List Of Vegetables
- Absinthe Interesting Facts

- Ahipa Nutritional Values

- Akudjura Various Uses

- Amaranth Health Benefits

- American Pokeweed

- Aniseed Myrtle Properties

- Aonori Summary

- Apple Mint Uses

- Arame Medicinal Uses

- Arracacha Nutritional Value

- Artichoke Nutrition Values

 Arugula Health Summary
Arugula Health Summary- Asarabacca Various Uses

- Asparagus Healthy Eating

- Avocado Nutrition Benefits

- Bamboo shoots

- Basil Nutrition Guide

- Beans Beneficial Properties

- Bean sprouts

- Beet Greens Nutrition Facts

- Beets Health Benefits
- Bishop’s weed Various Uses

- Bitter Gourd Nutritional Value

- Black Beans Benefits

- Blue Fenugreek Various Uses

- Boldo Medicinal Values

- Bok Choy Health Benefits

- Borage Greens Medicinal Purposes

- Bottle Guard Aspects

- Broccoli Health Properties

- Broccoflower Nutrition Guide

- Broccoli Raab Nutrition Values

- Broadleaf Arrowhead Health Benefits

- Brussel sprouts Nutrition Summary

- Burdock Health Benefits

- Cabbage Health Facts

- Camas Health Benefits

- Cantaloupe Nutrition Guide

- Canella Uses

- Carrots Health Properties

- Cardoon Nutritional Value

- Carola Summary

- Cassava Health Properties

- Catnip Oil Benefits

- Catsear Flower Uses

- Celeriac Nutritional Value

- Celery Health Benefits

- Chard(Swiss & red)Nutrition Values

- Chaya Nutrition Facts

- Chervil Properties

- Good King Henry

- Chickweed Health Benefits

- Chickpeas Nutrition Summary

- Chile peppers Health Benefits

- Chinese Artichoke Uses

- Chinese Broccoli Nutritional Valu

- Chinese cabbage Nutrition Values

- Chinese Mallow Aspects

- Chives Nutrition Guide

- Chrysanthemum Leaves Uses

- Cicely Unknown Benefits

- Cinnamon Myrtle Medicinal Value

- Collards Nutrition Facts

- Common Purslane Benefits

- Corn Health Values

- Corn Salad Interesting Facts

- Cress Medicinal Values

- Cucumber Health Benefits

- Culantro Leaves

- Curry Leaf Tree Origin

- Collard Greens Nutrition Facts

- Dabberlocks Interesting Facts

- Dandelion Health Benefits

- Dill Health requirements

- Drumstick Nutritional Value

- Dulse Health Benefits

- Earthnut Pea Properties

- Eggplant Nutrition Guide

- Elephant Foot yam Health Benefits

- Elephant Garlic Uses

- Endive Medicinal Properties

- Ensete Health Benefits

- Epazote Properties

- Fat Hen Interesting Facts

- Fingerroot Uses

- French Sorrel Health Facts

- Garlic Nutrition Values

- Gim seaweed Uses

- Ginger Flower Properties

- Ginger Medicinal Values

- Golden Samphire Aspects

- Greater Plantain Medicinal Uses

- Green onions Health Facts

- Green peas Nutrition Values

- Hijiki Nutritional Aspects

- Holy Basil Leaves

- Horseradish Health Benefits

- Onions Nutrition Guide

- Sea Beet Aspects

- Sea Lettuce Health Benefits

- Yam Nutritional Value

- Yarrow Medicinal Uses

- Zucchini Health Guide

- Veggies by seasons

- Veggies did you know??

- Comparison of veggies!!!

