowroot flour. It has higher protein content and folate than any other tuber. It also contains a fair amount of phosphorus, iron, potassium and fiber. It promotes weight loss, healthy immune system and healthy digestion. The high starch content present in arrowroot may help you to treat diarrhea and abdominal pain.
It can be easily incorporated into sweet and savory dishes.
- Arrowroot Fixes Blood Circulation Issues:It contains a rich blend of nutrients which incorporates significantly high levels of iron and copper. These minerals are the essential components of the red blood cells and actively help in avoiding anaemia. Furthermore, the arrowroot encourages oxygenation in the body organs which is good for boosting your energy levels.
- It Protects Unborn Babies From Birth Defects: It contains Folate in the adequate levels which is another member of the Vitamin B family. A few studies conducted on Folate reveal that it is highly beneficial for expecting mothers by preventing neural tube defects in the expected child. Folate also plays a crucial role during DNA synthesis which promotes rapid healing.
- Arrowroot is Friendly With Stomach: When the world is facing threats from Celiac disease which is a result of consuming diet rich in gluten, the arrowroot is a perfect gluten-free solution. It doesn't cause gastrointestinal discomfort and perfect for those who have allergies to gluten containing foods.
- Arrowroot is The Right Answer To Your Weight Loss Concerns: Being low in calories Arrowroot adds to a healthy diet. For this reason, it is a perfect diet for those individuals who are struggling to remain on a diet low in calories but high in nutrients. It is also a recommended dietary fibre which reduces the urge for snacks between the meals. Altogether, Arrowroot fills you up with the essential minerals and vitamins that you were in dire need of.
It is one of the healthiest foods and the best for the individuals with conscious about their daily cholesterol intake. It contains almost zero cholesterol per serving which makes it counts in the healthiest foods.
| Principle | Nutrient Value | Percentage of RDA |
|---|---|---|
| Calories | 65 | |
| Total Fat | 0.20g | 1% |
| Saturated | 0.039 g | 0% |
| Trans | 0g | |
| Cholesterol | 0 mg | 0% |
| Sodium |
26 mg | 0% |
| Total Carbs |
13.39g | 1% |
| Dietary Fiber |
0.039g | 10% |
| Sugars |
0g | 0% |
| Protein | 4.24g | |
| Vitamin A | 19mg | 0% |
| Vitamin C | 1.9mg | 2% |
| Calcium | 6mg | 0% |
| Iron | 2.22mg | 0% |