- Veggies and it's origin

- Comical View of Veggiess

- Categories of veggies

- Top Veggiess 100 To 91

- Top Veggiess 90 To 81

- Top Veggiess 80 To 71

- Top Veggiess 70 To 61

- Top Veggiess 60 To 51

- Top Veggiess 50 To 41

- Top Veggiess 40 To 31
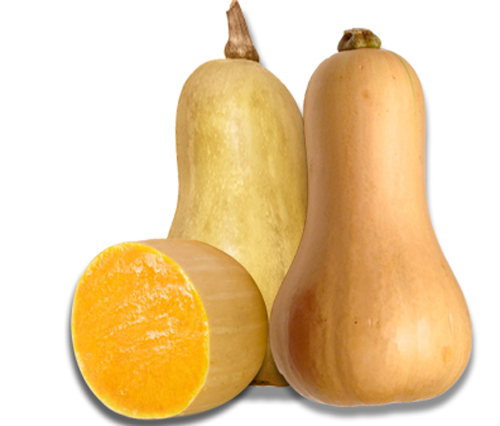

- Top Veggiess 30 To 21
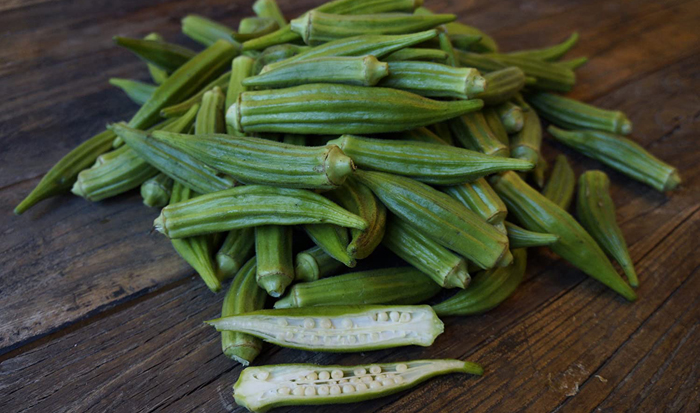

- Top Veggiess 20 To 11
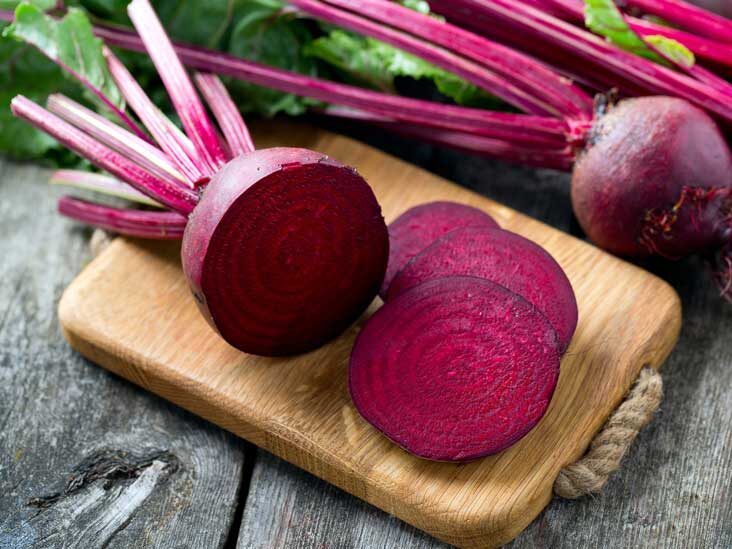

- Top Veggiess 10 To 01
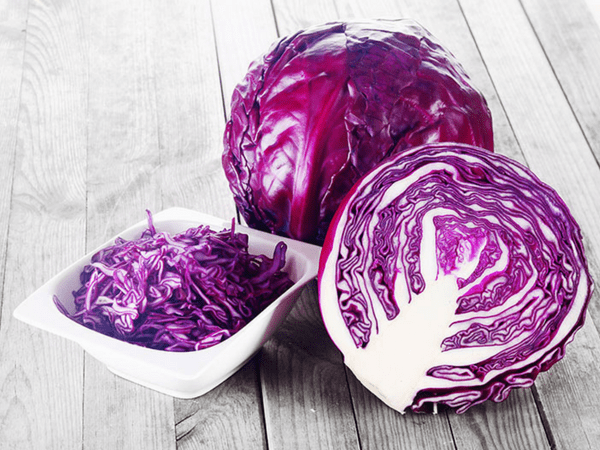

Veggie Picks
Top Veggiess 20 To 11 For Health Benefits
20. Tomato
Tomatoes are botanically a fruit, but it is considered as a vegetable all over the world. Tomato is red berry with a mixed combination of sweet, sour, tangy and bitter flavor. It is loaded with nutrients including Vitamin A, C and K , potassium, magnesium, iron, folate, zinc and phosphorus. It also has a fair amount of Vitamin B, choline and chromium. It benefits your skin, heart and hair health. Lycopene present in tomatoes prevents the growth of cancer cells and promotes your bone health. It helps to eliminate the harmful free radicals in our body.
Tomatoes can be added to your diet in plentiful ways including soup, sandwich, salads and curries.
- Tomatoes are a rich source of vitamins A and C and folic acid.
- Contain a wide array of beneficial nutrients and antioxidants, including alpha-lipoic acid, lycopene, choline, folic acid, beta-carotene and lutein.
- Tomatoes provides 2 grams of fiber.
- Tomatoes contain many vitamins and antioxidants.
- Prevent damage caused by the sun, pollution and smoke,smooth wrinkles.
- Improve overall skin texture.
- Tomatoes can help to keep you hydrated and your bowel movements regular.
- Minimizing constipation and adding bulk to the stool.
- Essential for pregnant women to protect against neural tube defects in infant.
- Tomatoes are good for your skin.
- Tomatoes help Repair Damage Caused by Smoking.
- Tomatoes are good for your hair.
The French used to refer to the tomato as the "apple of love."
Tomato juice is ideal for athletes as it quickly replenishes lost nutrients and sodium.
Tomatoes are high in nutrition value and there are no doubts about its credibility. Tomato contains anti oxidants and lycopene;a compound that is known for its anti cancer properties. This vegetable can evade the dangers of prostate cancer, stomach cancer and colorectal cancer. Lycopene is also very useful in treating skin burns caused by sun and removal of tan. They are much better and safer than over the counter medicines. Tomatoes are also a very rich source of calcium and vitamin K both known for good bone health; maintaining the body frame. Couramic acid and cholrogenic acid present in tomatoes helps to reduce the damage caused by carcinogenic substance that are by products of smoking. Eating tomatoes will not give you benefits of a non smoker but will definitely reduce the damage caused by smoking. Vitamin B and potassium present in tomato is the ingredient to good health as it helps in lowering cholesterol and keeps the blood pressure under control.
When all these parameters are under check,the heart functions smoothly without any problems that is life threatening. One stop ingredient for good hair, eyes and skin is tomato; as it rich in vitamin A tomato are proven to be a secret beauty hack. Vitamin A also prevents night blindness so eating tomato is a must for a healthy eye sight.
| Principle | Nutrient Value | Percentage Of RDA |
| Energy | 18 Kcal | 1% |
| Carbohydrates | 3.9 g | 3% |
| Protein | 0.9 g | 1.6% |
| Total Fat | 0.2 g | 0.7% |
| Cholesterol | 0 mg | 0% |
| Dietary Fiber | 1.2 g | 3% |
| Vitamins | ||
| Folates | 15 µg | 4% |
| Niacin | 0.594 mg | 4% |
| Pyridoxine | 0.080 mg | 6% |
| Thiamin | 0.037 mg | 3% |
| Vitamin A | 833 IU | 28% |
| Vitamin C | 13 mg | 21.5% |
| Vitamin E | 0.54 mg | 4% |
| Vitamin K | 7.9 µg | 6.5% |
| Electrolytes | ||
| Sodium | 5 mg | >1% |
| Potassium | 237 mg | 5% |
| Minerals | ||
| Calcium | 10 mg | 1% |
| Iron | 0.3 mg | 4% |
| Magnesium | 11 mg | 3% |
| Manganese | 0.15 mg | 6.5% |
| Phosphorus | 24 mg | 3% |
| Zinc | 0.17 mg | 1.5% |
| Phyto-nutrients | ||
| Carotene-ß | 449 µg | — |
| Carotene-a | 101 µg | — |
| Lutein-zeaxanthin | 123 µg | — |
| Lycopene | 2573 µg | — |
Tomatoes are widely consumed in every part of the world. Tomatoes can be added to salads, the famous tomato and feta cheese salad is a delight on plate. Tomatoes can be added in chunks in fresh green salads and dressed with olive oil. Pureed tomatoes can be used as a sauce for making pasta or making a base for the pizza. Cherry tomatoes or sun dried tomatoes go really well in hand tossed pizza or baked ravioli in red sauce.
Tomatoes are used to make the spicy salsa dip that is accompaniment to breads, croutons and chips. Tomato slices added to sandwiches and subs make it a fresh and light and favourite on the move snack. Tomato soup is a classic that one can never go wrong with it. Tomato ketchup a food that is processed and preserved is renowned worldwide and can be eaten with almost everything. It is a lifeline for every fast food lover.

19. Beetroot
Beetroot is a bulbous, root vegetable also known as beet, red beet and garden beet. They have a unique aroma and taste that we either love or hate completely. Beetroots are the abundant source of folate, manganese, potassium, iron and Vitamin C. Beetroots also have high sugar and fiber content. They will help to maintain blood pressure, reduce heart disease and promote the digestive system. Beetroots improve stamina and athletic performance.
Beetroots can be either eaten raw, cooked or consumed as juice.
- Rich in Valuable Nutrients and Fiber.
- Detoxification Support.
- Nutrients like protein, phosphorus, zinc, fiber, vitamin B6, magnesium, potassium, copper, and manganese.
- Beet greens also supply significant amounts of vitamin A, vitamin C, calcium, and iron.
- Lower Your Blood Pressure.
- Boost Your Stamina.
- Fight Inflammation.
- Anti-Cancer Properties.
- Boosting bone strength.
- Fight Alzheimer's disease.
- Strengthen your immune system by stimulating the production of antibodies and white blood cells.
- Beets are high in many vitamins and minerals.
- Wonderful tonic for the liver, works as a Purifier For the Blood.
- Beets help your mental health.
- Beets are used as a stomach acid tester.
- Beets are a high source of energy.
Beetroot is very popular and has been used for the production of sugar over the years.
If you boil beets in water and then massage the cooled down water into your scalp each night, it is said to be an effective cure for dandruff.
It is a fact well known that beets are highly nutritious and health benefiting. They are low in calorie and contain zero cholesterol and a very minimal amount of fat. This food gets its nutrition benefit from fibre, vitamins, manganese minerals and also folate. Apart from all these nutrients beets also is a house of potassium, vitamin C and antioxidants. A cup of beets raw consist of 58 calories and 13 grams of carbohydrates. The health benefits provided by consuming beets is many, some of them are mentioned as follows. Betaine a bio active agent that is present in beets protects the liver and aids in weight loss as it breaks down the food that is consumed. There is always a good cholesterol and bad cholesterol, beets consist of oxidants such as carotenoids and flavnoids that prevent the body from bad cholesterol and protect the arteries from clogging. Consuming beets while a woman is conceiving a baby is essential as beets consist of folic acid that is essential to form a back bone of the baby thus preventing spinal bifida. Potassium is highly responsible for the smooth contraction and expansion of the heart, apart from spinach beets form a very good source for potassium thus ensuring a good life with a healthy heart. Beet is also known as Nature's Viagra since it is highly aphrodisiac in nature and is responsible for generating sex hormones in humans. Beet also has a cultural belief attached to it, it is believed that a man and a woman who eat from the same beet will fall in love.
| Principle | Nutrient value | Percentage of RDA |
|---|---|---|
| Energy | 43 cal | 2% |
| Carbohydrates | 9.56 g | 7% |
| Protein | 1.61 g | 1% |
| Total Fat | 0.17 g | 0.5% |
| Cholesterol | 0 mg | 0% |
| Dietary Fiber | 2.80 g | 7% |
| Vitamins | ||
| Folates | 109 µg | 27% |
| Niacin | 0.334 mg | 2% |
| Pantothenic acid | 0.155 mg | 3% |
| Pyridoxine | 0.067 mg | 5% |
| Riboflavin | 0.057 mg | 4% |
| Thiamin | 0.031 mg | 2.5% |
| Vitamin A | 33 IU | 1% |
| Vitamin C | 4.9 mg | 8% |
| Vitamin E | 0.04 mg | 0.5% |
| Vitamin K | 0.2 µg | 0% |
| Electrolytes | ||
| Sodium | 78 mg | 5% |
| Potassium | 325 mg | 7% |
| Minerals | ||
| Calcium | 16 mg | 1.5% |
| Copper | 0.075 mg | 8% |
| Iron | 0.80 mg | 10% |
| Magnesium | 23 mg | 6% |
| Manganese | 0.329 mg | 14% |
| Zinc | 0.35 mg | 3% |
| Phyto-nutrients | ||
| Carotene-ß | 20 µg | — |
| Betaine | 128.7 mg | — |
| Lutein-zeaxanthin | 0 µg | — |
Beets have a distinctive red colour that is bright and tempting. It is often used in salads to add more colour to the food. Beetroot is also used as a natural food colouring agent in many dishes. This tap root can be consumed in many ways from salads to soups this food goes well in every cuisine. Pickled beets are traditionally made in states of Southern America. In India beet is prepared in different ways depending on the region. South of India likes its beets as a pooriyal or also added in making beetroot rice. Northern part of India adds boiled beet to their curries just like other vegetables such as tomato, potato etc . Beetroot juice is a popular health drink that is often recommended to weight watchers and people looking out for healthier lifestyle options.
All in all this food is harmless with no side effects and is a must have in everyone's diet.
18. Cauliflower
Cauliflower has a large pale green that surrounds the white flower head. Cauliflower has a pleasant and unique taste that can be eaten in many ways, both raw and cooked. Cauliflower is an excellent source of VItamin C, Vitamin K, folate, potassium, manganese, magnesium and phosphorus. It is a good source of antioxidants that protects you from lung, breast and prostate cancer. Cauliflower also helps to prevent the risk of heart disease, diabetes and promotes weight loss.
It makes fantastic additions in many dishes like soups, salads and casseroles.
- Rich in Vitamins and Minerals - Cauliflower has 77% of your daily allowance of Vitamin C, which has been shown to prevent colds, boost immunity and improve skin health. You can get 20% of your requirements of Vitamin K, which aids in blood clotting, bone health and keeps track of calcium levels. And also Cauliflower has 11% of B6 and 14% of folate.
- Low in Carbohydrates and Gluten-Free - Cauliflower can make gluten-free diets easier because it can serve as a replacement for pasta and can even be the basis for gluten-free pizza crusts.
- Rich in Fiber - Fiber is not actually digested but goes right through the intestines and the bowels keep them in condition and help prevent constipation. One serving of cauliflower has 3 grams of fiber, which comprises 10% of the body's fiber needs.
- Contains Antioxidants - Antioxidants include Vitamin C, beta carotene, quercetin, rutin, and cinnamic acid. In addition, cauliflower is a cruciferous vegetable that has specific antioxidants, including glucosinolates and isothiocyanates, which can slow prevent malignant cells from reproducing.
- Can Help you Lose Weight - Cauliflower is low in calories at 25 per cup, but its low-calorie count belies the fact that it is one of the most nutritious and high fiber vegetables you can find. You can get a lot of nutrition from cauliflower, with its rich offering of antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals.
- Cancer Prevention - The fiber content of cauliflower can also help prevent the development of colon cancer. As it moves through the gut, cauliflower promotes the health of the digestive system and encourages the growth of healthy gut bacteria.
- Improve Cardiovascular Health - Eating cauliflower is excellent for your heart health. This cruciferous vegetable contains glucoraphanin and vitamin K, critical minerals and vitamins responsible for maintaining circulation and health of blood vessels.
- Keep Skin and Hair Healthy - As a result of eating cauliflower regularly, you'll find that your skin feels soft and supple, well-hydrated, and has a youthful look. The silicon and sulfur found in cauliflower increase hair growth while strengthening the hair and nourishing the follicles. Keep your hair healthy and eat more cauliflower in your diet.
- PROTEINS: 1.92
- IRON : 0.43
- CARBOHYDRATES : 4.97
- FATS : 0.28
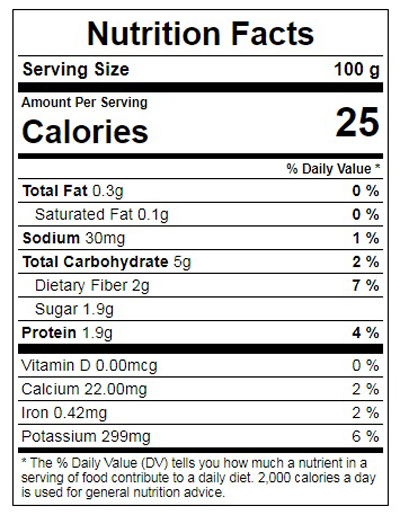
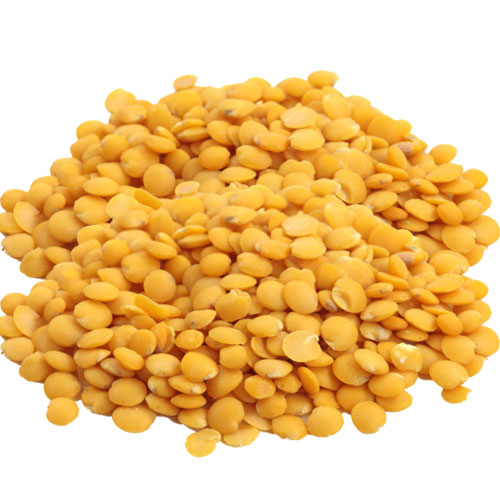
17. Lentils
Lentils are edible seeds of the legumes that resemble a tiny bean having a wide range of color from red, brown, black and green. Each one has a unique size, flavor and nutrient content. Lentils are a good source of protein,folate, iron, magnesium, zinc and potassium. It also contains thiamine, Vitamin B6, phosphorus, manganese and copper. Lentils have the potential to reduce the risk of heart disease and cancer. It also helps to maintain body weight and blood sugar level.
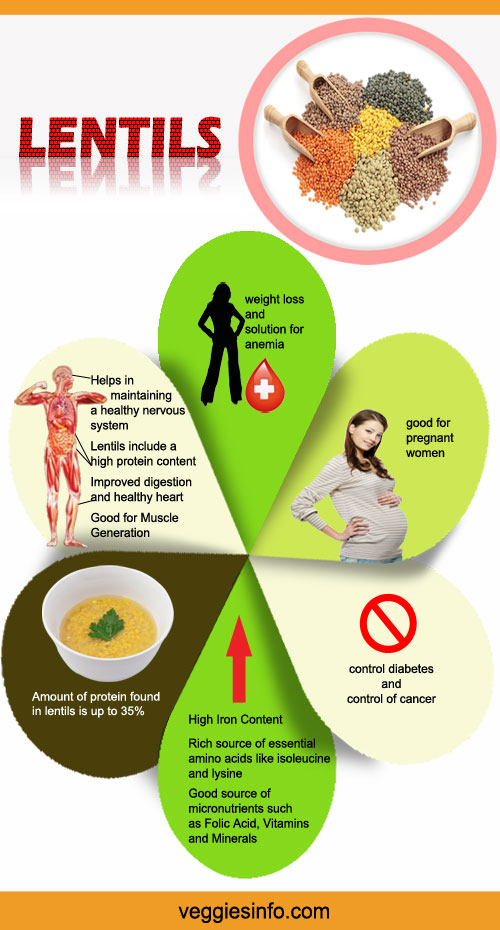
- Rich source of essential amino acids like isoleucine and lysine.
- Good source of micronutrients such as vitamins and minerals.
- Amount of protein found in lentils is up to 35%.
- Good for Muscle Generation.
- Good Source of Folic Acid.
- High Iron Content.
- It includes a High Protein Content.
- Improved digestion and healthy heart.
- Control diabetes and control of cancer.
- Weight loss and solution for anemia.
- Good for pregnant women.
- Helps in maintaining a healthy nervous system.
Even though lentils is considered to be a less important food as it is cheaply priced and easily available it is very nutritious and health benefiting. A cup of lentils of 190g consist of 230 calories which is moderately low. It consist of cholesterol lowering compounds that help in keeping the cholesterol levels under check. If you love your heart and want to know what to do in order to take care of it? Switch over to lentils and see the difference. This is not because of the fibre content available in lentils but also the magnesium and folate content that is found abundance in lentils. Folate helps in reducing a compound called homocysteine that is responsible to in damaging arteries and thus keeping it under control will lead to a good heart health and a healthy future. Magnesium content in lentil helps in easy flow of blood and oxygen through the veins without clogging the arteries.
It has both soluble and insoluble fibre, soluble fibre helps in controlling and stabilizing blood sugar levels in the body; also regulates the excretion of insulin by the pancreas. Iron rich foods are a must for growing children and aging adults as it is a good for generating haemoglobin that helps transporting oxygen from the lungs to various other parts of the body such as brain, heart and lungs.
| Principle | Nutrient | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamins | Value | of RDA |
| Choline | 96.4 mg | |
| Folate | 479.00 mcg | |
| Folic acid | 0.00 mcg | |
| Niacin | 2.605 mg | 13 % |
| Pantothenic acid | 2.140 mg | 21 % |
| Riboflavin | 0.211 mg | 12 % |
| Thiamin | 0.873 mg | 58 % |
| Vitamin A | 39.00 IU | 1 % |
| Vitamin A, RAE | 2.00 mcg | |
| Carotene, alpha | 0.00 mcg | |
| Carotene, beta | 23.00 mcg | |
| Cryptoxanthin, beta | 0.00 mcg | |
| Lutein + zeaxanthin | 0.00 mcg | |
| Lycopene | 0.00 mcg | |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.00 mcg | 0 % |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.540 mg | 27 % |
| Vitamin C | 4.5 mg | 8 % |
| Vitamin D | 0.00 IU | 0 % |
| Vitamin E | 0.49 mg | 2 % |
| Tocopherol, alpha | 0.49 mg | |
| Tocopherol, beta | 0.00 mg | |
| Tocopherol, delta | 0.00 mg | |
| Tocopherol, gamma | 4.23 mg | |
| Tocotrienol, alpha | 0.00 mg | |
| Tocotrienol, beta | 0.00 mg | |
| Tocotrienol, delta | 0.00 mg | |
| Tocotrienol, gamma | 0.00 mg | |
| Vitamin K | 5.0 mcg | 6 % |
| Minerals | ||
| Calcium, Ca | 35.00 mg | 4 % |
| Copper, Cu | 0.754 mg | 38 % |
| Iron, Fe | 6.51 mg | 36 % |
| Magnesium, Mg | 47.00 mg | 12 % |
| Manganese, Mn | 1.393 mg | 70 % |
| Phosphorus, P | 281.00 mg | 28 % |
| Potassium, K | 677.00 mg | 14 % |
| Selenium, Se | 0.1 mcg | 0 % |
| Sodium, Na | 6.00 mg | 0 % |
| Zinc, Zn | 3.27 mg | 22 % |
| Proteins and Aminoacids | ||
| Protein | 24.63 g | 49 % |
| Alanine | 1.029 g | |
| Arginine | 1.903 g | |
| Aspartic acid | 2.725 g | |
| Cystine | 0.322 g | |
| Glutamic acid | 3.819 g | |
| Glycine | 1.002 g | |
| Histidine | 0.693 g | |
| Isoleucine | 1.065 g | 76 % |
| Leucine | 1.786 g | 65 % |
| Lysine | 1.720 g | 82 % |
| Methionine | 0.210 g | 20 % |
| Phenylalanine | 1.215 g | 69 % |
| Proline | 1.029 g | |
| Serine | 1.136 g | |
| Threonine | 0.882 g | 84 % |
| Tryptophan | 0.221 g | 79 % |
| Tyrosine | 0.658 g | 38 % |
| Valine | 1.223 g | 67 % |
| Carbohydrates | ||
| Carbohydrate | 63.35 g | 21 % |
| Fiber | 10.7 g | 43 % |
| Sugars | 2.03 g | |
| Fructose | 0.27 g | |
| Galactose | 0.00 g | |
| Glucose (dextrose) | 0.00 g | |
| Lactose | 0.00 g | |
| Maltose | 0.30 g | |
| Starch | 49.90 g | |
| Sucrose | 1.47 g | |
| Fats and Fatty Acids | ||
| Fat | 1.06 g | 2 % |
| Saturated fatty acids | 0.154 g | 1 % |
| Butanoic acid | 0.000 g | |
| Decanoic acid | 0.000 g | |
| Dodecanoic acid | 0.000 g | |
| Hexadecanoic acid | 0.136 g | |
| Hexanoic acid | 0.000 g | |
| Octadecanoic acid | 0.015 g | |
| Octanoic acid | 0.000 g | |
| Tetradecanoic acid | 0.003 g | |
| Monounsaturated fatty acids | 0.193 g | |
| Docosenoic acid | 0.000 g | |
| Eicosenoic acid | 0.006 g | |
| Hexadecenoic acid | 0.003 g | |
| Octadecenoic acid | 0.184 g | |
| Polyunsaturated fatty acids | 0.526 g | |
| Docosahexaenoic n-3 acid | 0.000 g | |
| Docosapentaenoic n-3 acid | 0.000 g | |
| Eicosapentaenoic n-3 acid | 0.000 g | |
| Eicosatetraenoic acid | 0.000 g | |
| Octadecadienoic acid | 0.414 g | |
| Octadecatetraenoic acid | 0.000 g | |
| Octadecatrienoic acid | 0.112 g | |
| Fatty acids, total trans | 0.000 g | |
| Sterols | ||
| Cholesterol | 0.00 mg | 0 % |
| Others | ||
| Alcohol, ethyl | 0.0 g | |
| Ash | 2.71 g | |
| Caffeine | 0.00 mg | |
| Theobromine | 0.00 mg | |
| Water | 8.26 g |
Lentils are legumes that are not just healthy but tasty as well. Cooked lentil can be added to salads of tomatoes and chopped onions and finished it with a dash of lemon juice making it a healthy cold salad. Indians make dal chawal a dish made in every house hold; cooked lentil in turmeric and other condiments often accompaniment to steamed rice. The Moroccans enjoy the nutrition of lentils in thick lentil soups.
16. Turnips
Turnip is a root vegetable with edible roots and leaves. It has white, purple or greenish exterior with white spicy and crunchy bulb. The taste of turnip tends to be sweet when cooked. Turnip is packed with Vitamin C, folate, phosphorus, calcium, fiber and protein. Turnip leaves are particularly rich in Vitamin K and have other essential nutrients. Turnip contains bioactive plant compounds that have anti-cancer properties including lung, colon and rectal cancers. It maintains blood sugar level and weight. Turnip may promote bone and have anticancer, anti-bacterial and anti-inflammatory effects.
Turnips can be eaten raw or cooked and make a great addition to salad.
- Turnips provide an excellent source of vitamin C.
- Contains fiber, folic acid, manganese, pantothenic acid, and copper.
- Very good source of thiamine, potassium, niacin, and magnesium.
- Contains vitamin B6 and E, folic acid, and riboflavin.
- It Promotes Good Hair and Skin and also purifies blood.
- Aids in smooth functioning of cardiovascular muscles.
Turnips were originally fed to cattle! It is a popular eating vegetable for humans now since the nutritional value of turnips has been recognized!
Turnips provides a rich source of calcium and potassium.
Marked as one of the rare vegetable that is highly nutritious and on the other hand is filling to stomach as it satisfies hunger and keeps you full for a longer period. One cup of raw turnips of about 122 grams contains 34 calories which is quite low for diet enthusiast. Being a good source of dietary fibre turnips helps is healing digestive disorders and has diuretic quality that leads to smooth bowel movements. It is a rich source of vitamin C; each turnip consists of 53% of vitamin C recommended for daily intake. This vitamin promotes good hair and skin and also purifies blood and aids in smooth functioning of cardiovascular muscles. Turnips like other plants of its genre, is a cruciferous plant that is rich in anti cancer properties. Since 1980's it has been over the time proven continuously by all medical experiments that turnips help in treating and preventing cancer. It prevents the body from various types of cancer such as breast cancer, colon cancer and prostate cancer. The phosphorus content present in turnips helps in instigating compounds that manage blood pressure levels. The anti oxidant properties present in turnips makes it an ailment for asthma and lung related problems. Apart from these vital nutrients turnip takes on board many other nutrients as well as minerals.
| Principle | Nutrient Value | Percentage of RDA |
| Energy | 28 Kcal | 1.5% |
| Carbohydrates | 6.43 g | 5% |
| Protein | 0.90 g | 1.5% |
| Total Fat | 0.10 g | <1% |
| Cholesterol | 0 mg | 0% |
| Dietary Fiber | 1.8 g | 5% |
| Vitamins | ||
| Folates | 15 µg | 4% |
| Niacin | 0.400 mg | 2.5% |
| Pantothenic acid | 0.200 mg | 4% |
| Pyridoxine | 0.090 mg | 7% |
| Riboflavin | 0.030 mg | 2.5% |
| Thiamin | 0.040 mg | 4% |
| Vitamin A | 0 IU | 0% |
| Vitamin C | 21 mg | 35% |
| Vitamin E | 0.03 mg | <1% |
| Vitamin K | 0.1 µg | <1% |
| Electrolytes | ||
| Sodium | 39 mg | 2.5% |
| Potassium | 233 mg | 5% |
| Minerals | ||
| Calcium | 30 mg | 3% |
| Copper | 0.085 mg | 9% |
| Iron | 0.30 mg | 4% |
| Magnesium | 11 mg | 2.5% |
| Manganese | 0.134 mg | 6% |
| Zinc | 0.27 mg | 2% |
| Phyto-nutrients | ||
| Carotene-ß | 0 µg | — |
| Carotene-a | 0 µg | — |
| Lutein-zeaxanthin | 0 µg | — |
Turnips are rich in nutrition and one need to incorporate it in their diet for a healthy body and fit body. Young turnips do not taste as strong and spicy as the matured ones; they taste similar to that of potatoes. Since they taste like potatoes they can be prepared like potatoes and also be used in dishes instead of potatoes. Boiled turnips can be used as a replacement of mash potatoes, mash turnips similar to that of potatoes and serve alongside sizzlers or grilled vegetables.
Turnip stews and soups can be enjoyed during cold winters. Turnips can be used as an ornamental vegetable in salads or even as carved vegetable as a garnish. Turnips can bring an interesting twist to the regular coleslaw and make it a nice spread for a sandwich.

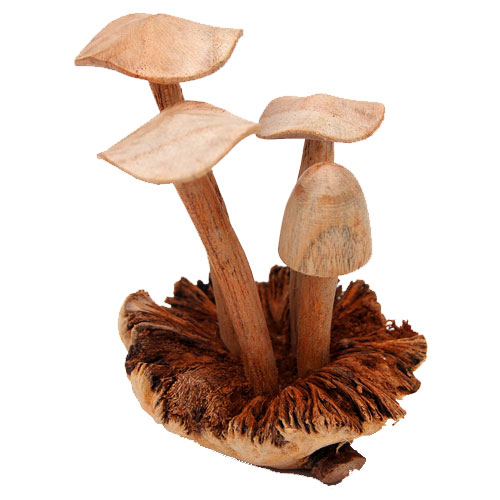
15. Mushroom
Mushrooms are edible fungus in umbrella shape. It has a spongy texture with mild flavors that go well with many dishes. They are abundant sources of Vitamin D and selenium. It also has phosphorus, folate, protein and fiber. The antioxidants present in mushrooms eliminate the free radicals that lead to serious health conditions. Mushrooms prevent you from premature aging and boost our immune system. It also helps to reduce the risk of cancer and heart diseases.
Mushrooms can be available in fresh, frozen, canned, dried and powder form. It is easy to incorporate mushrooms with any dish.
- Contain almost no fat and sodium.
- Provide several minerals such as selenium, potassium, copper, iron, and phosphorus.
- Helping to reduce blood pressure.
- Maintain healthy red blood cells.
- Promotes good vision and healthy skin.
- Help reduce the risk of cancer.
- Good Source Of Zinc
- Boost your immune system.
Popular types of mushrooms include Portobello, Shiitake, Field, Button, Chestnut, Maitake and Morel mushrooms.
| Principle | Nutrient Value | Percentage of RDA |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamins | ||
| Folate | 2.00 mcg | |
| Folic acid | 0.00 mcg | |
| Niacin | 4.085 mg | 20 % |
| Pantothenic acid | 1.075 mg | 11 % |
| Riboflavin | 0.215 mg | 13 % |
| Thiamin | 0.015 mg | 1 % |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.044 mg | 2 % |
| Vitamin D | 212.00 IU | 53 % |
| Minerals | ||
| Calcium, Ca | 15.00 mg | 2 % |
| Copper, Cu | 0.353 mg | 18 % |
| Iron, Fe | 3.47 mg | 19 % |
| Magnesium, Mg | 13.00 mg | 3 % |
| Manganese, Mn | 0.286 mg | 14 % |
| Phosphorus, P | 57.00 mg | 6 % |
| Potassium, K | 506.00 mg | 11 % |
| Selenium, Se | 2.2 mcg | 3 % |
| Sodium, Na | 9.00 mg | 0 % |
| Zinc, Zn | 0.71 mg | 5 % |
| Proteins and Aminoacids | ||
| Protein | 1.49 g | 3 % |
| Carbohydrates | ||
| Carbohydrate | 6.86 g | 2 % |
| Fiber | 3.8 g | 15 % |
| Sugars | 1.16 g | |
| Fructose | 0.00 g | |
| Galactose | 0.00 g | |
| Glucose (dextrose) | 1.16 g | |
| Lactose | 0.00 g | |
| Maltose | 0.00 g | |
| Sucrose | 0.00 g | |
| Fat and fatty Acids | ||
| Fat | 0.53 g | 1 % |
| Fatty acids, total trans | 0.000 g | |
| Sterols | ||
| Beta-sitosterol | 0.00 mg | |
| Campesterol | 1.00 mg | |
| Stigmasterol | 0.00 mg | |
| Others | ||
| Ash | 1.26 g | |
| Vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) | 5.3 mcg | |
| Vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) | 0.0 mcg | |
| Water | 89.85 g |
Store mushrooms in a paper bag as this will keep them fresher for longer.
Mushrooms are fungi that are rich in nutritional value. This is rich in vitamin D as they are naturally exposed to sunlight and it helps in enhancing the bones strength. Deficiency of this vitamin leads to rickets and osteoporosis and also reduces the risk of heart diseases and type 2 diabetes. Mushrooms are rich in cancer fighting properties as the inhibit proteins, lectins and other compounds that curb the growth of cancer. Consumption of mushrooms have proven to reduce the risk of breast cancer.
Mushrooms are rich in nutrients such as vitamins and minerals that are must add on to everyman's staple diet. It consist riboflavin, niacin, biotin, folate, vitamin D , phosphorus , potassium and manganese. Niacin aids in healthy skin and calms down the nerves of the body, riboflavin helps in generation of blood cells and pantothenic acid helps in hormone production.Mushroom allergies are a common sight and one must consult doctors to check if they are mushroom tolerant.
The culinary use of mushroom is very highly owing to its popularity worldwide. Mushrooms are added to cold meat salads, cream of mushroom soup is a rich delicacy enjoyed during winters, mushroom risotto is a Italian favourite that makes any one fall in love with it. Mushrooms are added to pasta, and also as a favourite pizza topping by many. Mushroom also acts as a meat substitute in many of the meat driven dishes.
Their salty flavour and juicy texture makes them a star of every dish they are added to

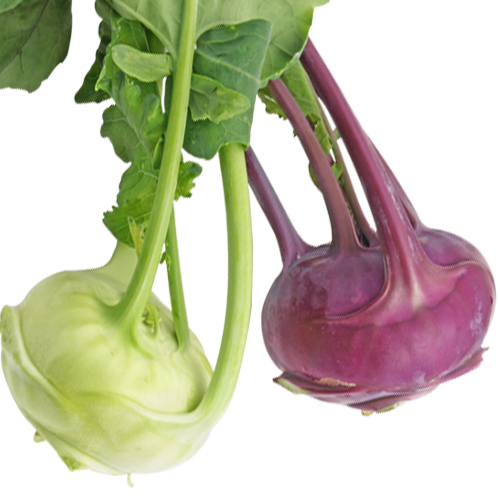
14. Kohlrabi
Kohlrabi is a cruciferous vegetable and is a member of the cabbage family. It has a round bulb with a long leafy stem. The crunchy and spicy bulb tastes more like radish and turnip. It is particularly rich in Vitamin C and a good source of Vitamin B6, potassium, magnesium, manganese and folate. The high antioxidant content in kohlrabi has the potential to reduce the risk of diabetes, metabolic disease and premature death. Kohlrabi benefits your heart health, immune system and digestive system.
Kohlrabi leaves and bulb can be added into salads and are boiled, roasted and fried to make recipes.
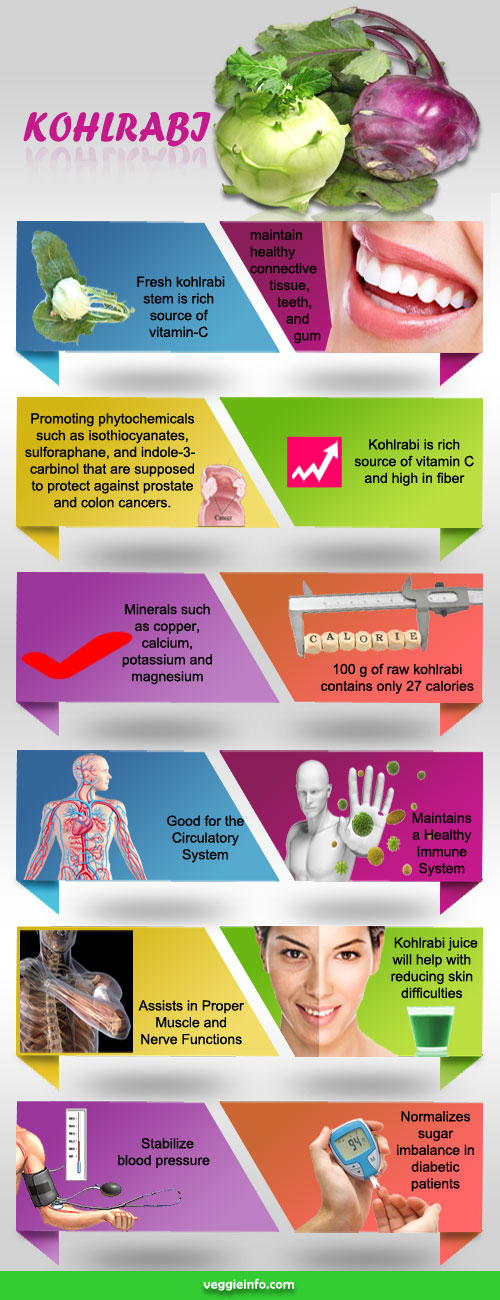
- Fresh kohlrabi stem is rich source of vitamin-C.
- Promoting phytochemicals such as isothiocyanates, sulforaphane, and indole-3-carbinol that are supposed to protect against prostate and colon cancers.
- Kohlrabi is rich source of vitamin C and high in fiber.
- Minerals such as copper, calcium, potassium and magnesium.
- 100 g of raw kohlrabi contains only 27 calories.
- Maintain healthy connective tissue, teeth, and gum.
- Good for the Circulatory System.
- Maintains a Healthy Immune System.
- Assists in Proper Muscle and Nerve Functions.
- Kohlrabi juice will help with Reducing Skin Difficulties.
- Stabilize blood pressure.
- Normalizes sugar imbalance in diabetic patients.
Kohlrabi was Being Grown in Germany,England,Italy and Spain by the Early 1600's but did not Arrive to the US until the 1800's.
Marked as one of the rare vegetable that is highly nutritious and on the other hand is filling to stomach as it satisfies hunger and keeps you full for a longer period. One cup of raw kohlrabi contains 36 calories which is quite low for diet enthusiast. A cup of kohlrabi can be a definite replacement for a packet of fried snack to munch on. Being a good source of dietary fibre kohlrabi helps is healing digestive disorders and has diuretic quality that leads to smooth bowel movements. Kohlrabi is a rich source of vitamin C; this vitamin promotes good hair and skin and also purifies blood and aids in smooth functioning of cardiovascular muscles. Kohlrabi like other plants of its genre is a cruciferous plant that is rich in anti cancer properties. It prevents the body from various types of cancer such as breast cancer, colon cancer and prostate cancer. The phosphorus content present in kohlrabi helps in instigating compounds that manage blood pressure levels. The anti oxidant properties present in kale makes it an ailment for asthma and lung related problems. Apart from these vital nutrients kohlrabi takes on board many other nutrients such as minerals.
| Principle | Nutrient Value | Percentage of RDA |
|---|---|---|
| Energy | 27 Kcal | 1.5% |
| Carbohydrates | 6.20 g | 5% |
| Protein | 1.70 g | 3% |
| Total Fat | 0.10 g | <1% |
| Cholesterol | 0 mg | 0% |
| Dietary Fiber | 3.6 g | 10% |
| Vitamins | ||
| Folates | 16 µg | 4% |
| Niacin | 0.400 mg | 2.5% |
| Pantothenic acid | 0.165 mg | 3% |
| Pyridoxine | 0.150 mg | 11.5% |
| Riboflavin | 0.020 mg | 1.5% |
| Thiamin | 0.050 mg | 4% |
| Vitamin A | 36 IU | 1% |
| Vitamin C | 62 mg | 102% |
| Vitamin K | 0.1 µg | <1% |
| Electrolytes | ||
| Sodium | 20 mg | 1% |
| Potassium | 350 mg | 7% |
| Minerals | ||
| Calcium | 24 mg | 2.5% |
| Copper | 0.129 mg | 14% |
| Iron | 0.40 mg | 5% |
| Magnesium | 19 mg | 5% |
| Manganese | 0.139 mg | 6% |
| Phosphorus | 46 mg | 6.5% |
| Selenium | 0.7 µg | 1% |
| Zinc | 0.03 mg | <1% |
| Phyto-nutrients | ||
| Carotene-ß | 22 µg | — |
| Crypto-xanthin-ß | 0 µg | — |
| Lutein-zeaxanthin | 0 µg | — |
Kohlrabi might come across as an alien vegetable but it should not be overlooked as just another vegetable. Kohlrabi can be prepared in a multiple simple ways everything using the culinary skill and ingredient of every home cook. Eating kohlrabi raw is the healthiest way to eat it; bad them to a salad of radish or simply toss it in olive oil and garlic with a drizzle of lime juice and sea salt making it a nice healthy snack. Kohlrabi soup can be made by fusing multiple vegetables together and making a cream soup of it similar to that of cream of onion soup or cream of peas soup. Barbeque this veggie delight for some char grilled flavoured veggies and accompaniments of rice. Bake or steam kohlrabi in oven and caramelize it with flavours of condiments such as peppers or rock salt.
This vegetable might be less popular in the vegetable kingdom but its bountiful of nutrition and flavour and one should not miss on such a delight.
13. Collard greens
Collard is the loose-leafed vegetable from the cabbage family. They have bitter green leaves with hard stems that need to be removed before eating. Collard greens are an excellent source of Vitamins C, A and K. It also contains a fair amount of iron, Vitamin B6 and magnesium. Collard greens play a crucial role in blood clotting and reduce the risk of a number of health conditions including diabetes, heart diseases and obesity. It helps to benefit our skin and hair health. Collard has the anticancer and anti-inflammatory properties to benefit our body.
It makes an excellent side dish and can be eaten in salad, sandwich and soups.
- Collard greens are an extremely rich source of vitamin K and also contain folate, thiamin, niacin, pantothenic acid, choline, phosphorus and potassium.
- One cup of boiled collard greens contains 63 calories, 5 grams of protein, 1 gram of fat, 11 grams of carbohydrates (including 8 grams of fiber and 1 gram of sugar), over 250% of your daily needs for vitamin A, over 50% of your daily needs for vitamin C, 26% of calcium needs, 12% of iron and 10% of both vitamin B-6 and magnesium.
| Nutrients | Nutrition Value | % DV of RDA |
|---|---|---|
| Energy | 32 Kcal | 1.50% |
| Carbohydrates | 5.42 g | 4% |
| Protein | 3.02 g | 6% |
| Total Fat | 0.61 g | 2% |
| Cholesterol | 0 mg | 0% |
| Dietary Fiber | 4 g | 10% |
| Vitamins | ||
| Folates | 129 µg | 32% |
| Niacin | 0.742 mg | 5% |
| Pantothenic acid | 0.267 mg | 5% |
| Pyridoxine | 0.165 mg | 13% |
| Riboflavin | 0.130 mg | 10% |
| Thiamin | 0.054 mg | 4.50% |
| Vitamin A | 5019 IU | 170% |
| Vitamin C | 35.3 mg | 59% |
| Vitamin E | 2.26 mg | 15% |
| Vitamin K | 437.1 µg | 37% |
| Electrolytes | ||
| Sodium | 17 mg | 1% |
| Potassium | 213 mg | 4.50% |
| Minerals | ||
| Calcium | 232 mg | 23% |
| Copper | 0.039 mg | 4.50% |
| Iron | 0.47 mg | 6% |
| Magnesium | 27 mg | 7% |
| Manganese | 0.658 mg | 30% |
| Selenium | 1.3 µg | 2% |
| Zinc | 0.21 mg | 2% |
| Phyto-nutrients | ||
| Carotene-ß | 2991 µg | — |
| Crypto-xanthin-ß | 28 µg | — |
| Lutein-zeaxanthin | 4323 µg | — |
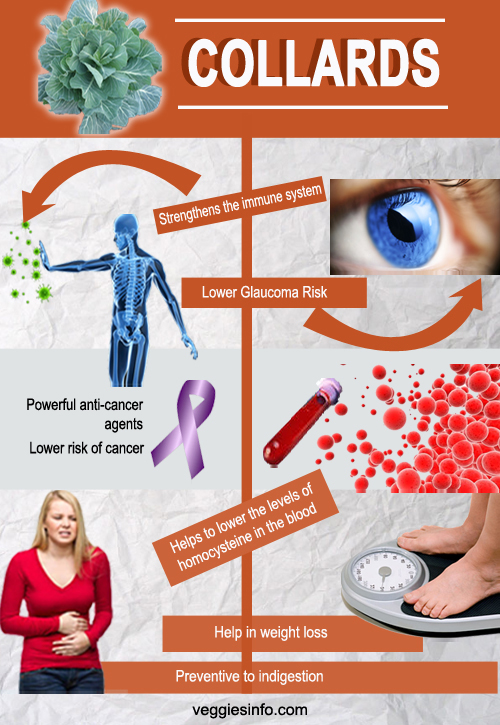
- Strengthens the immune system.
- Powerful anti-cancer agents.
- Lower risk of cancer.
- Helps to lower the levels of homocysteine in the blood.
- They are low in calories, they also Help in Weight Loss.
- Lower Glaucoma Risk.
- It as a preventive to indigestion.
Collards are a cruciferous plant known for its high nutrition level. It is a delight to every dieter because of its low calorific value and less fat content. A cup of boiled collards (100g) consist of only 32 calories. Owing to its cruciferous quality it comes across as a no surprise that collard aid in cancer prevention; the anti inflammatory property and high oxidation levels boost the body's immune system for it to fight against cancer such as breast cancer, prostate cancer, and colon cancer . Collards are a rich source of vitamin K, Vitamin B, Vitamin B1 and folate that forms a compound that regulates the blood sugar level , blood pressure level and also prevents clogging of arteries that in future prevents the body from facing cardiovascular diseases.
The fibre rich collard supports the smooth functioning of the digestive system thereby preventing the body to be prone to any digestive disorders. This leafy vegetable is highly recommended by dieticians to people prone with Type 2 diabetes; this regulates the sugar levels in the blood and is also used to prevent diseases like rheumatoid, arthritis, obesity and other inflammations caused in the body.
It is rare to see that a vegetable has more nutrition value to it when cooked compared to when its raw form; collards are such vegetables. The best way to consume collards in its healthiest way possible is by steaming it and sprinkling some fresh lemon juice before cooking it; this in turn activates all the nutrients of the food. Add them to fresh salads or cook them with black eyed peas collards go well with sushi as well.
Collard greens are oxalate rich food and it is a strict no – no to any person diagnosed with problems in their kidney; consumption of oxalate rich food will in turn only aggravate the situation.
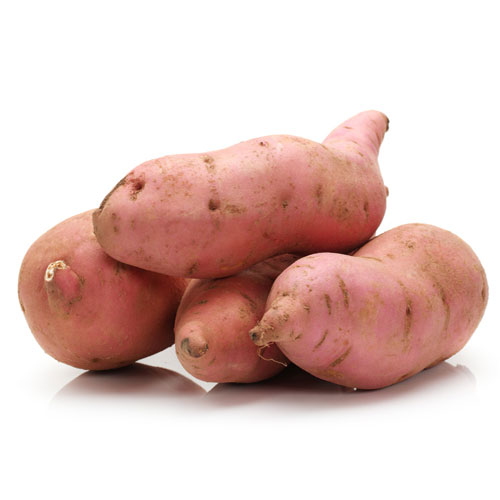
12. Sweet potato
Sweet potato is a root vegetable with sweet and delicious filling. Sweet potatoes are available in a wide range of colors including white, red, pink, yellow, orange and purple. Sweet potato is a starchy vegetable with high fiber content that reduces the risk of diabetes and improves gut health. It is a natural and good source of beta-carotene, Vitamin C and potassium. It also contains manganese, Vitamins B6, B5 and E. Vitamin C present in sweet potatoes improves your skin health and reduces the common cold. Sweet potatoes reduce the risk of cancer and oxidative damage.
Sweet potatoes can be baked, fried, steamed and boiled to add in your diet.
Sweet potato grows throughout the year and considered as a perennial plant. This dicotyledonous tuberous plant has large, starchy, sweet-tasting tuberous roots. This plant is a native of tropical regions in the Americas. This herbaceous perennial vine plant has heart shaped leaves and some cultivars are grown in the garden as ornamental plants. The flowers which generally look beautiful are medium-sized. The edible tuberous root is long and tapered with smooth skins and the color changes between, yellow, brown, red, purple and beige. The colors of the flesh are beige, white, pink, violet, yellow, orange and purple. Sweet potatoes with white or pale flesh are less sweet than other varieties.
- The sweet potatoes were first tasted by the members of the Columbus's expedition in 1942. The first record of this name was found oxford dictionary of 1775.
- Potato is generally called as patata in Spain and that is why it is called as ipomoea batatas.
- Many countries such as Argentina, Venezuela, Puerto Rico and the Dominican Republic the sweet potato is called batata.
- In Mexico, Peru, Chile, Central America, and the Philippines, this delicious potato is called camote.
- In Peru and New Zealand this plant is called kumar which originated from the word kumala.
- In New Zealand it is also called as kumara a named derived from maori name.
This plant grows well in many soils, but prefers well-drained, light and medium-textured soils. This plant does not tolerate frost, drought and water-logging, but grows well under full sunshine and warmer nights and the temperature is cool. The tubers can be harvested after two to nine months. This plant is pest resistant and only few pests attack this plant. The nationwide yield in Senegal was 33.3 tons per hectare and in Israel the yield that was reported is 80 m tons. As per the production statistics of 2004, China topped the chart by producing around 105 million tons.
- Chinese consume only a minute proportion and use this crop for feeding the livestock.
- Many countries around the world produce tons of sweet potatoes and use it in many ways.
- The sweet potatoes are very rich in vitamins and supplements.
- This plant is rich in Vitamin A and people in Uganda the children do not suffer from Vitamin A deficiencies since they consume this plant regularly.
- The root, leaves and shoots are all edible and can be consumed lavishly.
- In India many states consume sweet potatoes throughout the year.
- Most of the countries throughout the world add the tubers in their regular diets.
| Principle | Nutrient Value | Percentage of RDA |
|---|---|---|
| Energy | 86 Kcal | 4% |
| Carbohydrates | 20.12 g | 15.50% |
| Protein | 1.6 g | 3% |
| Total Fat | 0.05 g | <0.5% |
| Cholesterol | 0 mg | 0% |
| Dietary Fiber | 3 g | 8% |
| Vitamins | ||
| Folates | 11 µg | 3% |
| Niacin | 0.557 mg | 3.50% |
| Pantothenic acid | 0.80 mg | 16% |
| Pyridoxine | 0.209 mg | 15% |
| Riboflavin | 0.061 mg | 5.50% |
| Thiamin | 0.078 mg | 6.50% |
| Vitamin A | 14187 IU | 473% |
| Vitamin C | 2.4 mg | 4% |
| Vitamin E | 0.26 mg | 2% |
| Vitamin K | 1.8 µg | 1.50% |
| Electrolytes | ||
| Sodium | 55 mg | 3.50% |
| Potassium | 337 mg | 7% |
| Minerals | ||
| Calcium | 30 mg | 3% |
| Iron | 0.61 mg | 7.50% |
| Magnesium | 25 mg | 6% |
| Manganese | 0.258 mg | 11% |
| Phosphorus | 47 mg | 7% |
| Zinc | 0.30 mg | 3% |
| Phyto-nutrients | ||
| Carotene-α | 7 µg | — |
| Carotene-ß | 8509 µg | — |
| Crypto-xanthin-ß | 0 µg | — |

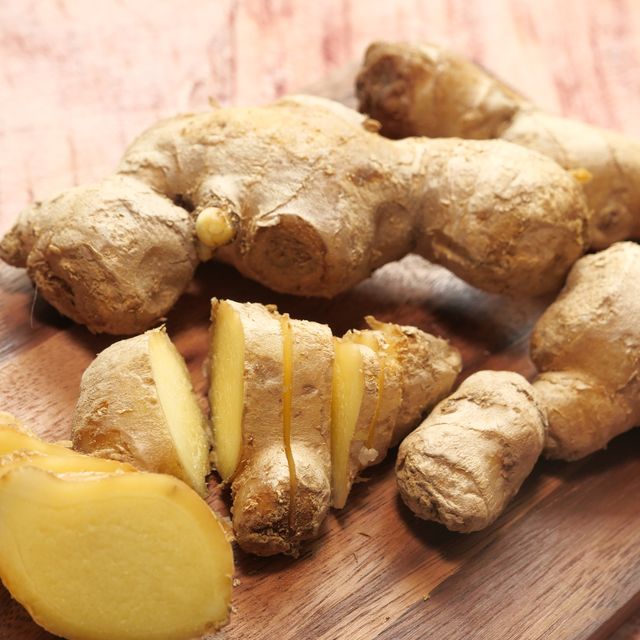
11. Ginger
Ginger root is the underground part of the flowering plant that is mainly used as spices and traditional medicine. Ginger is closely related to turmeric and cardamom. The unique flavor of the natural oil, gingerol. Ginger helps to treat nausea, morning sickness, muscle pain and soreness. Ginger has the potential to reduce blood sugar, cholesterol level and reduce the risk of heart diseases. It has an active ingredient that fights infections and plays a crucial role in treating chronic digestion and menstrual pain. Ginger has the anti-inflammatory and anticancer property to benefit our health.
Ginger can be easily added to your diet in fresh, dried, powdered form or as juice and oil.
Ginger originated in the jungles of southern asia during mid 14th century and now it is not found in the wild. During first century AD ginger was exported to Rome through India.These plants produce white and pink flower buds that ultimately bloom into spectacular yellow flowers. The name ginger originated from the French word gingibre and some researchers are of the opinion that it originated from Tamil word "inchi". Since these plants have wonderful flowers are extremely ornamental it is grown as a garden plant in many homes throughout the world. These plants grow throughout the year and are considered as perennial reed-like plants with leafy stems. The size of the stem is around 4 feet tall. When the stalks wither it will be washed and scraped to kill it and prevent sprouting.
- The fragrant perisperm of ginger is used as sweetmeats and condiment by Bantu community.
- It is used widely in India and the Indians use it in their cuisine.
- Younger ginger plays an important role in India kitchens and restaurants since hundreds of homemakers use these wonderful rhizomes as an important ingredient in their food.
- They spice up the food with the help of ginger.
- It is also used as a culinary item in Malaysia, Philippines, Burma, Japan, Thailand, Jamaica, Vietnam, Arab and many parts of the world.
- Ginger wine is a ginger-flavored wine manufactured in UK and sold traditionally in green glass bottle.
- It has lots of essential nutrients like mineral manganese, carbohydrates, fat, proteins and other important vitamins.
- Raw ginger root is made up of 80% of water.
- The odor and the flavor emitting from the ginger is due to the chemicals present in it. The chemicals that are found in ginger are zingerone, shogaols and gingerols.
- The pungent taste is caused due to the presence of nonvolatile phenylpropanoid- derived compounds present in it.
- They are used for the treatment of ulcer, gastric disorders, nausea, constipation and dyspepsia.
| Principle | Nutrient Value | Percentage of RDA |
|---|---|---|
| Energy | 80 Kcal | 4% |
| Carbohydrates | 17.77 g | 13.50% |
| Protein | 1.82 g | 3% |
| Total Fat | 0.75 g | 3% |
| Cholesterol | 0 mg | 0% |
| Dietary Fiber | 2.0 g | 5% |
| Vitamins | ||
| Folates | 11 µg | 3% |
| Niacin | 0.750 mg | 4.50% |
| Pantothenic acid | 0.203 mg | 4% |
| Pyridoxine | 0.160 mg | 12% |
| Vitamin A | 0 IU | 0% |
| Vitamin C | 5 mg | 8% |
| Vitamin E | 0.26 mg | 1.50% |
| Vitamin K | 0.1 µg | 0% |
| Electrolytes | ||
| Sodium | 13 mg | 1% |
| Potassium | 415 mg | 9% |
| Minerals | ||
| Calcium | 16 mg | 1.60% |
| Copper | 0.226 mg | 25% |
| Iron | 0.60 mg | 7.50% |
| Magnesium | 43 mg | 11% |
| Manganese | 0.229 mg | 10% |
| Phosphorus | 34 mg | 5% |
| Zinc | 0.34 mg | 3% |